Page 395 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 395
Ventilator Waveform Analysis 361
PIP (from 30 to 40 cm H O) is proportionate to the increase in P ALV (from 25 to
2
(Figure 11-39) A decrease 35 cm H O) that is caused by the reduction in C . The P gradient throughout
in C LT causes the pressure- 2 LT TA
volume loop to shift toward the inspiration (and between PIP and peak P ALV ) is held constant. P is affected by
TA
pressure axis.
changes in resistance, not by the changes in C .
LT
It is essential to note that on some ventilators (e.g., Servo 300), pressure and
volume may be assigned to the y- and x-axis, respectively. A reduction in C would
LT
shift the PVL up and to the left (i.e., toward the pressure axis).
(Figure 11-39) A decrease
in C LT will not affect the P TA
because the PIP- P ALV gradient
(P TA ) remains unchanged. Effect of Airflow Resistance on PVL
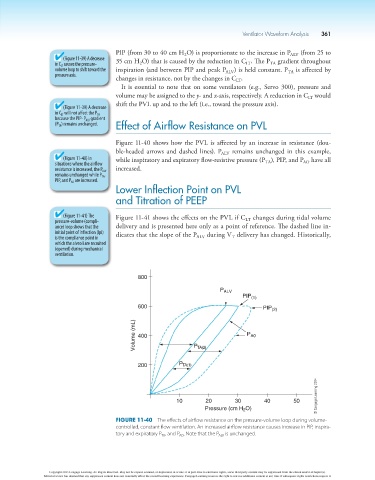
Figure 11-40 shows how the PVL is affected by an increase in resistance (dou-
ble-headed arrows and dashed lines). P ALV remains unchanged in this example,
(Figure 11-40) In while inspiratory and expiratory flow-resistive pressure (P ), PIP, and P have all
situations where the airflow TA AO
resistance is increased, the P ALV increased.
remains unchanged while P TA ,
PIP, and P AO are increased.
Lower Inflection Point on PVL
and Titration of PEEP
(Figure 11-41) The Figure 11-41 shows the effects on the PVL if C changes during tidal volume
pressure-volume (compli- LT
ance) loop shows that the delivery and is presented here only as a point of reference. The dashed line in-
initial point of inflection (Ipi) dicates that the slope of the P during V delivery has changed. Historically,
is the compliance point in ALV T
which the alveoli are recruited
(opened) during mechanical
ventilation.
800
P ALV
PIP (1)
600 PIP (2)
Volume (mL) 400 P TA(2) P A0
200 P TA(1)
© Cengage Learning 2014
10 20 30 40 50
Pressure (cm H O)
2
Figure 11-40 The effects of airflow resistance on the pressure-volume loop during volume-
controlled, constant flow ventilation. An increased airflow resistance causes increase in PIP, inspira-
tory and expiratory P TA , and P AO . Note that the P ALV is unchanged.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.