Page 473 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 473
Pa
Pa
M
M
Pa
g
e 4
g
g
9 P
/09
1
/09
/09
1
1:2
9 P
1
1:2
e 4
a
a
ara
a
a
c.
c.
In
In
ara
A
A
49
49
p
t
t
p
p
/29
9-4
59.
43
9-4
q
q
59.
59.
0-c
K34
20_
20_
LWB K34 0-c 20_ p p pp439-459.qxd 6/29/09 11:29 PM Page 449 Aptara Inc.
43
LWBK340-c20_
LWB
q
6
6
/29
xd
xd
C HAPTER 2 0 / Cardiac Catheterization 449
A B C D
E F G
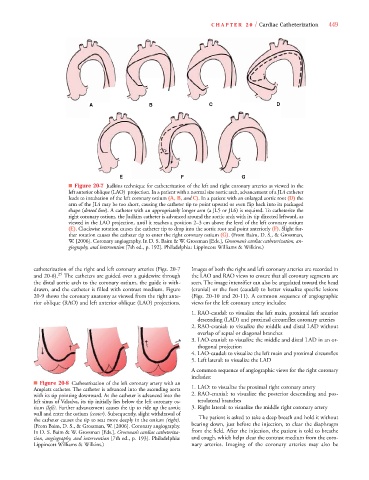
■ Figure 20-7 Judkins technique for catheterization of the left and right coronary arteries as viewed in the
left anterior oblique (LAO) projection. In a patient with a normal size aortic arch, advancement of a JL4 catheter
leads to intubation of the left coronary ostium (A, B, and C). In a patient with an enlarged aortic root (D) the
arm of the JL4 may be too short, causing the catheter tip to point upward or even flip back into its packaged
e
shape (dotted line). A catheter with an appropriately longer arm (a JL5 or JL6) is required. To catheterize the
right coronary ostium, the Judkins catheter is advanced around the aortic arch with its tip directed leftward, as
viewed in the LAO projection, until it reaches a position 2–3 cm above the level of the left coronary ostium
(E). Clockwise rotation causes the catheter tip to drop into the aortic root and point anteriorly (F). Slight fur-
ther rotation causes the catheter tip to enter the right coronary ostium (G). (From Baim, D. S., & Grossman,
W. [2006]. Coronary angiography. In D. S. Baim & W. Grossman [Eds.], Grossman’s cardiac catheterization, an-
giography, and intervention [7th ed., p. 192]. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.)
catheterization of the right and left coronary arteries (Figs. 20-7 Images of both the right and left coronary arteries are recorded in
and 20-8). 25 The catheters are guided over a guidewire through the LAO and RAO views to ensure that all coronary segments are
the distal aortic arch to the coronary ostium, the guide is with- seen. The image intensifier can also be angulated toward the head
drawn, and the catheter is filled with contrast medium. Figure (cranial) or the foot (caudal) to better visualize specific lesions
20-9 shows the coronary anatomy as viewed from the right ante- (Figs. 20-10 and 20-11). A common sequence of angiographic
rior oblique (RAO) and left anterior oblique (LAO) projections. views for the left coronary artery includes:
1. RAO-caudal: to visualize the left main, proximal left anterior
descending (LAD) and proximal circumflex coronary arteries
2. RAO-cranial: to visualize the middle and distal LAD without
overlap of septal or diagonal branches
3. LAO-cranial: to visualize the middle and distal LAD in an or-
thogonal projection
4. LAO-caudal: to visualize the left main and proximal circumflex
5. Left lateral: to visualize the LAD
A common sequence of angiographic views for the right coronary
includes:
■ Figure 20-8 Catheterization of the left coronary artery with an
Amplatz catheter. The catheter is advanced into the ascending aorta 1. LAO: to visualize the proximal right coronary artery
with its tip pointing downward. As the catheter is advanced into the 2. RAO-cranial: to visualize the posterior descending and pos-
left sinus of Valsalva, its tip initially lies below the left coronary os- terolateral branches
tium (left). Further advancement causes the tip to ride up the aortic 3. Right lateral: to visualize the middle right coronary artery
wall and enter the ostium (center). Subsequently, slight withdrawal ofr r
the catheter causes the tip to seat more deeply in the ostium (right). The patient is asked to take a deep breath and hold it without
(From Baim, D. S., & Grossman, W. [2006]. Coronary angiography. bearing down, just before the injection, to clear the diaphragm
In D. S. Baim & W. Grossman [Eds.], Grossman’s cardiac catheteriza- from the field. After the injection, the patient is told to breathe
tion, angiography, and intervention [7th ed., p. 193]. Philadelphia: and cough, which helps clear the contrast medium from the coro-
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.) nary arteries. Imaging of the coronary arteries may also be