Page 396 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 396
362 Chapter 11
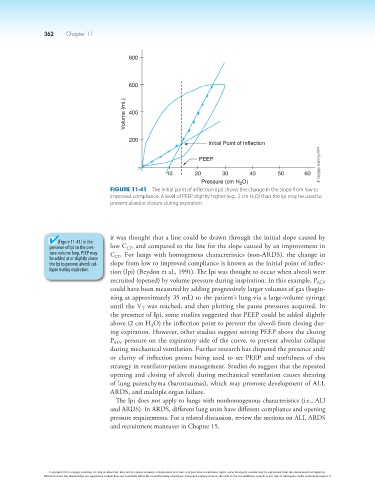
800
600
Volume (mL) 400
200
Initial Point of Inflection
© Cengage Learning 2014
PEEP
10 20 30 40 50 60
Pressure (cm H O)
2
Figure 11-41 The initial point of inflection (Ipi) shows the change in the slope from low to
improved compliance. A level of PEEP slightly higher (e.g., 2 cm H 2 O) than the Ipi may be used to
prevent alveolar closure during expiration.
it was thought that a line could be drawn through the initial slope caused by
(Figure 11-41) In the
presence of Ipi on the pres- low C , and compared to the line for the slope caused by an improvement in
LT
sure-volume loop, PEEP may C . For lungs with homogenous characteristics (non-ARDS), the change in
be added at or slightly above LT
the Ipi to prevent alveoli col- slope from low to improved compliance is known as the initial point of inflec-
lapse during expiration. tion (Ipi) (Beydon et al., 1991). The Ipi was thought to occur when alveoli were
recruited (opened) by volume pressure during inspiration. In this example, P ALV
could have been measured by adding progressively larger volumes of gas (begin-
ning at approximately 35 mL) to the patient’s lung via a large-volume syringe
until the V was reached, and then plotting the pause pressures acquired. In
T
the presence of Ipi, some studies suggested that PEEP could be added slightly
above (2 cm H O) the inflection point to prevent the alveoli from closing dur-
2
ing expiration. However, other studies suggest setting PEEP above the closing
P ALV pressure on the expiratory side of the curve, to prevent alveolar collapse
during mechanical ventilation. Further research has disputed the presence and/
or clarity of inflection points being used to set PEEP and usefulness of this
strategy in ventilator-patient management. Studies do suggest that the repeated
opening and closing of alveoli during mechanical ventilation causes shearing
of lung parenchyma (barotraumas), which may promote development of ALI,
ARDS, and multiple organ failure.
The Ipi does not apply to lungs with nonhomogenous characteristics (i.e., ALI
and ARDS). In ARDS, different lung units have different compliance and opening
pressure requirements. For a related discussion, review the sections on ALI, ARDS
and recruitment maneuver in Chapter 15.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.