Page 374 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 374
340 Chapter 11
Based on research, auto-PEEP should be avoided if possible, and external PEEP
applied instead. A valuable advantage of having graphics is that auto-PEEP can be
readily observed and prevented whenever lung conditions have changed or ventila-
Graphics can be used to
titrate and increase the T I to tor settings have been altered. Graphics can be used to titrate and increase the T
I
an appropriate inverse-ratio to an appropriate inverse-ratio level without causing gas trapping or auto-PEEP.
level without causing gas
trapping or auto-PEEP. This management technique serves to increase mean P ALV and improve oxygenation
at lower peak P ALV to reduce the potential of barotraumas.
PRESSURE SUPPORT AND SPONTANEOUS
VENTILATION
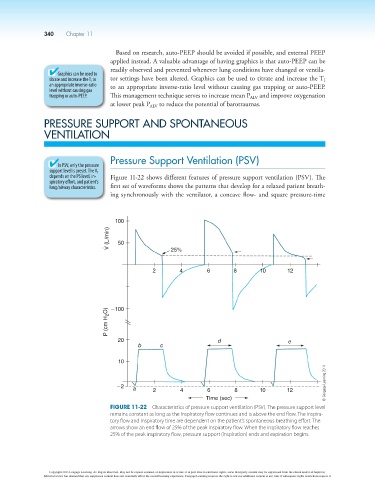
Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV)
In PSV, only the pressure
support level is preset. The V T
depends on the PS level, in- Figure 11-22 shows different features of pressure support ventilation (PSV). The
spiratory effort, and patient’s
lung/airway characteristics. first set of waveforms shows the patterns that develop for a relaxed patient breath-
ing synchronously with the ventilator, a concave flow- and square pressure-time
100
V (L/min) 50 25%
2 4 6 8 10 12
P (cm H 2 O) 2100
20 d e
b c
10
© Cengage Learning 2014
22 a 2 4 6 8 10 12
Time (sec)
Figure 11-22 Characteristics of pressure support ventilation (PSV). The pressure support level
remains constant as long as the inspiratory flow continues and is above the end flow. The inspira-
tory flow and inspiratory time are dependent on the patient’s spontaneous breathing effort. The
arrows show an end flow of 25% of the peak inspiratory flow. When the inspiratory flow reaches
25% of the peak inspiratory flow, pressure support (inspiration) ends and expiration begins.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.