Page 589 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 589
3 P
5-5
5-5
1:4
94.
94.
1:4
3 P
Pa
Pa
g
M
M
55
55
0
0/0
0/0
3
009
6/2
6/2
009
3
q
q
0
q
3
xd
xd
ara
ara
t
p
t
24_
LWBK340-c24_
LWB K34 0-c 24_ p p pp555-594.qxd 30/06/2009 01:43 PM Page 565 Aptara
LWB
0-c
K34
p
65
g
g
65
e 5
A
p
e 5
A
C HAPTER 24 / Heart Failure and Cardiogenic Shock 565
IL-8, IL-12). The cardiac myocytes themselves are capable of syn-
thesizing these proinflammatory cytokines in response to various
34
forms of cardiac injury. The local inflammatory response can ap-
Brain pear within minutes of an abnormal stress. Local inflammation of
the cytokines and other mediators includes deleterious effects of
Paraventricular
Supraoptic neurons LV remodeling, which include myocyte hypertrophy, alteration in
neurons fetal gene expression, contractile defects, and progressive myocyte
loss through apoptosis. In addition, there may be promotion of
LV remodeling through alterations of the extracellular matrix. A
number of studies have shown that the local proinflammatory
Pituitary, molecules are activated as early as New York Heart Association
posterior (NYHA) class I, which is before some of the classic neurohor-
lobe
monal responses, that tend to be activated in the latter stages
(NYHA II thru IV). There are important signaling interactions
between the RAAS and the sympathetic nervous system, along
with the proinflammatory cytokines. 35
Baroreceptors Activation of the systemic inflammatory response is found in
Angiotensin II
Hyperosmolarity Vasopressin Natriuretic advanced HF. Cardiac cachexia and skeletal muscle myopathy,
peptides
which contributes to the fatigue and muscle weakness seen in HF,
is a part of the systemic inflammatory response; the elevation of
the proinflammatory cytokines correlates with the severity of the
Vasoconstriction Inhibition of syndrome. The knowledge of the role of inflammation remains in-
renin secretion complete. As with the hemodynamic defence reaction, the in-
flammatory response may be initially beneficial, but when sus-
Increased arterial tained becomes deleterious.
baroreceptor Renal H 2O
sensitivity reabsorption
Systolic and Diastolic Dysfunction
HF is commonly subdivided into two entities. Patients with
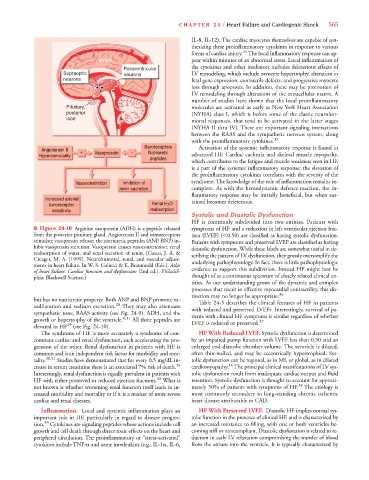
■ Figure 24-10 Arginine vasopressin (ADH) is a peptide released symptoms of HF and a reduction in left ventricular ejection frac-
from the posterior pituitary gland. Angiotensin II and osmoreceptors tion (LVEF) ( 0.50) are classified as having systolic dysfunction.
stimulate vasopressin release; the natriuretic peptides (ANP, BNP) in- Patients with symptoms and preserved LVEF are classified as having
hibit vasopressin secretion. Vasopressin causes vasoconstriction, renal diastolic dysfunction. While these labels are somewhat useful in de-
reabsorption of water, and renal secretion of renin. (Cusco, J. A. & scribing the pattern of LV dysfunction, they grossly oversimplify the
Creager, M. A. [1999]. Neurohumoral, renal, and vascular adjust-
ments in heart failure. In W. S. Colucci & E. Braunwald (Eds.), Atlas underlying pathophysiology. In fact, there is little pathophysiologic
of heart failure. Cardiac function and dysfunction [2nd ed.]. Philadel- evidence to support this subdivision. Instead HF might best be
phia: Blackwell Science.) thought of as a continuous spectrum of closely related clinical en-
tities. As our understanding grows of the dynamic and complex
processes that result in effective myocardial contractility, this dis-
tinction may no longer be appropriate. 36
but has no natriuretic property. Both ANP and BNP promote va- Table 24-5 describes the clinical features of HF in patients
sodilatation and sodium excretion. 28 They may also attenuate with reduced and preserved LVEFs. Interestingly, survival of pa-
sympathetic tone, RAAS activity (see Fig. 24-9), ADH, and the tients with clinical HF symptoms is similar regardless of whether
growth or hypertrophy of the ventricle. 6,11 All three peptides are LVEF is reduced or preserved. 37
elevated in HF 29 (see Fig. 24-10).
The syndrome of HF is more accurately a syndrome of con- HF With Reduced LVEF. Systolic dysfunction is determined
comitant cardiac and renal dysfunction, each accelerating the pro- by an impaired pump function with LVEF less than 0.50 and an
gression of the other. Renal dysfunction in patients with HF is enlarged end-diastolic chamber volume. The ventricle is dilated,
common and is an independent risk factor for morbidity and mor- often thin-walled, and may be eccentrically hypertrophied. Sys-
tality. 30,31 Studies have demonstrated that for every 0.5 mg/dL in- tolic dysfunction can be regional, as in MI, or global, as in dilated
16
crease in serum creatinine there is an associated 7% risk of death. 26 cardiomyopathy. The principal clinical manifestations of LV sys-
Interestingly, renal dysfunction is equally prevalent in patients with tolic dysfunction result from inadequate cardiac output and fluid
HF with either preserved or reduced ejection fractions. 32 What is retention. Systolic dysfunction is thought to account for approxi-
not known is whether worsening renal function itself leads to in- mately 50% of patients with symptoms of HF. 38 The etiology is
creased morbidity and mortality or if it is a marker of more severe most commonly secondary to long-standing chronic ischemic
cardiac and renal diseases. heart disease attributable to CAD.
Inflammation. Local and systemic inflammation plays an HF With Preserved LVEF. Diastolic HF implies normal sys-
important role in HF, particularly in regard to disease progres- tolic function in the presence of clinical HF, and is characterized by
33
sion. Cytokines are signaling peptides whose actions include cell an increased resistance to filling, with one or both ventricles be-
growth and cell death through direct toxic effects on the heart and coming stiff or noncompliant. Diastolic dysfunction is related to re-
peripheral circulation. The proinflammatory or “stress-activated” duction in early LV relaxation compromising the transfer of blood
cytokines include TNF- and some interleukins (e.g., IL-1 , IL-6, from the atrium into the ventricle. It is typically characterizedby