Page 35 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 35
Plate 2-8 Benign Growths
LENTIGINES
EPHELIDES AND LENTIGINES
(Continued)
non-melanoma skin cancer due to their chronic use of
PUVA treatment.
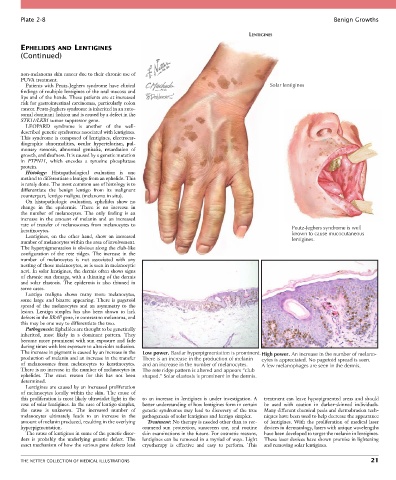
Patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome have clinical Solar lentigines
findings of multiple lentigines of the oral mucosa and
lips and of the hands. These patients are at increased
risk for gastrointestinal carcinomas, particularly colon
cancer. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is inherited in an auto-
somal dominant fashion and is caused by a defect in the
STK11/LKB1 tumor suppressor gene.
LEOPARD syndrome is another of the well-
described genetic syndromes associated with lentigines.
This syndrome is composed of lentigines, electrocar-
diographic abnormalities, ocular hypertelorism, pul-
monary stenosis, abnormal genitalia, retardation of
growth, and deafness. It is caused by a genetic mutation
in PTPN11, which encodes a tyrosine phosphatase
protein.
Histology: Histopathological evaluation is one
method to differentiate a lentigo from an ephelide. This
is rarely done. The most common use of histology is to
differentiate the benign lentigo from its malignant
counterpart, lentigo maligna (melanoma in situ).
On histopathologic evaluation, ephelides show no
change in the epidermis. There is no increase in
the number of melanocytes. The only finding is an
increase in the amount of melanin and an increased
rate of transfer of melanosomes from melanocytes to
keratinocytes. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is well
Lentigines, on the other hand, show an increased known to cause mucocutaneous
number of melanocytes within the area of involvement. lentigines.
The hyperpigmentation is obvious along the club-like
configuration of the rete ridges. The increase in the
number of melanocytes is not associated with any
nesting of those melanocytes, as is seen in melanocytic
nevi. In solar lentigines, the dermis often shows signs
of chronic sun damage, with a thinning of the dermis
and solar elastosis. The epidermis is also thinned in
some cases.
Lentigo maligna shows many more melanocytes,
some large and bizarre appearing. There is pagetoid
spread of the melanocytes and an asymmetry to the
lesion. Lentigo simplex has also been shown to lack
defects in the BRAF gene, in contrast to melanoma, and
this may be one way to differentiate the two.
Pathogenesis: Ephelides are thought to be genetically
inherited, most likely in a dominant pattern. They
become more prominent with sun exposure and fade
during times with less exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The increase in pigment is caused by an increase in the Low power. Basilar hyperpigmentation is prominent. High power. An increase in the number of melano-
production of melanin and an increase in the transfer There is an increase in the production of melanin cytes is appreciated. No pagetoid spread is seen.
of melanosomes from melanocytes to keratinocytes. and an increase in the number of melanocytes. A few melanophages are seen in the dermis.
There is no increase in the number of melanocytes in The rete ridge pattern is altered and appears “club
ephelides. The exact reason for this has not been shaped.” Solar elastosis is prominent in the dermis.
determined.
Lentigines are caused by an increased proliferation
of melanocytes locally within the skin. The cause of
this proliferation is most likely ultraviolet light in the to an increase in lentigines is under investigation. A treatment can leave hypopigmented areas and should
case of solar lentigines. In the case of lentigo simplex, better understanding of how lentigines form in certain be used with caution in darker-skinned individuals.
the cause is unknown. The increased number of genetic syndromes may lead to discovery of the true Many different chemical peels and dermabrasion tech-
melanocytes ultimately leads to an increase in the pathogenesis of solar lentigines and lentigo simplex. niques have been used to help decrease the appearance
amount of melanin produced, resulting in the overlying Treatment: No therapy is needed other than to rec- of lentigines. With the proliferation of medical laser
hyperpigmentation. ommend sun protection, sunscreen use, and routine devices in dermatology, lasers with unique wavelengths
The cause of lentigines in some of the genetic disor- skin examinations in the future. For cosmetic reasons, have been developed to target the melanin in lentigines.
ders is probably the underlying genetic defect. The lentigines can be removed in a myriad of ways. Light These laser devices have shown promise in lightening
exact mechanism of how the various gene defects lead cryotherapy is effective and easy to perform. This and removing solar lentigines.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 21