Page 352 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 352
M
Pa
0 P
M
Pa
g
e 3
g
g
/09
/09
/29
/29
1
0:3
0 P
1
0:3
p
p
t
t
p
28
28
A
A
c.
In
e 3
c.
In
ara
ara
a
a
0-3
0-3
30
q
32.
32.
30
0-c
K34
LWBK340-c15_
p
p
15_
q
LWB
6
6
LWB K34 0-c 15_ pp300-332.qxd 6/29/09 10:30 PM Page 328 Aptara Inc.
q
xd
xd
328 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
V
V1
V1
V1
V V V V V V
V4
R R R R R R R R
R
a a
VR
V4
V4
V
VR
V V V V V V V V
V
I I I I a a a a a aV R V V V1 V4 4 4
VR
VR
1
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
2
V
2
V
V
VL
aVL
a a aVL
V
aVL
V
V
II II II II II II II a a a a a aVL L L L L L L L L V V V V2 V5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
VL
V2
2
2
V2
V
VL
V
2
2
2
2
V2
V5
V5
V V V5
V V V5
V
V
V
V V V V2
V V V V2
V V V V2
V
V V V V
V V V5
V V V5
F
F
F
V
F
F
V V V V3
V3
V V V V3
F
V3
V3
V
V
V
V
V
VF
V
V
V
VF
V
V
V6
a a aVF
V V V6
V6
III III III III III III aVF V V V V3 V V V6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
V6
a a a aVF
a a aVF
V V V6
3
3
3 3 3
3
3
3
3
A
I I I aV R R R R R R R R R R R R V V 1 V4
V V V4
a a a a a a a a
V4
V1
V4
V
V V V V VR
V1
aV
V
4
aV
R
4
V1
V1
R
II II II II II II aVL L L V2 2 2 2 2 2 2 V V V5
5
5
5
VL
5
5
V
V
V
V
VL
5
V
V V V2
V V V5
V5
V V V2
V V V2
V2
V
aVL
aV
aVL
V5
V V V5
a a aVL
III III III III III III III aVF F F V3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 V6
6
6 6 6
6
6
6
6
6
V V V3
V V V3
V3
V V V3
V3
V V V6
V6
V6
V V V6
V V V6
V
V
aVF
V
V
V
aVF
aVF
aVF
a a aVF
B
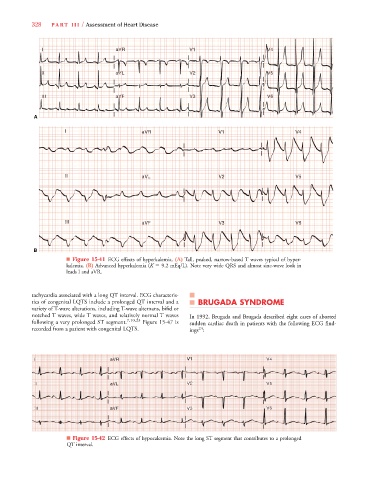
■ Figure 15-41 ECG effects of hyperkalemia. (A) Tall, peaked, narrow-based T waves typical of hyper-
kalemia. (B) Advanced hyperkalemia (K 9.2 mEq/L). Note very wide QRS and almost sine-wave look in
leads I and aVR.
tachycardia associated with a long QT interval. ECG characteris-
tics of congenital LQTS include a prolonged QT interval and a BRUGADA SYNDROME
variety of T-wave alterations, including T-wave alternans, bifid or
notched T waves, wide T waves, and relatively normal T waves In 1992, Brugada and Brugada described eight cases of aborted
following a very prolonged ST segment. 7,10,23 Figure 15-47 is sudden cardiac death in patients with the following ECG find-
recorded from a patient with congenital LQTS. ings :
24
4
4
V
V
1
V
4
4
V
V
V
V
V4
V44
V4
V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V
V V1
V
V
V1
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
4
4
4 4 4 4
4
V
V
V
V
V
V V V VR
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
R
R
R
aV
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I aV R V V V V V V V 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 V4
R R R R R R R R R R R R
R
a a a a a a a a a a a a
aV
R
R
2
2
V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V
2
V V V VL
V
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2
5
5
5
5
5 5 5 5
5
V2
V2
V2
5
5
aV
a a a a a a a a a a a a
V
aV
V5
V5
V55
V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I II I I I I I I I aV L L L L L L L L L L L L L L L V2 V5
6
aV
aV
6
6
6
6
6
6 6 6 6
F
F
3
F
F F F F F F F F F F F F
F
F
3
V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V
V3
V3
V3
3
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3
F
V
V
V66
V
V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V V
V6
V6
V
V
V
V
6
V
V V V VF
V
I I I I II II II II I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I a a a a a a a a a a a a aV F V3 V6
■ Figure 15-42 ECG effects of hypocalcemia. Note the long ST segment that contributes to a prolonged
QT interval.