Page 40 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 40
Plate 2-13 Integumentary System
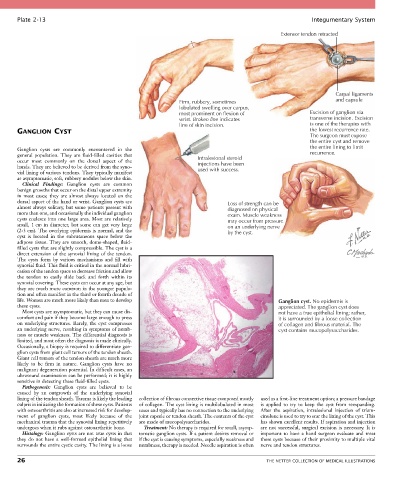
Extensor tendon retracted
Carpal ligaments
Firm, rubbery, sometimes and capsule
lobulated swelling over carpus,
most prominent on flexion of Excision of ganglion via
wrist. Broken line indicates transverse incision. Excision
line of skin incision. is one of the therapies with
GANGLION CYST the lowest recurrence rate.
The surgeon must expose
the entire cyst and remove
Ganglion cysts are commonly encountered in the the entire lining to limit
general population. They are fluid-filled cavities that Intralesional steroid recurrence.
occur most commonly on the dorsal aspect of the injections have been
hands. They are believed to be derived from the syno- used with success.
vial lining of various tendons. They typically manifest
as asymptomatic, soft, rubbery nodules below the skin.
Clinical Findings: Ganglion cysts are common
benign growths that occur on the distal upper extremity
in most cases; they are almost always located on the
dorsal aspect of the hand or wrist. Ganglion cysts are Loss of strength can be
almost always solitary, but some patients present with diagnosed on physical
more than one, and occasionally the individual ganglion exam. Muscle weakness
cysts coalesce into one large area. Most are relatively may occur from pressure
small, 1 cm in diameter, but some can get very large on an underlying nerve
(2-3 cm). The overlying epidermis is normal, and the by the cyst.
cyst is located in the subcutaneous space below the
adipose tissue. They are smooth, dome-shaped, fluid-
filled cysts that are slightly compressible. The cyst is a
direct extension of the synovial lining of the tendon.
The cysts form by various mechanisms and fill with
synovial fluid. This fluid is critical in the normal lubri-
cation of the tendon space to decrease friction and allow
the tendon to easily slide back and forth within its
synovial covering. These cysts can occur at any age, but
they are much more common in the younger popula-
tion and often manifest in the third or fourth decade of
life. Women are much more likely than men to develop Ganglion cyst. No epidermis is
these cysts. appreciated. The ganglion cyst does
Most cysts are asymptomatic, but they can cause dis- not have a true epithelial lining; rather,
comfort and pain if they become large enough to press it is surrounded by a loose collection
on underlying structures. Rarely, the cyst compresses of collagen and fibrous material. The
an underlying nerve, resulting in symptoms of numb- cyst contains mucopolysaccharides.
ness or muscle weakness. The differential diagnosis is
limited, and most often the diagnosis is made clinically.
Occasionally, a biopsy is required to differentiate gan-
glion cysts from giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath.
Giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath are much more
likely to be firm in nature. Ganglion cysts have no
malignant degeneration potential. In difficult cases, an
ultrasound examination can be performed; it is highly
sensitive in detecting these fluid-filled cysts.
Pathogenesis: Ganglion cysts are believed to be
caused by an outgrowth of the underlying synovial
lining of the tendon sheath. Trauma is likely the leading collection of fibrous connective tissue composed mostly used as a first-line treatment option; a pressure bandage
culprit in initiating the formation of these cysts. Patients of collagen. The cyst lining is multilobulated in most is applied to try to keep the cyst from reexpanding.
with osteoarthritis are also at increased risk for develop- cases and typically has no connection to the underlying After the aspiration, intralesional injection of triam-
ment of ganglion cysts, most likely because of the joint capsule or tendon sheath. The contents of the cyst cinolone is used to try to scar the lining of the cyst. This
mechanical trauma that the synovial lining repetitively are made of mucopolysaccharides. has shown excellent results. If aspiration and injection
undergoes when it rubs against osteoarthritic bone. Treatment: No therapy is required for small, asymp- are not successful, surgical excision is necessary. It is
Histology: Ganglion cysts are not true cysts in that tomatic ganglion cysts. If a patient desires removal or important to have a hand surgeon evaluate and treat
they do not have a well-formed epithelial lining that if the cyst is causing symptoms, especially weakness and these cysts because of their proximity to multiple vital
surrounds the entire cystic cavity. The lining is a loose numbness, therapy is needed. Needle aspiration is often nerve and tendon structures.
26 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS