Page 349 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 349
LWBK340-c15_p300-332.qxd 6/29/09 10:30 PM Page 325 Aptara Inc.
C HAPTER 1 5 / Electrocardiography 325
V V V V
VR
aV
a a a a a a a a
aVV
VR
V
V
V
VR
VR
R
R
I I I I I I I I I aV R R R R R R R R V1 1 1 1 1 V V V V V V V V V V4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
V V V V V V V V
V1
V1
a a a a a a a a a a
aV
VL
aVV
VL
V
VL
V
VL
aV
V V V V
V2
V2
V V V V V V V
V2
I I I I II II II II I I I II I aV L L L L L L L L L L V2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 V V V V V V V V V V5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
V
V V V V
VF
V
V
VF
VF
VF
aV
a a a a a a a a
aVV
V3
V V V V V V V
V3
V3
I I I I II II II II II II II II I I I I I I I aV F F F F F F F F F F F F F F V3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 V V V V V V V V V V6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
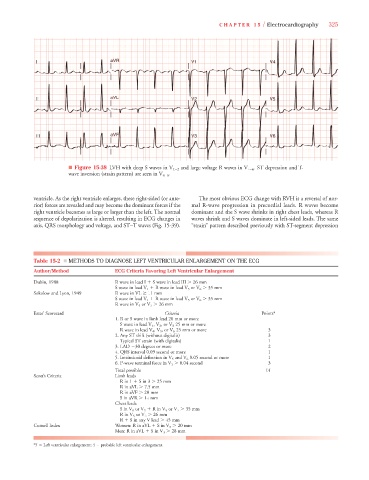
■ Figure 15-38 LVH with deep S waves in V 1–2 and large voltage R waves in V 4–6 . ST depression and T-
V
wave inversion (strain pattern) are seen in V 4–6 .
V
ventricle. As the right ventricle enlarges, these right-sided (or ante- The most obvious ECG change with RVH is a reversal of nor-
rior) forces are revealed and may become the dominant forces if the mal R-wave progression in precordial leads. R waves become
right ventricle becomes as large or larger than the left. The normal dominant and the S wave shrinks in right chest leads, whereas R
sequence of depolarization is altered, resulting in ECG changes in waves shrink and S waves dominate in left-sided leads. The same
axis, QRS morphology and voltage, and ST–T waves (Fig. 15-39). “strain” pattern described previously with ST-segment depression
Table 15-2 ■ METHODS TO DIAGNOSE LEFT VENTRICULAR ENLARGEMENT ON THE ECG
Author/Method ECG Criteria Favoring Left Ventricular Enlargement
Dubin, 1988 R wave in lead I
S wave in lead III 26 mm
S wave in lead V 1
R wave in lead V 5 or V 6 35 mm
Sokolow and Lyon, 1949 R wave in VL 11 mm
S wave in lead V 1
R wave in lead V 5 or V 6 35 mm
R wave in V 5 or V 6 26 mm
Estes’ Scorecard Criteria Points*
1. R or S wave in limb lead 20 mm or more
V
S wave in lead V 1 , V 2 , or V 3 25 mm or more
V
R wave in lead V 4 , V 5 , or V 6 25 mm or more 3
2. Any ST shift (without digitalis) 3
Typical ST strain (with digitalis) 1
3. LAD 30 degrees or more 2
4. QRS interval 0.09 second or more 1
5. Intrinsicoid deflection in V 5 and V 6 0.05 second or more 1
6. P-wave terminal force in V 1 0.04 second 3
Total possible 14
Scott’s Criteria Limb leads
R in 1
S in 3 25 mm
R in aVL 7.5 mm
R in aVF 20 mm
S in aVR 14 mm
Chest leads
S in V 1 or V 2
R in V 5 or V 6 35 mm
V
R in V 5 or V 6 26 mm
R
S in any V lead 45 mm
Cornell Index Women: R in aVL
S in V 3 20 mm
Men: R in aVL
S in V 3 28 mm
*5 Left ventricular enlargement; 4 probable left ventricular enlargement.