Page 30 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 30
Plate 2-3 Integumentary System
DERMATOFIBROMA (SCLEROSING
HEMANGIOMA)
Dermatofibromas are among the most common types
of benign skin growths. Usually, they occur on the
extremities, with a predilection for the legs. There is
some debate as to whether this is a true neoplasm or an
inflammatory reaction.
Clinical Findings: Dermatofibromas are seen almost
exclusively in adults, and females tend to be afflicted
slightly more often than males. There is no race predi-
lection. Dermatofibromas can range in diameter from
2 mm to 2 cm. They are round or oval. Most often
they are solitary, but numerous dermatofibromas may Low power. There is a dermal proliferation of
be present in an individual. Dermatofibromas are spindle-shaped fibroblasts. The epidermis centrally
usually small (4-5 mm), firm, red to slightly purple shows acanthosis and basilar hyperpigmentation.
papules that dimple with lateral pressure. This “dimple The tumor cells do not reach to the subcutaneous
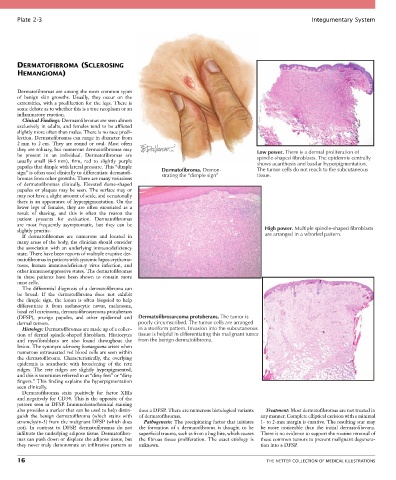
sign” is often used clinically to differentiate dermatofi- Dermatofibroma. Demon- tissue.
strating the “dimple sign”
bromas from other growths. There are many variations
of dermatofibromas clinically. Elevated dome-shaped
papules or plaques may be seen. The surface may or
may not have a slight amount of scale, and occasionally
there is an appearance of hyperpigmentation. On the
lower legs of females, they are often excoriated as a
result of shaving, and this is often the reason the
patient presents for evaluation. Dermatofibromas
are most frequently asymptomatic, but they can be
slightly pruritic. High power. Multiple spindle-shaped fibroblasts
If dermatofibromas are numerous and located in are arranged in a whorled pattern.
many areas of the body, the clinician should consider
the association with an underlying immunodeficiency
state. There have been reports of multiple eruptive der-
matofibromas in patients with systemic lupus erythema-
tosus, human immunodeficiency virus infection, and
other immunosuppressive states. The dermatofibromas
in these patients have been shown to contain more
mast cells.
The differential diagnosis of a dermatofibroma can
be broad. If the dermatofibroma does not exhibit
the dimple sign, the lesion is often biopsied to help
differentiate it from melanocytic nevus, melanoma,
basal cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
(DFSP), prurigo papules, and other epidermal and Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. The tumor is
dermal tumors. poorly circumscribed. The tumor cells are arranged
Histology: Dermatofibromas are made up of a collec- in a storiform pattern. Invasion into the subcutaneous
tion of dermal spindle-shaped fibroblasts. Histiocytes tissue is helpful in differentiating this malignant tumor
and myofibroblasts are also found throughout the from the benign dermatofibroma.
lesion. The synonym sclerosing hemangioma arises when
numerous extravasated red blood cells are seen within
the dermatofibroma. Characteristically, the overlying
epidermis is acanthotic with broadening of the rete
ridges. The rete ridges are slightly hyperpigmented,
and this is sometimes referred to as “dirty feet” or “dirty
fingers.” This finding explains the hyperpigmentation
seen clinically.
Dermatofibromas stain positively for factor XIIIa
and negatively for CD34. This is the opposite of the
pattern seen in DFSP. Immunohistochemical staining
also provides a marker that can be used to help distin- does a DFSP. There are numerous histological variants Treatment: Most dermatofibromas are not treated in
guish the benign dermatofibroma (which stains with of dermatofibromas. any manner. Complete elliptical excision with a minimal
stromelysin-3) from the malignant DFSP (which does Pathogenesis: The precipitating factor that initiates 1- to 2-mm margin is curative. The resulting scar may
not). In contrast to DFSP, dermatofibromas do not the formation of a dermatofibroma is thought to be be more noticeable than the initial dermatofibroma.
infiltrate the underlying adipose tissue. Dermatofibro- superficial trauma, such as from a bug bite, which causes There is no evidence to support the routine removal of
mas can push down or displace the adipose tissue, but the fibrous tissue proliferation. The exact etiology is these common tumors to prevent malignant degenera-
they never truly demonstrate an infiltrative pattern as unknown. tion into a DFSP.
16 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS