Page 173 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 173
Plate 5-10 Autoimmune Blistering Diseases
Pemphigus Variants
Pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus foliaceus
Endemic pemphigus
Pemphigus erythematosus
PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS
Paraneoplastic pemphigus
Pemphigus vegetans
Pemphigus vulgaris is the prototypical acantholytic
autoimmune blistering disease. It is one of the most IgA pemphigus
serious of all blistering diseases. Blister formation in
this subset of skin diseases occurs secondary to intraepi-
dermal acantholysis. The desmosomal plaque is the
target of the autoantibodies found in this disease.
Clinical Findings: The mean age at onset is approx-
imately 55 years. Patients present with rapid onset of
vesicles and bullae that rupture easily. The flaccid
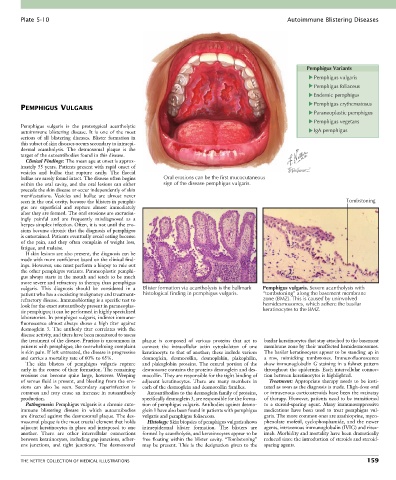
bullae are rarely found intact. The disease often begins Oral erosions can be the first mucocutaneous
within the oral cavity, and the oral lesions can either sign of the disease pemphigus vulgaris.
precede the skin disease or occur independently of skin
manifestations. Vesicles and bullae are almost never
seen in the oral cavity, because the blisters in pemphi- Tombstoning
gus are superficial and rupture almost immediately
after they are formed. The oral erosions are excruciat-
ingly painful and are frequently misdiagnosed as a
herpes simplex infection. Often, it is not until the ero-
sions become chronic that the diagnosis of pemphigus
is entertained. Patients eventually avoid eating because
of the pain, and they often complain of weight loss,
fatigue, and malaise.
If skin lesions are also present, the diagnosis can be
made with more confidence based on the clinical find-
ings. However, one must perform a biopsy to rule out
the other pemphigus variants. Paraneoplastic pemphi-
gus always starts in the mouth and tends to be much
more severe and refractory to therapy than pemphigus
vulgaris. This diagnosis should be considered in a Blister formation via acantholysis is the hallmark Pemphigus vulgaris. Severe acantholysis with
patient who has a coexisting malignancy and treatment- histological finding in pemphigus vulgaris. “tombstoning” along the basement membrane
refractory disease. Immunoblotting is a specific test to zone (BMZ). This is caused by uninvolved
look for the exact autoantibody present in paraneoplas- hemidesmosomes, which adhere the basilar
tic pemphigus; it can be performed in highly specialized keratinocytes to the BMZ.
laboratories. In pemphigus vulgaris, indirect immuno-
fluorescence almost always shows a high titer against
desmoglein 3. The antibody titer correlates with the
disease activity, and titers have been monitored to assess
the treatment of the disease. Pruritus is uncommon in plaque is composed of various proteins that act to basilar keratinocytes that stay attached to the basement
patients with pemphigus; the overwhelming complaint connect the intracellular actin cytoskeleton of one membrane zone by their unaffected hemidesmosomes.
is skin pain. If left untreated, the disease is progressive keratinocyte to that of another; these include various The basilar keratinocytes appear to be standing up in
and carries a mortality rate of 60% to 65%. desmoglein, desmocollin, desmoplakin, plakophilin, a row, mimicking tombstones. Immunofluorescence
The skin blisters of pemphigus vulgaris rupture and plakoglobin proteins. The central portion of the show immunoglobulin G staining in a fishnet pattern
early in the course of their formation. The remaining desmosome contains the proteins desmoglein and des- throughout the epidermis. Each intercellular connec-
erosions can become quite large, however. Weeping mocollin. They are responsible for the tight binding of tion between keratinocytes is highlighted.
of serous fluid is present, and bleeding from the ero- adjacent keratinocytes. There are many members in Treatment: Appropriate therapy needs to be insti-
sions can also be seen. Secondary superinfection is each of the desmoglein and desmocollin families. tuted as soon as the diagnosis is made. High-dose oral
common and may cause an increase in autoantibody Autoantibodies to the desmoglein family of proteins, or intravenous corticosteroids have been the mainstay
production. specifically desmoglein 3, are responsible for the forma- of therapy. However, patients need to be transitioned
Pathogenesis: Pemphigus vulgaris is a chronic auto- tion of pemphigus vulgaris. Antibodies against desmo- to a steroid-sparing agent. Many immunosuppressive
immune blistering disease in which autoantibodies glein 1 have also been found in patients with pemphigus medications have been used to treat pemphigus vul-
are directed against the desmosomal plaque. The des- vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceous. garis. The more common ones are azathioprine, myco-
mosomal plaque is the most crucial element that holds Histology: Skin biopsies of pemphigus vulgaris shows phenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide, and the newer
adjacent keratinocytes in place and juxtaposed to one intraepidermal blister formation. The blisters are agents, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and ritux-
another. There are other intercellular connections formed by acantholysis, and keratinocytes appear to be imab. Morbidity and mortality have been dramatically
between keratinocytes, including gap junctions, adher- free floating within the blister cavity. “Tombstoning” reduced since the introduction of steroids and steroid-
ens junctions, and tight junctions. The desmosomal may be present. This is the designation given to the sparing agents.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 159