Page 171 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 171
Plate 5-8 Autoimmune Blistering Diseases
Antibodies Found in Paraneoplastic Pemphigus
Bullous pemphigoid antigen II
PARANEOPLASTIC PEMPHIGUS
Bullous pemphigoid antigen I
Desmoglein 1
Paraneoplastic pemphigus was not described until the Desmoglein 3
early 1990s. It is a rare subset of the pemphigus family Desmoplakin 1
of diseases that is associated with the synchronous Desmoplakin 2
occurrence of a systemic neoplastic process. The neo-
plastic disease may precede the diagnosis of paraneo- Envoplakin
plastic pemphigus. This disease has been differentiated Periplakin
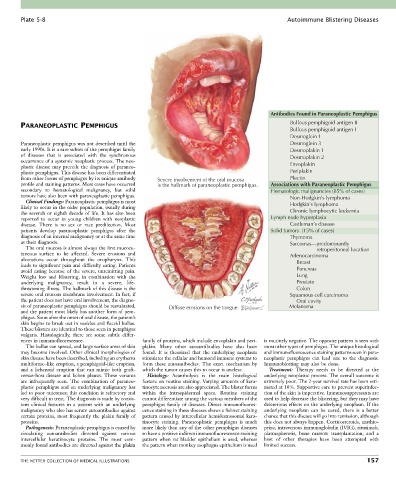
from other forms of pemphigus by its unique antibody Severe involvement of the oral mucosa Plectin
profile and staining patterns. Most cases have occurred is the hallmark of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Associations with Paraneoplastic Pemphigus
secondary to hematological malignancy, but solid Hematologic malignancies (85% of cases)
tumors have also been with paraneoplastic pemphigus. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Clinical Findings: Paraneoplastic pemphigus is most
likely to occur in the older population, usually during Hodgkin’s lymphoma
the seventh or eighth decade of life. It has also been Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
reported to occur in young children with neoplastic Lymph node hyperplasia
disease. There is no sex or race predilection. Most Castleman’s disease
patients develop paraneoplastic pemphigus after the Solid tumors (15% of cases)
diagnosis of an internal malignancy or at the same time Thymoma
as their diagnosis. Sarcomas—predominantly
The oral mucosa is almost always the first mucocu- retroperitoneal location
taneous surface to be affected. Severe erosions and Adenocarcinoma
ulcerations occur throughout the oropharynx. This Breast
leads to significant pain and difficulty eating. Patients
avoid eating because of the severe, unremitting pain. Pancreas
Weight loss and blistering, in combination with the Lung
underlying malignancy, result in a severe, life- Prostate
threatening illness. The hallmark of this disease is the Colon
severe oral mucous membrane involvement. In fact, if Squamous cell carcinoma
the patient does not have oral involvement, the diagno- Oral cavity
sis of paraneoplastic pemphigus should be reevaluated, Diffuse erosions on the tongue Melanoma
and the patient most likely has another form of pem-
phigus. Soon after the onset of oral disease, the patient’s
skin begins to break out in vesicles and flaccid bullae.
These blisters are identical to those seen in pemphigus
vulgaris. Histologically, there are some subtle differ-
ences in immunofluorescence. family of proteins, which include envoplakin and peri- is routinely negative. The opposite pattern is seen with
The bullae can spread, and large surface areas of skin plakin. Many other autoantibodies have also been most other types of pemphigus. The unique histological
may become involved. Other clinical morphologies of found. It is theorized that the underlying neoplasm and immunofluorescence staining patterns seen in para-
skin disease have been described, including an erythema stimulates the cellular and humoral immune systems to neoplastic pemphigus can lead one to the diagnosis.
multiforme–like eruption, a pemphigoid-like eruption, form these autoantibodies. The exact mechanism by Immunoblotting may also be done.
and a lichenoid eruption that can mimic both graft- which the tumor causes this to occur is unclear. Treatment: Therapy needs to be directed at the
versus-host disease and lichen planus. These variants Histology: Acantholysis is the main histological underlying neoplastic process. The overall outcome is
are infrequently seen. The combination of paraneo- feature on routine staining. Varying amounts of kera- extremely poor. The 2-year survival rate has been esti-
plastic pemphigus and an underlying malignancy has tinocyte necrosis are also appreciated. The blister forms mated at 10%. Supportive care to prevent superinfec-
led to poor outcomes; this condition is refractory and within the intraepidermal space. Routine staining tion of the skin is imperative. Immunosuppressants are
very difficult to treat. The diagnosis is made by consis- cannot differentiate among the various members of the used to help decrease the blistering, but they may have
tent clinical features in a patient with an underlying pemphigus family of diseases. Direct immunofluores- deleterious effects on the underlying neoplasm. If the
malignancy who also has serum autoantibodies against cence staining in these diseases shows a fishnet staining underlying neoplasm can be cured, there is a better
certain proteins, most frequently the plakin family of pattern caused by intercellular hemidesmosomal kera- chance that this disease will go into remission, although
proteins. tinocyte staining. Paraneoplastic pemphigus is much this does not always happen. Corticosteroids, azathio-
Pathogenesis: Paraneoplastic pemphigus is caused by more likely than any of the other pemphigus diseases prine, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), rituximab,
circulating autoantibodies directed against various to have a positive indirect immunofluorescence staining plasmapheresis, bone marrow transplantation, and a
intercellular keratinocyte proteins. The most com- pattern when rat bladder epithelium is used, whereas host of other therapies have been attempted with
monly found antibodies are directed against the plakin the pattern when monkey esophagus epithelium is used limited success.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 157