Page 169 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 169
Plate 5-6 Autoimmune Blistering Diseases
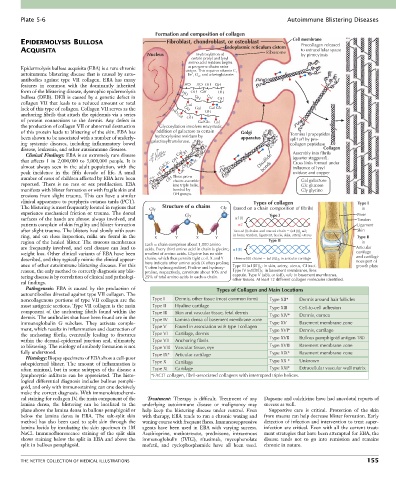
Formation and composition of collagen
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA Fibroblast, chondroblast, or osteoblast Cell membrane
Endoplasmic reticulum cistern Procollagen released
ACQUISITA Ribosome to extracellular space
Nucleus Hydroxylation of by pinocytosis
certain prolyl and lysyl
amino acid residues begins
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a rare chronic as pre-pro- chains enter
cistern. This requires vitamin C,
autoimmune blistering disease that is caused by auto- Fe , O , and -ketoglutarate.
2
2
antibodies against type VII collagen. EBA has many
features in common with the dominantly inherited HO HO OH OH
form of the blistering disease, dystrophic epidermolysis HO OH OH OH
bullosa (DEB). DEB is caused by a genetic defect in OH Gal OH
collagen VII that leads to a reduced amount or total Gal
lack of this type of collagen. Collagen VII serves as the OH Gal OH Gal Glc
anchoring fibrils that attach the epidermis via a series HO Gal
of protein connections to the dermis. Any defect in OH Gal Glc Gal
the production of collagen VII or abnormal destruction Glycosylation involves enzymatic
of this protein leads to blistering of the skin. EBA has addition of galactose to certain Golgi -s-s- Terminal propeptides
-s-s- -s-s-
been shown to be associated with a number of underly- hydroxylysine residues by apparatus -s-s- -s-s- split off by pro-
ing systemic diseases, including inflammatory bowel galactosyltransferase. -s-s- -s-s- -s-s- -s-s- collagen peptidase
disease, leukemia, and other autoimmune diseases. -s-s- -s-s- Collagen
Clinical Findings: EBA is an extremely rare disease Gal OH -s-s- Assembly into fibrils
that affects 1 in 2,000,000 to 3,000,000 people. It is OH GalGlc Disulfide (quarter staggered).
Cross links formed under
almost always seen in the adult population, with the GalGlc OH -s-s- bonds influence of lysyl
peak incidence in the fifth decade of life. A small HO Gal -s-s- oxidase and copper
number of cases of children affected by EBA have been -s-s- OH Three pro- -s-s- Gal galactose
chains assemble
reported. There is no race or sex predilection. EBA -s-s- into triple helix, Glc glucose
manifests with blister formation or with fragile skin and -s-s- bonded by Gly glycine
erosions from slight trauma. This can have a similar OH groups.
clinical appearance to porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT). Types of collagen Type I
The blistering is most frequently located in regions that Gly Structure of chains Gly (based on a chain composition of fibrils) in
experience mechanical friction or trauma. The dorsal Gly Type I Bone
surfaces of the hands are almost always involved, and 1(I) Tendon
patients complain of skin fragility and blister formation 2 Ligament
after slight trauma. The blisters heal slowly with scar- Two 1(I) chains and one 2 chain ( 1[I]) 2; Skin
2
ring, and on close inspection, milia are found in the X Y X Y in bone, tendon, ligament, fascia, skin, artery, uterus Type II
region of the healed blister. The mucous membranes Each chain comprises about 1,000 amino Type II in
are frequently involved, and oral disease can lead to acids. Every third amino acid in chain is glycine, 1(II) Articular
weight loss. Other clinical variants of EBA have been smallest of amino acids. Glycine has no side cartilage
described, and they typically mimic the clinical appear- chains, which thus permits tight coil. X and Y Three 1(II) chains ( 1[II]) 3 ; in articular cartilage and cartilagi-
nous part of
ance of other autoimmune blistering diseases. For this here indicate other amino acids (X often proline; Type III ( 1[III]) ; in skin, artery, uterus, GI tract. growth plate
Y often hydroxyproline). Proline and hydroxy-
3
reason, the only method to correctly diagnosis any blis- proline, respectively, constitute about 10% and Type IV ( 1[IV]) 3; in basement membranes, lens
tering disease is by correlation of clinical and pathologi- 25% of total amino acids in each chain. capsule. Type V ( B) 3 or ( B) A; in basement membranes,
2
other tissues. At least 12 different collagen molecules identified.
cal findings.
Pathogenesis: EBA is caused by the production of Types of Collagen and Main Locations
autoantibodies directed against type VII collagen. The
noncollagenous portions of type VII collagen are the Type I Dermis, other tissue (most common form) Type XII* Dermis around hair follicles
most antigenic sections. Type VII collagen is the main Type II Hyaline cartilage Type XIII Cell-to-cell adhesion
component of the anchoring fibrils found within the Type III Skin and vascular tissue, fetal dermis
dermis. The antibodies that have been found are in the Type IV Lamina densa of basement membrane zone Type XIV* Dermis, cornea
immunoglobulin G subclass. They activate comple- Type XV Basement membrane zone
ment, which results in inflammation and destruction of Type V Found in association with type I collagen Type XVI* Dermis, cartilage
the anchoring fibrils, eventually leading to fractures Type VI Cartilage, dermis
within the dermal-epidermal junction and, ultimately, Type VII Anchoring fibrils Type XVII Bullous pemphigoid antigen 180
to blistering. The etiology of antibody formation is not Type VIII Vascular tissue, eye Type XVIII Basement membrane zone
fully understood. Type IX* Articular cartilage Type XIX* Basement membrane zone
Histology: Biopsy specimens of EBA show a cell-poor
subepidermal blister. The amount of inflammation is Type X Cartilage Type XX * Unknown
often minimal, but in some subtypes of the disease a Type XI Cartilage Type XXI* Extracellular vascular wall matrix
lymphocytic infiltrate can be appreciated. The histo- *FACIT collagen, fibril-associated collagens with interrupted triple helices.
logical differential diagnosis includes bullous pemphi-
goid, and only with immunostaining can one decisively
make the correct diagnosis. With immunohistochemi-
cal staining for collagen IV, the main component of the Treatment: Therapy is difficult. Treatment of any Dapsone and colchicine have had anecdotal reports of
lamina densa, the blistering can be localized to the underlying autoimmune disease or malignancy may success as well.
plane above the lamina densa in bullous pemphigoid or help keep the blistering disease under control. Even Supportive care is critical. Protection of the skin
below the lamina densa in EBA. The salt-split skin with therapy, EBA tends to run a chronic waxing and from trauma can help decrease blister formation. Early
method has also been used to split skin through the waning course with frequent flares. Immunosuppressive detection of infection and intervention to treat super-
lamina lucida by incubating the skin specimen in 1M agents have been used in EBA with varying success. infection are critical. Even with all the current treat-
NaCl. Immunofluorescence staining of the split skin Azathioprine, methotrexate, prednisone, intravenous ment strategies that have been attempted for EBA, the
shows staining below the split in EBA and above the immunoglobulin (IVIG), rituximab, mycophenolate disease tends not to go into remission and remains
split in bullous pemphigoid. mofetil, and cyclophosphamide have all been used. chronic in nature.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 155