Page 697 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 697
qxd
qxd
04.
7
/1/
/1/
7
04.
Ap
tar
673
Ap
5-7
5-7
tar
09
g
a
a
g
673
e
e
P
49
9:
09
49
P
AM
AM
0-c
0-c
K34
K34
p65
28_
28_
p65
LWB
LWBK340-c28_p655-704.qxd 7/1/09 9:9:49 AM Page 673 Aptara a a
L L LWB
C HAPTER 2 8 / Pacemakers and Implantable Defibrillators 673
A
Table 28-2 ■ DUAL-CHAMBER PACING MODES Pacing Interval AV Interval
Chamber(s) Chamber(s)
Mode Paced Sensed Response to Sensing
DVI Atrium and Ventricle Ventricular sensing inhibits atrial
ventricle and ventricular pacing
VDD Ventricle Atrium and Atrial sensing—triggers
ventricle ventricular pacing
Ventricular sensing—inhibits
ventricular pacing Atrial Escape interval (V-A interval)
DDI Atrium and Atrium and Atrial sensing inhibits atrial
ventricle ventricle pacing
Ventricular sensing inhibits B
ventricular pacing
DDD Atrium and Atrium and Atrial sensing—inhibits atrial
ventricle ventricle pacing, triggers ventricular
pacing
Ventricular sensing—inhibits
atrial and ventricular pacing
AVI PVARP
triggered, depending on which chamber is sensed. When atrial ac-
tivity is sensed, atrial pacing is inhibited and ventricular pacing is
C
triggered at the end of the programmed AV delay. When ventricular
activity is sensed, all pacemaker output is inhibited. The following
timing cycles determine how a dual-chamber pacemaker functions,
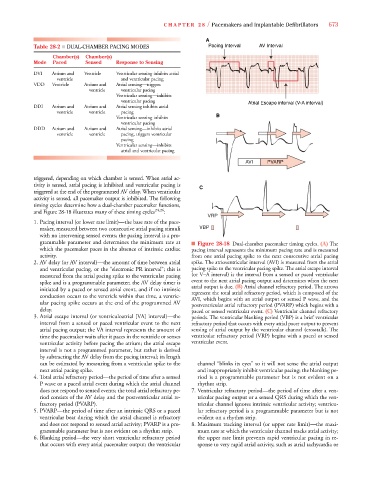
and Figure 28-18 illustrates many of these timing cycles 24,26 :
VRP
1. Pacing interval (or lower rate limit)—the base rate of the pace-
maker, measured between two consecutive atrial pacing stimuli VBP
with no intervening sensed events; the pacing interval is a pro-
grammable parameter and determines the minimum rate at ■ Figure 28-18 Dual-chamber pacemaker timing cycles. (A) The
which the pacemaker paces in the absence of intrinsic cardiac pacing interval represents the minimum pacing rate and is measured
activity. from one atrial pacing spike to the next consecutive atrial pacing
2. AV delay (or AV interval)—the amount of time between atrial spike. The atrioventricular interval (AVI) is measured from the atrial
and ventricular pacing, or the “electronic PR interval”; this is pacing spike to the ventricular pacing spike. The atrial escape interval
measured from the atrial pacing spike to the ventricular pacing (or V–A interval) is the interval from a sensed or paced ventricular
spike and is a programmable parameter; the AV delay timer is event to the next atrial pacing output and determines when the next
initiated by a paced or sensed atrial event, and if no intrinsic atrial output is due. (B) Atrial channel refractory period. The arrows
represent the total atrial refractory period, which is composed of the
conduction occurs to the ventricle within that time, a ventric- AVI, which begins with an atrial output or sensed P wave, and the
ular pacing spike occurs at the end of the programmed AV postventricular atrial refractory period (PVARP) which begins with a
delay. paced or sensed ventricular event. (C) Ventricular channel refractory
3. Atrial escape interval (or ventriculoatrial [VA] interval)—the periods. The ventricular blanking period (VBP) is a brief ventricular
interval from a sensed or paced ventricular event to the next refractory period that occurs with every atrial pacer output to prevent
atrial pacing output; the VA interval represents the amount of sensing of atrial output by the ventricular channel (crosstalk). The
time the pacemaker waits after it paces in the ventricle or senses ventricular refractory period (VRP) begins with a paced or sensed
ventricular activity before pacing the atrium; the atrial escape ventricular event.
interval is not a programmed parameter, but rather is derived
by subtracting the AV delay from the pacing interval; its length
can be estimated by measuring from a ventricular spike to the channel “blinks its eyes” so it will not sense the atrial output
next atrial pacing spike. and inappropriately inhibit ventricular pacing; the blanking pe-
4. Total atrial refractory period—the period of time after a sensed riod is a programmable parameter but is not evident on a
P wave or a paced atrial event during which the atrial channel rhythm strip.
does not respond to sensed events; the total atrial refractory pe- 7. Ventricular refractory period—the period of time after a ven-
riod consists of the AV delay and the postventricular atrial re- tricular pacing output or a sensed QRS during which the ven-
fractory period (PVARP). tricular channel ignores intrinsic ventricular activity; ventricu-
5. PVARP—the period of time after an intrinsic QRS or a paced lar refractory period is a programmable parameter but is not
ventricular beat during which the atrial channel is refractory evident on a rhythm strip.
and does not respond to sensed atrial activity; PVARP is a pro- 8. Maximum tracking interval (or upper rate limit)—the maxi-
grammable parameter but is not evident on a rhythm strip. mum rate at which the ventricular channel tracks atrial activity;
6. Blanking period—the very short ventricular refractory period the upper rate limit prevents rapid ventricular pacing in re-
that occurs with every atrial pacemaker output; the ventricular sponse to very rapid atrial activity, such as atrial tachycardia or