Page 698 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 698
9:
09
09
49
AM
AM
49
qxd
qxd
04.
7
/1/
/1/
7
674
674
e
Ap
tar
tar
Ap
a
P
P
a
e
g
g
K34
K34
LWB
0-c
p65
p65
0-c
04.
28_
28_
LWBK340-c28_p655-704.qxd 7/1/09 9:9:49 AM Page 674 Aptara a a
5-7
5-7
L L LWB
674 PA R T I V / Pathophysiology and Management Disease
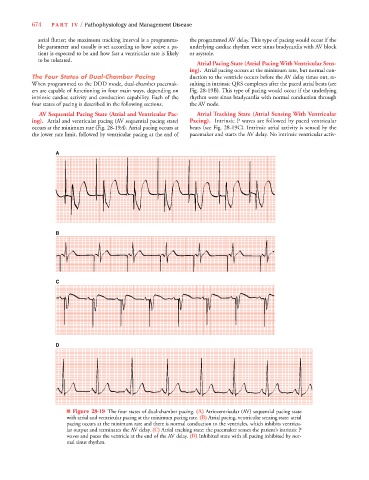
atrial flutter; the maximum tracking interval is a programma- the programmed AV delay. This type of pacing would occur if the
ble parameter and usually is set according to how active a pa- underlying cardiac rhythm were sinus bradycardia with AV block
tient is expected to be and how fast a ventricular rate is likely or asystole.
to be tolerated.
Atrial Pacing State (Atrial Pacing With Ventricular Sens-
ing). Atrial pacing occurs at the minimum rate, but normal con-
The Four States of Dual-Chamber Pacing duction to the ventricle occurs before the AV delay times out, re-
When programmed to the DDD mode, dual-chamber pacemak- sulting in intrinsic QRS complexes after the paced atrial beats (see
ers are capable of functioning in four main ways, depending on Fig. 28-19B). This type of pacing would occur if the underlying
intrinsic cardiac activity and conduction capability. Each of the rhythm were sinus bradycardia with normal conduction through
four states of pacing is described in the following sections. the AV node.
AV Sequential Pacing State (Atrial and Ventricular Pac- Atrial Tracking State (Atrial Sensing With Ventricular
ing). Atrial and ventricular pacing (AV sequential pacing state) Pacing). Intrinsic P waves are followed by paced ventricular
9
occurs at the minimum rate (Fig. 28-19A). Atrial pacing occurs at beats (see Fig. 28-19C). Intrinsic atrial activity is sensed by the
9
the lower rate limit, followed by ventricular pacing at the end of pacemaker and starts the AV delay. No intrinsic ventricular activ-
A
B
C
D
■ Figure 28-19 The four states of dual-chamber pacing. (A) Atrioventricular (AV) sequential pacing state
with atrial and ventricular pacing at the minimum pacing rate. (B) Atrial pacing, ventricular sensing state: atrial
pacing occurs at the minimum rate and there is normal conduction to the ventricles, which inhibits ventricu-
lar output and terminates the AV delay. (C) Atrial tracking state: the pacemaker senses the patient’s intrinsic P
waves and paces the ventricle at the end of the AV delay. (D) Inhibited state with all pacing inhibited by nor-
mal sinus rhythm.