Page 373 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 373
Ventilator Waveform Analysis 339
I E
V (L/min) 50 2:1 x
I:E
2 4 6 8 10 12
y
250
P (cm H 2 O) 40
© Cengage Learning 2014
2 4 6 8 10 12
Time (sec)
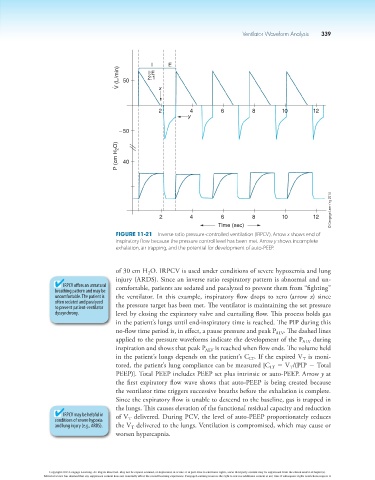
Figure 11-21 Inverse ratio pressure-controlled ventilation (IRPCV). Arrow x shows end of
inspiratory flow because the pressure control level has been met. Arrow y shows incomplete
exhalation, air trapping, and the potential for development of auto-PEEP.
of 30 cm H O. IRPCV is used under conditions of severe hypoxemia and lung
2
injury (ARDS). Since an inverse ratio respiratory pattern is abnormal and un-
IRPCV offers an unnatural comfortable, patients are sedated and paralyzed to prevent them from “fighting”
breathing pattern and may be
uncomfortable. The patient is the ventilator. In this example, inspiratory flow drops to zero (arrow x) since
often sedated and paralyzed
to prevent patient-ventilator the pressure target has been met. The ventilator is maintaining the set pressure
dyssynchrony. level by closing the expiratory valve and curtailing flow. This process holds gas
in the patient’s lungs until end-inspiratory time is reached. The PIP during this
no-flow time period is, in effect, a pause pressure and peak P ALV . The dashed lines
applied to the pressure waveforms indicate the development of the P ALV during
inspiration and shows that peak P ALV is reached when flow ends. The volume held
in the patient’s lungs depends on the patient’s C . If the expired V is moni-
LT
T
tored, the patient’s lung compliance can be measured [C 5 V /(PIP 2 Total
T
LT
PEEP)]. Total PEEP includes PEEP set plus intrinsic or auto-PEEP. Arrow y at
the first expiratory flow wave shows that auto-PEEP is being created because
the ventilator time triggers successive breaths before the exhalation is complete.
Since the expiratory flow is unable to descend to the baseline, gas is trapped in
the lungs. This causes elevation of the functional residual capacity and reduction
IRPCV may be helpful in of V delivered. During PCV, the level of auto-PEEP proportionately reduces
conditions of severe hypoxia T
and lung injury (e.g., ARDS). the V delivered to the lungs. Ventilation is compromised, which may cause or
T
worsen hypercapnia.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.