Page 290 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 290
256 Chapter 9
A decreased PaO , an increased P (A-a) O , a decreased PaO /P O , or a decreased
2
2
A
2
2
PaO /F O reflects tissue hypoxia. Table 9-8 outlines the guideline for interpretation
I
2
2
of a patient’s oxygenation status.
In general, a decrease in PaO with concurrent increase in P (A-a) O is indicative of
2
2
hypoxemia due to diffusion defect, V/Q mismatch, or shunt. A decrease in PaO
diffusion defect: Pathologic 2
condition leading to impaired with little or no increase in P (A-a) O is probably due to hypoventilation and this can
2
gas exchange through the be confirmed by an elevated PaCO (Tobin, 1990).
alveolar-capillary membrane 2
(e.g., interstitial or pulmonary P (A-a) O is the difference of P O and PaO . It can be calculated as follows:
2
2
2
A
edema).
P (A@a) O = P O - PaO 2
2
A
2
PaO is obtained from arterial blood gas analysis and P O can be calculated by
2
2
A
the simplified alveolar air equation, as follows:
(PaCO )
P O = (P - P H 2 O ) * F O - R 2
2
B
I
2
A
where P 5 barometric pressure, P H 2 O 5 water vapor pressure (generally 47 mm
B
Hg at 37°C), and R 5 respiratory quotient (estimated to be 0.8 and it may be
deleted from equation when the F O is greater than 60%). P O is mainly affected
2
A
I
2
by changes of F O , PaCO , and P .
B
2
I
2
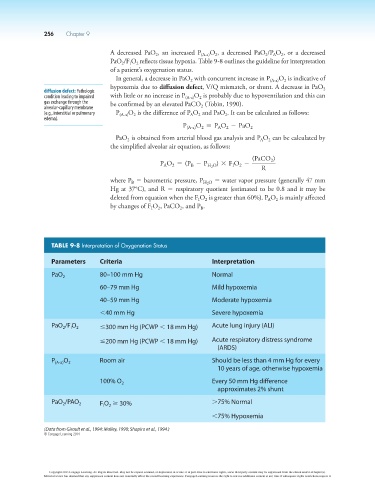
TABLE 9-8 Interpretation of Oxygenation Status
Parameters Criteria Interpretation
PaO 2 80–100 mm Hg Normal
60–79 mm Hg Mild hypoxemia
40–59 mm Hg Moderate hypoxemia
,40 mm Hg Severe hypoxemia
PaO /F O 2 ≤300 mm Hg (PCWP , 18 mm Hg) Acute lung injury (ALI)
2
I
≤200 mm Hg (PCWP , 18 mm Hg) Acute respiratory distress syndrome
(ARDS)
P (A-a) O 2 Room air Should be less than 4 mm Hg for every
10 years of age, otherwise hypoxemia
100% O 2 Every 50 mm Hg difference
approximates 2% shunt
PaO /PAO 2 F O ≥ 30% .75% Normal
2
2
I
,75% Hypoxemia
(Data from Girault et al., 1994; Malley, 1990; Shapiro et al., 1994.)
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.