Page 394 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 394
2:1
2:1
1
1
1
6 A
Pa
Pa
M
6 A
M
/09
xd
xd
q
q
q
6
/09
/09
/30
6
/30
Pa
ara
ara
t
p
t
a
c.
c.
In
a
In
p
e 3
e 3
g
g
g
70
A
p
A
70
70
87.
16_
0-c
33
33
LWB
LWB K34 0-c 16_ p p pp333-387.qxd 6/30/09 12:16 AM Page 370 Aptara Inc.
K34
LWBK340-c16_
3-3
87.
3-3
370 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
V V V
V1
I I aV VR R V1 V4V4 4 4 4 4 4
V
VR
a aV
aVVR
aVR
V V V V4
V V V V V V4
V2
V2
V V V
VL
V
aV VL
aV
I I II II II I II V V V V V5
V5
V
V
V5
V3
V3
V3
V3
V V V3
V3
V3
V3
V V V6
V6
aVVP P P P V V V V6 6 6 6 6
VP
a aV
VP
V
V
a aVP
A III III I
V1
V4
aVR
I I aVR V1 V4
R
V5
V5 5 5 5
V V V V5
V5
V5
V5
V2
II II I aVL L V2
aVL
B III III III I aVP V3 V6
aVP
aVP
aVP
V3
V6
V3
V3
V
V6
V6
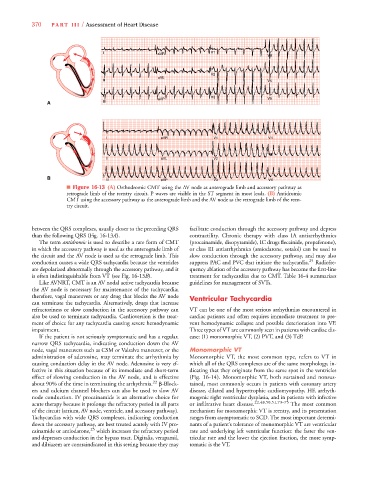
■ Figure 16-13 (A) Orthodromic CMT using the AV node as anterograde limb and accessory pathway as
retrograde limb of the reentry circuit. P waves are visible in the ST segment in most leads. (B) Antidromic
CMT using the accessory pathway as the anterograde limb and the AV node as the retrograde limb of the reen-
try circuit.
between the QRS complexes, usually closer to the preceding QRS facilitate conduction through the accessory pathway and depress
3
3
than the following QRS (Fig. 16-13A). contractility. Chronic therapy with class IA antiarrhythmics
The term antidromic is used to describe a rare form of CMT (procainamide, disopyramide), IC drugs flecainide, propafenone),
in which the accessory pathway is used as the anterograde limb of or class III antiarrhythmics (amiodarone, sotalol) can be used to
the circuit and the AV node is used as the retrograde limb. This slow conduction through the accessory pathway, and may also
conduction causes a wide QRS tachycardia because the ventricles suppress PAC and PVC that initiate the tachycardia. 25 Radiofre-
are depolarized abnormally through the accessory pathway, and it quency ablation of the accessory pathway has become the first-line
is often indistinguishable from VT (see Fig. 16-13B). treatment for tachycardias due to CMT. Table 16-4 summarizes
B
Like AVNRT, CMT is an AV nodal active tachycardia because guidelines for management of SVTs.
the AV node is necessary for maintenance of the tachycardia;
therefore, vagal maneuvers or any drug that blocks the AV node Ventricular Tachycardia
can terminate the tachycardia. Alternatively, drugs that increase
refractoriness or slow conduction in the accessory pathway can VT can be one of the most serious arrhythmias encountered in
also be used to terminate tachycardia. Cardioversion is the treat- cardiac patients and often requires immediate treatment to pre-
ment of choice for any tachycardia causing severe hemodynamic vent hemodynamic collapse and possible deterioration into VF.
impairment. Three types of VT are commonly seen in patients with cardiac dis-
If the patient is not seriously symptomatic and has a regular, ease: (1) monomorphic VT, (2) PVT, and (3) TdP.
narrow QRS tachycardia, indicating conduction down the AV
node, vagal maneuvers such as CSM or Valsalva maneuver, or the Monomorphic VT
administration of adenosine, may terminate the arrhythmia by Monomorphic VT, the most common type, refers to VT in
causing conduction delay in the AV node. Adenosine is very ef- which all of the QRS complexes are of the same morphology, in-
fective in this situation because of its immediate and short-term dicating that they originate from the same spot in the ventricles
effect of slowing conduction in the AV node, and is effective (Fig. 16-14). Monomorphic VT, both sustained and nonsus-
22
about 90% of the time in terminating the arrhythmia. -Block- tained, most commonly occurs in patients with coronary artery
ers and calcium channel blockers can also be used to slow AV disease, dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, HF, arrhyth-
node conduction. IV procainamide is an alternative choice for mogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and in patients with infective
acute therapy because it prolongs the refractory period in all parts or infiltrative heart disease. 22,48,50,51,73–75 The most common
of the circuit (atrium, AV node, ventricle, and accessory pathway). mechanism for monomorphic VT is reentry, and its presentation
Tachycardias with wide QRS complexes, indicating conduction ranges from asymptomatic to SCD. The most important determi-
down the accessory pathway, are best treated acutely with IV pro- nants of a patient’s tolerance of monomorphic VT are ventricular
cainamide or amiodarone, 25 which increases the refractory period rate and underlying left ventricular function: the faster the ven-
and depresses conduction in the bypass tract. Digitalis, verapamil, tricular rate and the lower the ejection fraction, the more symp-
and diltiazem are contraindicated in this setting because they may tomatic is the VT.