Page 41 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 41
Plate 2-14 Benign Growths
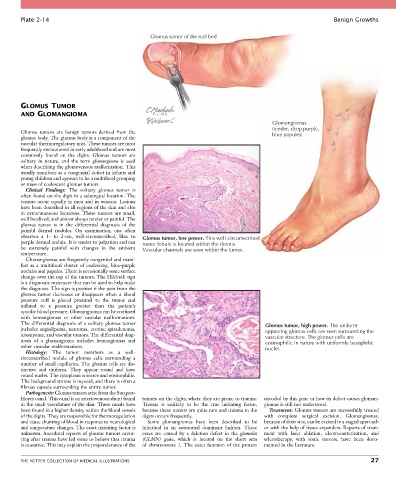
Glomus tumor of the nail bed
GLOMUS TUMOR
AND GLOMANGIOMA
Glomangiomas
(tender, deep purple,
Glomus tumors are benign tumors derived from the blue papules)
glomus body. The glomus body is a component of the
vascular thermoregulatory unit. These tumors are most
frequently encountered in early adulthood and are most
commonly found on the digits. Glomus tumors are
solitary in nature, and the term glomangioma is used
when describing the glomuvenous malformation. This
usually manifests as a congenital defect in infants and
young children and appears to be a multifocal grouping
or mass of coalescent glomus tumors.
Clinical Findings: The solitary glomus tumor is
often found on the digit in a subungual location. The
tumors occur equally in men and in women. Lesions
have been described in all regions of the skin and also
in extracutaneous locations. These tumors are small,
well localized, and almost always tender or painful. The
glomus tumor is in the differential diagnosis of the
painful dermal nodules. On examination, one often
observes a 1- to 2-cm, well-circumscribed, blue to Glomus tumor, low power. This well-circumscribed
purple dermal nodule. It is tender to palpation and can tumor lobule is located within the dermis.
be extremely painful with changes in the ambient Vascular channels are seen within the tumor.
temperature.
Glomangiomas are frequently congenital and mani-
fest as a multifocal cluster of coalescing, blue-purple
nodules and papules. There is occasionally some surface
change over the top of the tumors. The Hildreth sign
is a diagnostic maneuver that can be used to help make
the diagnosis. The sign is positive if the pain from the
glomus tumor decreases or disappears when a blood
pressure cuff is placed proximal to the tumor and
inflated to a pressure greater than the patient’s
systolic blood pressure. Glomangiomas can be confused
with hemangiomas or other vascular malformations.
The differential diagnosis of a solitary glomus tumor Glomus tumor, high power. The uniform-
includes angiolipoma, neuroma, eccrine spiradenoma, appearing glomus cells are seen surrounding the
leiomyoma, and vascular tumors. The differential diag- vascular structure. The glomus cells are
nosis of a glomangioma includes hemangiomas and eosinophilic in nature with uniformly basophilic
other vascular malformations. nuclei.
Histology: The tumor manifests as a well-
circumscribed nodule of glomus cells surrounding a
number of small capillaries. The glomus cells are dis-
tinctive and uniform. They appear round and have
round nuclei. The cytoplasm is scarce and eosinophilic.
The background stroma is myxoid, and there is often a
fibrous capsule surrounding the entire tumor.
Pathogenesis: Glomus tumors arise from the Sucquet-
Hoyer canal. This canal is an arteriovenous shunt found tumors on the digits, where they are prone to trauma. encoded by this gene or how its defect causes gloman-
in the small vasculature of the skin. These canals have Trauma is unlikely to be the true initiating factor, giomas is still not understood.
been found in a higher density within the blood vessels because these tumors are quite rare and trauma to the Treatment: Glomus tumors are successfully treated
of the digits. They are responsible for thermoregulation digits occurs frequently. with complete surgical excision. Glomangiomas,
and cause shunting of blood in response to neurological Some glomangiomas have been described to be because of their size, can be excised in a staged approach
and temperature changes. The exact initiating factor is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. These or with the help of tissue expanders. Reports of treat-
unknown. Anecdotal reports of glomus tumors occur- cases are caused by a deletion defect in the glomulin ment with laser ablation, electrocauterization, and
ring after trauma have led some to believe that trauma (GLMN) gene, which is located on the short arm sclerotherapy, with some success, have been docu-
is causative. This may explain the preponderance of the of chromosome 1. The exact function of the protein mented in the literature.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 27