Page 177 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 177
Plate 6-2 Infectious Diseases
BLASTOMYCOSIS
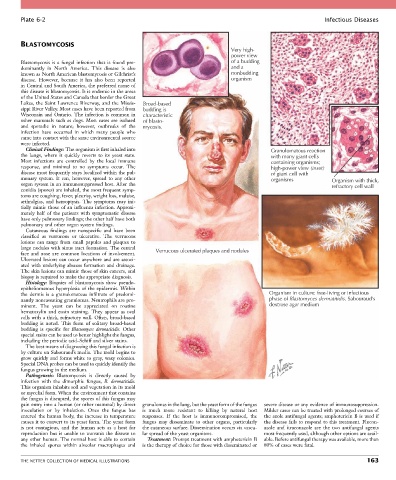
Very high-
power view
Blastomycosis is a fungal infection that is found pre- of a budding
dominantly in North America. This disease is also and a
known as North American blastomycosis or Gilchrist’s nonbudding
disease. However, because it has also been reported organism
in Central and South America, the preferred name of
this disease is blastomycosis. It is endemic in the areas
of the United States and Canada that border the Great
Lakes, the Saint Lawrence Riverway, and the Missis- Broad-based
sippi River Valley. Most cases have been reported from budding is
Wisconsin and Ontario. The infection is common in characteristic
other mammals such as dogs. Most cases are isolated of blasto-
and sporadic in nature; however, outbreaks of the mycosis.
infection have occurred in which many people who
came into contact with the same environmental source
were infected.
Clinical Findings: The organism is first inhaled into Granulomatous reaction
the lungs, where it quickly reverts to its yeast state. with many giant cells
Most infections are controlled by the local immune containing organisms;
response, and minimal to no symptoms occur. The high-power view (inset)
disease most frequently stays localized within the pul- of giant cell with
monary system. It can, however, spread to any other organisms Organism with thick,
organ system in an immunosuppressed host. After the refractory cell wall
conidia (spores) are inhaled, the most frequent symp-
toms are coughing, fever, pleurisy, weight loss, malaise,
arthralgias, and hemoptysis. The symptoms may ini-
tially mimic those of an influenza infection. Approxi-
mately half of the patients with symptomatic disease
have only pulmonary findings; the other half have both
pulmonary and other organ system findings.
Cutaneous findings are nonspecific and have been
classified as verrucous or ulcerative. The verrucous
lesions can range from small papules and plaques to
large nodules with sinus tract formation. The central Verrucous ulcerated plaques and nodules
face and nose are common locations of involvement.
Ulcerated lesions can occur anywhere and are associ-
ated with underlying abscess formation and drainage.
The skin lesions can mimic those of skin cancers, and
biopsy is required to make the appropriate diagnosis.
Histology: Biopsies of blastomycosis show pseudo-
epitheliomatous hyperplasia of the epidermis. Within
the dermis is a granulomatous infiltrate of predomi- Organism in culture: free-living or infectious
nantly noncaseating granulomas. Neutrophils are pro- phase of Blastomyces dermatitidis. Sabouraud’s
minent. The yeast can be appreciated on routine dextrose agar medium
hematoxylin and eosin staining. They appear as oval
cells with a thick, refractory wall. Often, broad-based
budding is noted. This form of solitary broad-based
budding is specific for Blastomyces dermatitidis. Other
special stains can be used to better highlight the fungus,
including the periodic acid–Schiff and silver stains.
The best means of diagnosing this fungal infection is
by culture on Sabouraud’s media. The mold begins to
grow quickly and forms white to gray, waxy colonies.
Special DNA probes can be used to quickly identify the
fungus growing in the medium.
Pathogenesis: Blastomycosis is directly caused by
infection with the dimorphic fungus, B. dermatitidis.
This organism inhabits soil and vegetation in its mold
or mycelial form. When the environment that contains
the fungus is disrupted, the spores of this fungus may
gain entry into a human (or other mammal) by direct granulomas in the lung, but the yeast form of the fungus severe disease or any evidence of immunosuppression.
inoculation or by inhalation. Once the fungus has is much more resistant to killing by natural host Milder cases can be treated with prolonged courses of
entered the human body, the increase in temperature responses. If the host is immunocompromised, the the azole antifungal agents; amphotericin B is used if
causes it to convert to its yeast form. The yeast form fungus may disseminate to other organs, particularly the disease fails to respond to this treatment. Flucon-
is not contagious, and the human acts as a host for the cutaneous surface. Dissemination occurs via vascu- azole and itraconazole are the two antifungal agents
reproduction but is unable to transmit the disease to lar spread of the yeast organisms. most frequently used, although other options are avail-
any other human. The normal host is able to contain Treatment: Prompt treatment with amphotericin B able. Before antifungal therapy was available, more than
the inhaled spores within alveolar macrophages and is the therapy of choice for those with disseminated or 80% of cases were fatal.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 163