Page 218 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 218
Plate 7-7 Integumentary System
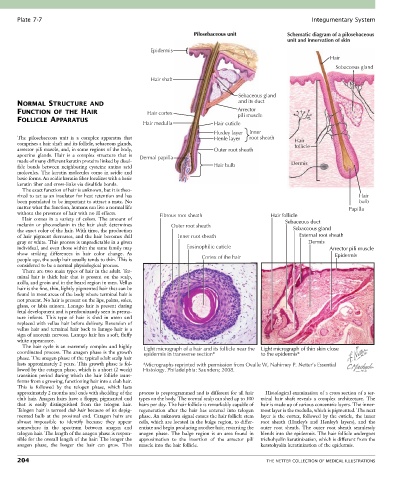
Pilosebaceous unit Schematic diagram of a pilosebaceous
unit and innervation of skin
Epidermis
Hair
Sebaceous gland
Hair shaft
Sebaceous gland
NORMAL STRUCTURE AND and its duct
FUNCTION OF THE HAIR Hair cortex Arrector
pili muscle
FOLLICLE APPARATUS
Hair medulla Hair cuticle
Huxley layer Inner
The pilosebaceous unit is a complex apparatus that Henle layer root sheath Hair
comprises a hair shaft and its follicle, sebaceous glands, follicle
arrector pili muscle, and, in some regions of the body, Outer root sheath
apocrine glands. Hair is a complex structure that is Dermal papilla
made of many different keratin proteins linked by disul- Dermis
fide bonds between neighboring cysteine amino acid Hair bulb
molecules. The keratin molecules come in acidic and
basic forms. An acidic keratin fiber localizes with a basic
keratin fiber and cross-links via disulfide bonds.
The exact function of hair is unknown, but it is theo-
rized to act as an insulator for heat retention and has Hair
been postulated to be important to attract a mate. No bulb
matter what the function, humans can live a normal life Papilla
without the presence of hair with no ill effects. Fibrous root sheath Hair follicle
Hair comes in a variety of colors. The amount of
melanin or pheomelanin in the hair shaft determines Outer root sheath Sebaceous duct
the exact color of the hair. With time, the production Sebaceous gland
of hair pigment decreases, and the hair becomes dull Inner root sheath External root sheath
gray or white. This process is unpredictable in a given Dermis
individual, and even those within the same family may Eosinophilic cuticle Arrector pili muscle
show striking differences in hair color change. As Epidermis
people age, the scalp hair usually tends to thin. This is Cortex of the hair
considered to be a normal physiological process.
There are two main types of hair in the adult. Ter-
minal hair is thick hair that is present on the scalp,
axilla, and groin and in the beard region in men. Vellus
hair is the fine, thin, lightly pigmented hair that can be
found in most areas of the body where terminal hair is
not present. No hair is present on the lips, palms, soles,
glans, or labia minora. Lanugo hair is present during
fetal development and is predominantly seen in prema-
ture infants. This type of hair is shed in utero and
replaced with vellus hair before delivery. Reversion of
vellus hair and terminal hair back to lanugo hair is a
sign of anorexia nervosa. Lanugo hair has a soft, fluffy
white appearance.
The hair cycle is an extremely complex and highly Light micrograph of a hair and its follicle near the Light micrograph of thin skin close
coordinated process. The anagen phase is the growth epidermis in transverse section* to the epidermis*
phase. The anagen phase of the typical adult scalp hair
lasts approximately 2 years. This growth phase is fol- *Micrographs reprinted with permission from Ovalle W, Nahirney P. Netter’s Essential
lowed by the catagen phase, which is a short (2 week) Histology. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2008.
transition period during which the hair follicle trans-
forms from a growing, functioning hair into a club hair.
This is followed by the telogen phase, which lasts
approximately 2 months and ends with shedding of the process is preprogrammed and is different for all hair Histological examination of a cross section of a ter-
club hair. Anagen hairs have a floppy, pigmented end types on the body. The normal scalp can shed up to 100 minal hair shaft reveals a complex architecture. The
that is easily distinguished from the telogen hair. hairs per day. The hair follicle is remarkably capable of hair is made up of various concentric layers. The inner-
Telogen hair is termed club hair because of its depig- regeneration after the hair has entered into telogen most layer is the medulla, which is pigmented. The next
mented bulb at the proximal end. Catagen hairs are phase. An unknown signal causes the hair follicle stem layer is the cortex, followed by the cuticle, the inner
almost impossible to identify because they appear cells, which are located in the bulge region, to differ- root sheath (Huxley’s and Henley’s layers), and the
somewhere in the spectrum between anagen and entiate and begin producing another hair, restarting the outer root sheath. The outer root sheath seamlessly
telogen hair. The length of the anagen phase is respon- anagen phase. The bulge region is an area found in blends into the epidermis. The hair follicle undergoes
sible for the overall length of the hair: The longer the approximation to the insertion of the arrector pili trichohyalin keratinization, which is different from the
anagen phase, the longer the hair can grow. This muscle into the hair follicle. keratohyalin keratinization of the epidermis.
204 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS