Page 376 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 376
342 Chapter 11
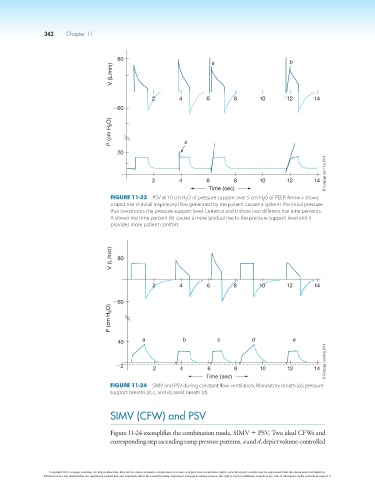
80 a b
V (L/min)
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
260
P (cm H 2 O) x
20
© Cengage Learning 2014
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Time (sec)
Figure 11-23 PSV at 10 cm H 2 O of pressure support over 5 cm H 2 O of PEEP. Arrow x shows
a rapid rise in initial inspiratory flow generated by the patient causes a spike in the initial pressure
that overshoots the pressure support level. Letters a and b show two different rise time percents.
A slower rise time percent (b) causes a more gradual rise to the pressure support level and it
provides more patient comfort.
V (L/min) 80
2 4 6 8 10 12 14
260
P (cm H 2 O)
40 a b c d e
© Cengage Learning 2014
22 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Time (sec)
Figure 11-24 SIMV and PSV during constant flow ventilation. Mandatory breath (a); pressure
support breaths (b, c, and e); assist breath (d).
SIMV (CFW) and PSV
Figure 11-24 exemplifies the combination mode, SIMV 1 PSV. Two ideal CFWs and
corresponding step ascending ramp pressure patterns, a and d, depict volume-controlled
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.