Page 396 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 396
6 A
6 A
2:1
1
2:1
M
Pa
g
Pa
M
Pa
6
/30
6
xd
xd
/30
1
1
/09
/09
/09
ara
ara
t
p
t
a
c.
c.
In
a
In
e 3
72
e 3
g
g
72
p
p
A
72
A
16_
K34
LWB
3-3
K34
p
16_
p
33
33
87.
87.
q
q
q
3-3
0-c
0-c
LWBK340-c16_ pp333-387.qxd 6/30/09 12:16 AM Page 372 Aptara Inc.
LWB
372 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
I
II
III
aVR
aVL
aVF
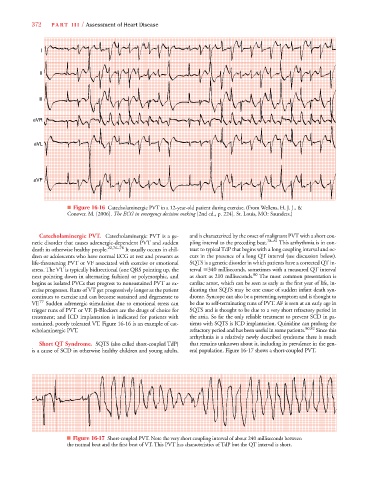
■ Figure 16-16 Catecholaminergic PVT in a 12-year-old patient during exercise. (From Wellens, H. J. J., &
Conover. M. [2006]. The ECG in emergency decision making [2nd ed., p. 224]. St. Louis, MO: Saunders.)
Catecholaminergic PVT. Catecholaminergic PVT is a ge- and is characterized by the onset of malignant PVT with a short cou-
netic disorder that causes adrenergic-dependent PVT and sudden pling interval to the preceding beat. 78–81 This arrhythmia is in con-
death in otherwise healthy people. 22,76–78 It usually occurs in chil- trast to typical TdP that begins with a long coupling interval and oc-
dren or adolescents who have normal ECG at rest and presents as curs in the presence of a long QT interval (see discussion below).
life-threatening PVT or VF associated with exercise or emotional SQTS is a genetic disorder in which patients have a corrected QT in-
stress. The VT is typically bidirectional (one QRS pointing up, the terval 340 milliseconds, sometimes with a measured QT interval
next pointing down in alternating fashion) or polymorphic, and as short as 210 milliseconds. 80 The most common presentation is
begins as isolated PVCs that progress to nonsustained PVT as ex- cardiac arrest, which can be seen as early as the first year of life, in-
ercise progresses. Runs of VT get progressively longer as the patient dicating that SQTS may be one cause of sudden infant death syn-
continues to exercise and can become sustained and degenerate to drome. Syncope can also be a presenting symptom and is thought to
VF. 77 Sudden adrenergic stimulation due to emotional stress can be due to self-terminating runs of PVT. AF is seen at an early age in
trigger runs of PVT or VF. -Blockers are the drugs of choice for SQTS and is thought to be due to a very short refractory period in
treatment; and ICD implantation is indicated for patients with the atria. So far the only reliable treatment to prevent SCD in pa-
sustained, poorly tolerated VT. Figure 16-16 is an example of cat- tients with SQTS is ICD implantation. Quinidine can prolong the
echolaminergic PVT. refractory period and has been useful in some patients. 80,82 Since this
arrhythmia is a relatively newly described syndrome there is much
Short QT Syndrome. SQTS (also called short-coupled TdP) that remains unknown about it, including its prevalence in the gen-
is a cause of SCD in otherwise healthy children and young adults, eral population. Figure 16-17 shows a short-coupled PVT.
■ Figure 16-17 Short-coupled PVT. Note the very short coupling interval of about 240 milliseconds between
the normal beat and the first beat of VT. This PVT has characteristics of TdP but the QT interval is short.