Page 312 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 312
2 A
M
0:4
2 A
Pa
Pa
M
M
0:4
6/2
6/2
0/0
0/0
1
1
009
009
p
t
p
p
ara
ara
t
ara
A
g
e 2
g
g
88
A
e 2
88
27
LWB K34 0-c 13_ p p pp277-290.qxd 30/06/2009 10:42 AM Page 288 Aptara
27
7-2
7-2
0-c
13_
K34
LWB
LWBK340-c13_
3
3
xd
xd
q
3
90.
90.
q
q
288 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
that do appear in the left side of the heart are indicative of a right-
to-left shunt (i.e., atrial septal defect, patent foramen ovale, pul-
monary arterial venous malformation). Saline microbubbles are
created by connecting a two-way stopcock to an intravenous
catheter with two 10-cc syringes. One syringe is filled with 9 cc of
normal saline and 1 cc of air and then transferred to the empty sy-
ringe back and forth. This action makes bubbles of air throughout
the saline. The full 10 cc is then quickly injected into the intra-
venous catheter. Emphasis is placed on quickly so as to achieve bo-
lus opacification of contrast and not streaming of contrast of the
right heart structures.
Lipid (Definity) or albumin (Optison) microspheres are com-
mercially available contrast agents. They have a diameter of 1.1 to
4.5 μm and contain a gas (perfluoropropane) within their shell, 4,5
permitting opacification of the left ventricle because the micros-
pheres are small enough to cross the pulmonary capillaries (Fig.
13-21). Opacification of the left ventricle allows improved endo-
cardial definition, which enhances the diagnostic accuracy of
global and regional wall motion assessment. Contraindications to
the use of these contrast agents include: cardiac shunts, unstable
congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, ventricular
arrhythmias, respiratory failure, pulmonary hypertension, intra-
arterial injection, hypersensitivity to perflutren, or hypersensitiv-
ity to albumin (Optison). 4,5 Adverse effects are uncommon but
can include back/chest pain, headache, dizziness, nausea, flushing,
altered taste sensation, palpitations, urticaria, or anaphylaxis. 4,5
Stress Echo
Stress echo is performed in combination with continuous 12-lead
ECG monitoring to improve the diagnostic accuracy of coronary
artery detection or risk stratification of patients with known coro-
nary artery disease. Image acquisition is performed in the same
standard views, as described previously and optimal endocardial
definition is necessary. Sometimes, contrast is needed to provide
endocardial definition to visualize wall motion. Global and re-
gional wall motion is compared from rest to stress periods. A nor-
mal finding: a myocardial segment has normal function at rest and
hyperdynamic function at stress. An abnormal finding suggestive
of obstructive coronary artery disease: a myocardial segment has
normal function at rest and becomes hypokinetic or akinetic at
stress (Fig. 13-22).
The preferred method of stress testing is exercise, provided the
patient is able. With echo, exercise is usually done on a treadmill
or supine bicycle. For treadmill exercise, rest images are per-
formed while the patient is lying on the examination bed. The
patient then exercises on the treadmill with continuous ECG
monitoring. When peak exercise is achieved, the patient is
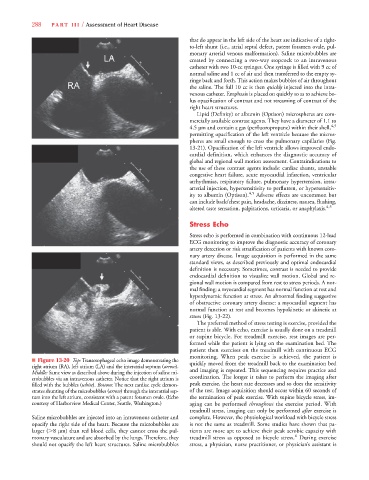
■ Figure 13-20 Top: Transesophageal echo image demonstrating the
right atrium (RA), left atrium (LA) and the interatrial septum (arrow).w quickly moved from the treadmill back to the examination bed
Middle: Same view as described above during the injection of saline mi- and imaging is repeated. This sequencing requires practice and
crobubbles via an intravenous catheter. Notice that the right atrium is coordination. The longer it takes to perform the imaging after
filled with the bubbles (white).e Bottom: The next cardiac cycle demon- peak exercise, the heart rate decreases and so does the sensitivity
strates shunting of the microbubbles (arrow) through the interatrial sep- of the test. Image acquisition should occur within 60 seconds of
w
tum into the left atrium, consistent with a patent foramen ovale. (Echo the termination of peak exercise. With supine bicycle stress, im-
courtesy of Harborview Medical Center, Seattle, Washington.) aging can be performed throughout the exercise period. With
treadmill stress, imaging can only be performed after exercise is
Saline microbubbles are injected into an intravenous catheter and complete. However, the physiological workload with bicycle stress
opacify the right side of the heart. Because the microbubbles are is not the same as treadmill. Some studies have shown that pa-
larger ( 8 μm) than red blood cells, they cannot cross the pul- tients are more apt to achieve their peak aerobic capacity with
6
monary vasculature and are absorbed by the lungs. Therefore, they treadmill stress as opposed to bicycle stress. During exercise
should not opacify the left heart structures. Saline microbubbles stress, a physician, nurse practitioner, or physician’s assistant is