Page 230 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 230
Plate 8-7 Integumentary System
NORMAL AND ABNORMAL METABOLISM OF PHENYLALANINE
Normal phenylalanine metabolism
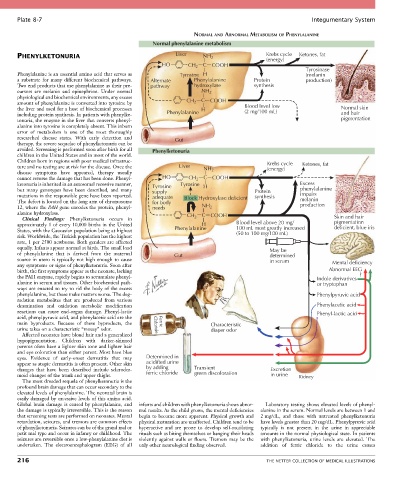
PHENYLKETONURIA Liver NH 2 Krebs cycle Ketones, fat
(energy)
HO CH 2 C COOH
Tyrosinase
Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid that serves as Tyrosine H (melanin
a substrate for many different biochemical pathways. Alternate Phenylalanine Protein production)
Two end products that use phenylalanine as their pre- pathway hydroxylase synthesis
cursors are melanin and epinephrine. Under normal NH 2
physiological and biochemical environments, any excess
amount of phenylalanine is converted into tyrosine by CH 2 C COOH
the liver and used for a host of biochemical processes H Blood level low Normal skin
(2 mg/100 mL)
including protein synthesis. In patients with phenylke- Phenylalanine and hair
tonuria, the enzyme in the liver that converts phenyl- pigmentation
alanine into tyrosine is completely absent. This inborn
error of metabolism is one of the most thoroughly
researched disease states. With early detection and Gut
therapy, the severe sequelae of phenylketonuria can be
avoided. Screening is performed soon after birth for all Phenylketonuria
children in the United States and in most of the world.
Children born in regions with poor medical infrastruc- Krebs cycle
ture and no testing are at risk for the disease. Once the Liver NH 2 (energy) Ketones, fat
disease symptoms have appeared, therapy usually
cannot reverse the damage that has been done. Phenyl- HO CH 2 C COOH
ketonuria is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, Tyrosine Tyrosine H Excess
but many genotypes have been described, and many supply Protein phenylalanine
mutations in the responsible gene have been reported. adequate Block Hydroxylase deficient synthesis impairs
The defect is located on the long arm of chromosome for body melanin
12, where the PAH gene encodes the protein, phenyl- needs NH 2 production
alanine hydroxylase. C COOH
Clinical Findings: Phenylketonuria occurs in CH 2 Skin and hair
approximately 1 of every 10,000 births in the United H Blood level above 20 mg/ pigmentation
deficient, blue iris
States, with the Caucasian population being at highest Phenylalanine 100 mL most greatly increased
(50 to 100 mg/100 mL)
risk. Worldwide, the Turkish population has the highest
rate, 1 per 2500 newborns. Both genders are affected
equally. Infants appear normal at birth. The small load May be
of phenylalanine that is derived from the maternal Gut determined
source in utero is typically not high enough to cause in serum
any symptoms or signs of phenylketonuria. Soon after Mental deficiency
birth, the first symptoms appear as the neonate, lacking Abnormal EEG
the PAH enzyme, rapidly begins to accumulate phenyl- Indole derivatives ?
alanine in serum and tissues. Other biochemical path- or tryptophan
ways are enacted to try to rid the body of the excess
phenylalanine, but these make matters worse. The deg- Phenylpyruvic acid
radation metabolites that are produced from various
deamination and oxidation metabolic modification Phenylacetic acid
reactions can cause end-organ damage. Phenyl-lactic Phenyl-lactic acid
acid, phenylpyruvic acid, and phenylacetic acid are the
main byproducts. Because of these byproducts, the Chloride Ferric Characteristic
urine takes on a characteristic “mousy” odor. diaper odor
Affected neonates have blond hair and a generalized
hypopigmentation. Children with darker-skinned
parents often have a lighter skin tone and lighter hair
and eye coloration than either parent. Most have blue
eyes. Evidence of early-onset dermatitis that may Determined in
appear as atopic dermatitis is often present. Other skin acidified urine
changes that have been described include scleroder- by adding Transient Excretion
moid changes of the trunk and upper thighs. ferric chloride green discoloration in urine Kidney
The most dreaded sequela of phenylketonuria is the
profound brain damage that can occur secondary to the
elevated levels of phenylalanine. The neonatal brain is
easily damaged by excessive levels of this amino acid.
Global brain damage is caused by phenylalanine, and infants and children with phenylketonuria shows abnor- Laboratory testing shows elevated levels of phenyl-
the damage is typically irreversible. This is the reason mal results. As the child grows, the mental deficiencies alanine in the serum. Normal levels are between 1 and
that screening tests are performed on neonates. Mental begin to become more apparent. Physical growth and 2 mg/dL, and those with untreated phenylketonuria
retardation, seizures, and tremors are common effects physical maturation are unaffected. Children tend to be have levels greater than 20 mg/dL. Phenylpyruvic acid
of phenylketonuria. Seizures can be of the grand mal or hyperactive and are prone to develop self-mutilating typically is not present in the urine in appreciable
petit mal type and occur in infancy or childhood. The rituals such as biting themselves or banging their heads amounts in the normal physiological state. In patients
seizures are reversible once a low-phenylalanine diet is violently against walls or floors. Tremors may be the with phenylketonuria, urine levels are elevated. The
undertaken. The electroencephalogram (EEG) of all only other neurological finding observed. addition of ferric chloride to the urine causes
216 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS