Page 390 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 390
Pa
Pa
M
Pa
g
e 3
e 3
g
g
1
1
/09
1
2:1
6 A
M
2:1
6 A
ara
a
t
ara
a
c.
c.
In
In
66
A
66
66
A
p
t
p
p
3-3
3-3
33
87.
q
q
87.
K34
16_
0-c
LWBK340-c16_
33
LWB K34 0-c 16_ p p pp333-387.qxd 6/30/09 12:16 AM Page 366 Aptara Inc.
LWB
/30
6
6
/09
/09
/30
q
xd
xd
366 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
A A
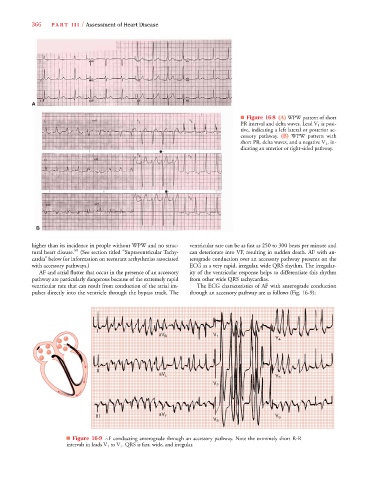
■ Figure 16-8 (A) WPW pattern of short
PR interval and delta waves. Lead V 1 is posi-
tive, indicating a left lateral or posterior ac-
cessory pathway. (B) WPW pattern with
short PR, delta waves, and a negative V 1 , in-
dicating an anterior or right-sided pathway.
B
higher than its incidence in people without WPW and no struc- ventricular rate can be as fast as 250 to 300 beats per minute and
tural heart disease. 59 (See section titled “Supraventricular Tachy- can deteriorate into VF, resulting in sudden death. AF with an-
cardia” below for information on reentrant arrhythmias associated terograde conduction over an accessory pathway presents on the
with accessory pathways.) ECG as a very rapid, irregular, wide QRS rhythm. The irregular-
AF and atrial flutter that occur in the presence of an accessory ity of the ventricular response helps to differentiate this rhythm
pathway are particularly dangerous because of the extremely rapid from other wide QRS tachycardias.
ventricular rate that can result from conduction of the atrial im- The ECG characteristics of AF with anterograde conduction
pulses directly into the ventricle through the bypass track. The through an accessory pathway are as follows (Fig. 16-9):
I I I
aV
aV
a R R R V V 1 1 1 V V V V 4 4 4
II II
aV L L L V V V V V 5 5 5
aV
a aV
V V V V V 2 2 2
aV
aV
a aV
III III III aV F F F V V V 6 6 6
V V V V 3 3 3
■ Figure 16-9 AF conducting anterograde through an accessory pathway. Note the extremely short R-R
intervals in leads V 1 to V 3 . QRS is fast, wide, and irregular.