Page 225 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 225
Plate 8-2 Nutritional and Metabolic Diseases
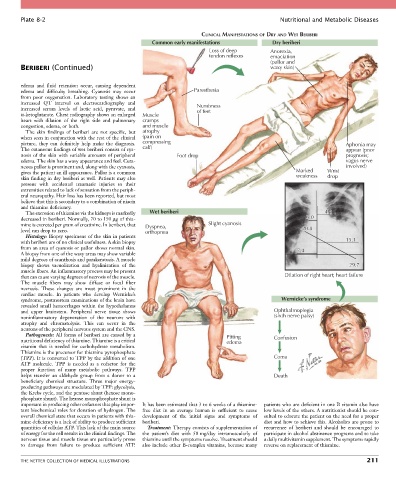
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF DRY AND WET BERIBERI
Common early manifestations Dry beriberi
Loss of deep Anorexia,
tendon reflexes emaciation
(pallor and
BERIBERI (Continued) waxy skin)
edema and fluid retention occur, causing dependent
edema and difficulty breathing. Cyanosis may occur Paresthesia
from poor oxygenation. Laboratory testing shows an
increased QT interval on electrocardiography and Numbness
increased serum levels of lactic acid, pyruvate, and of feet
α-ketoglutarate. Chest radiography shows an enlarged Muscle
heart with dilation of the right side and pulmonary cramps
congestion, edema, or both. and muscle
The skin findings of beriberi are not specific, but atrophy
when seen in conjunction with the rest of the clinical (pain on
picture, they can definitely help make the diagnosis. compressing Aphonia may
The cutaneous findings of wet beriberi consist of cya- calf) appear (poor
nosis of the skin with variable amounts of peripheral Foot drop prognosis;
edema. The skin has a waxy appearance and feel. Cuta- vagus nerve
neous pallor is prominent and, along with the cyanosis, involved)
gives the patient an ill appearance. Pallor is a common Marked Wrist
skin finding in dry beriberi as well. Patients may also weakness drop
present with accidental traumatic injuries to their
extremities related to lack of sensation from the periph-
eral neuropathy. Hair loss has been reported, but most
believe that this is secondary to a combination of niacin
and thiamine deficiency.
The excretion of thiamine via the kidneys is markedly Wet beriberi 4.8
decreased in beriberi. Normally, 70 to 150 µg of thia- 3.0
mine is excreted per gram of creatinine. In beriberi, that Dyspnea, Slight cyanosis
level can drop to zero. orthopnea 20.8
Histology: Biopsy specimens of the skin in patients
with beriberi are of no clinical usefulness. A skin biopsy 15.1
from an area of cyanosis or pallor shows normal skin. 7.4
A biopsy from one of the waxy areas may show variable
mild degrees of acanthosis and parakeratosis. A muscle
biopsy shows vacuolization and hyalinization of the 29.7
muscle fibers. An inflammatory process may be present
that can cause varying degrees of necrosis of the muscle. Dilation of right heart; heart failure
The muscle fibers may show diffuse or focal fiber
necrosis. These changes are most prominent in the
cardiac muscle. In patients who develop Wernicke’s
syndrome, postmortem examinations of the brain have Wernicke’s syndrome
revealed small hemorrhages within the hypothalamus
and upper brainstem. Peripheral nerve tissue shows Ophthalmoplegia
noninflammatory degeneration of the neurons with (sixth nerve palsy)
atrophy and chromatolysis. This can occur in the
neurons of the peripheral nervous system and the CNS.
Pathogenesis: All forms of beriberi are caused by a Pitting
nutritional deficiency of thiamine. Thiamine is a critical edema Confusion
vitamin that is needed for carbohydrate metabolism.
Thiamine is the precursor for thiamine pyrophosphate
(TPP). It is converted to TPP by the addition of one Coma
ATP molecule. TPP is needed as a cofactor for the
proper function of many metabolic pathways. TPP
helps transfer an aldehyde group from a donor to a Death
beneficiary chemical structure. Three major energy-
producing pathways are modulated by TPP: glycolysis,
the Krebs cycle, and the pentose shunt (hexose mono-
phosphate shunt). The hexose monophosphate shunt is
important in producing other cofactors that play impor- It has been estimated that 3 to 6 weeks of a thiamine- patients who are deficient in one B vitamin also have
tant biochemical roles for donation of hydrogen. The free diet in an average human is sufficient to cause low levels of the others. A nutritionist should be con-
overall chemical state that occurs in patients with thia- development of the initial signs and symptoms of sulted to educate the patient on the need for a proper
mine deficiency is a lack of ability to produce sufficient beriberi. diet and how to achieve this. Alcoholics are prone to
quantities of cellular ATP. This lack of the main source Treatment: Therapy consists of supplementation of recurrence of beriberi and should be encouraged to
of energy for the cell results in the clinical findings. The the patient’s diet with 50 mg/day intramuscularly of participate in alcohol abstinence programs and to take
nervous tissue and muscle tissue are particularly prone thiamine until the symptoms resolve. Treatment should a daily multivitamin supplement. The symptoms rapidly
to damage from failure to produce sufficient ATP. also include other B-complex vitamins, because many reverse on replacement of thiamine.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 211