Page 741 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 741
718 S P E C I A LT Y P R A C T I C E I N C R I T I C A L C A R E
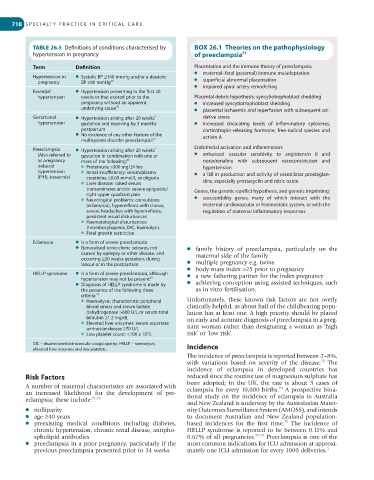
TABLE 26.5 Definitions of conditions characterised by BOX 26.1 Theories on the pathophysiology
hypertension in pregnancy of preeclampsia 71
Term Definition Placentation and the immune theory of preeclampsia:
l maternal–fetal (paternal) immune maladaptation
Hypertension in l Systolic BP ≥140 mmHg and/or a diastolic
pregnancy BP ≥90 mmHg 65 l superficial abnormal placentation
l impaired spiral artery remodelling
Essential l Hypertension presenting in the first 20
hypertension weeks or that existed prior to the Placental debris hypothesis: syncytiotrophoblast shedding
pregnancy without an apparent l increased syncytiotrophoblast shedding
underlying cause 65 l placental ischaemia and reperfusion with subsequent oxi-
Gestational l Hypertension arising after 20 weeks’ dative stress
hypertension gestation and resolving by 3 months l increased circulating levels of inflammatory cytokines,
postpartum corticotropin-releasing hormone, free-radical species and
l No evidence of any other feature of the activin A
multisystem disorder preeclampsia 65
Preeclampsia l Hypertension arising after 20 weeks’ Endothelial activation and inflammation:
(Also referred to gestation in combination with one or l enhanced vascular sensitivity to angiotensin II and
as pregnancy more of the following: 65 noradrenaline with subsequent vasoconstriction and
induced l Proteinuria >300 mg/24 hrs hypertension
hypertension l Renal insufficiency: serum/plasma l a fall in production and activity of vasodilator prostaglan-
(PIH), toxaemia) creatinine ≥0.09 mmol/L or oliguria
l Liver disease: raised serum dins, especially prostacyclin and nitric oxide
transaminases and/or severe epigastric/ Genes, the genetic-conflict hypothesis, and genetic imprinting:
right upper quadrant pain
l Neurological problems: convulsions l susceptibility genes, many of which interact with the
(eclampsia), hyperreflexia with clonus, maternal cardiovascular or haemostatic system, or with the
severe headaches with hyperreflexia, regulation of maternal inflammatory responses
persistent visual disturbances
l Haematological disturbances:
thrombocytopenia, DIC, haemolysis
l Fetal growth restriction
Eclampsia l Is a form of severe preeclampsia
l Generalised tonic-clonic seizures, not l family history of preeclampsia, particularly on the
caused by epilepsy or other disease, and maternal side of the family
occurring ≥20 weeks gestation, during
labour or in the postpartum l multiple pregnancy e.g. twins
l body mass index >25 prior to pregnancy
HELLP syndrome l Is a form of severe preeclampsia, although l a new fathering partner for the index pregnancy
hypertension may not be present 69
l Diagnosis of HELLP syndrome is made by l achieving conception using assisted techniques, such
the presence of the following three as in vitro fertilisation.
criteria: 70
l Haemolysis: characteristic peripheral Unfortunately, these known risk factors are not overly
blood smear and serum lactate clinically helpful, as about half of the childbearing popu-
dehydrogenase >600 U/L or serum total lation has at least one. A high priority should be placed
bilirubin ≥1.2 mg/dL on early and accurate diagnosis of preeclampsia in a preg-
l Elevated liver enzymes: serum aspartate
aminotransferase ≥70 U/L nant woman rather than designating a woman as ‘high
9
l Low platelet count: <100 x 10 /L risk’ or ‘low risk’.
DIC – disseminated intravascular coagulopathy; HELLP – haemolysis, Incidence
elevated liver enzymes and low platelets.
The incidence of preeclampsia is reported between 2–8%,
73
with variations based on severity of the disease. The
incidence of eclampsia in developed countries has
Risk Factors reduced since the routine use of magnesium sulphate has
A number of maternal characteristics are associated with been adopted; in the UK, the rate is about 3 cases of
74
an increased likelihood for the development of pre- eclampsia for every 10,000 births. A prospective bina-
eclampsia; these include: 71,73 tional study on the incidence of eclampsia in Australia
and New Zealand is underway by the Australasian Mater-
l nulliparity nity Outcomes Surveillance System (AMOSS), and intends
l age ≥40 years to document Australian and New Zealand population-
75
l preexisting medical conditions including diabetes, based incidences for the first time. The incidence of
chronic hypertension, chronic renal disease, antipho- HELLP syndrome is reported to be between 0.11% and
spholipid antibodies 0.67% of all pregnancies. 76,77 Preeclampsia is one of the
l preeclampsia in a prior pregnancy, particularly if the most common indications for ICU admission at approxi-
previous preeclampsia presented prior to 34 weeks mately one ICU admission for every 1000 deliveries. 3