Page 1355 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1355
Chapter 73 The Pathologic Basis for the Classification of Non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin Lymphomas 1201
CD21 CD20
A B C C D D
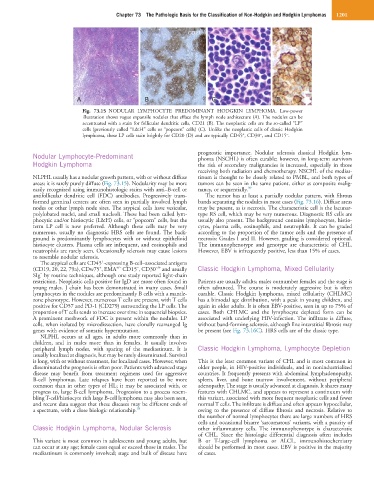
Fig. 73.15 NODULAR LYMPHOCYTE PREDOMINANT HODGKIN LYMPHOMA. Low-power
illustration shows vague expansile nodules that efface the lymph node architecture (A). The nodules can be
accentuated with a stain for follicular dendritic cells, CD21 (B). The neoplastic cells are the so-called “LP”
cells (previously called “L&H” cells or “popcorn” cells) (C). Unlike the neoplastic cells of classic Hodgkin
−
−
+
lymphoma, these LP cells stain brightly for CD20 (D) and are typically CD45 , CD30 , and CD15 .
Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant prognostic importance. Nodular sclerosis classical Hodgkin lym-
phoma (NSCHL) is often curable; however, in long-term survivors
Hodgkin Lymphoma the risk of secondary malignancies is increased, especially in those
receiving both radiation and chemotherapy. NSCHL of the medias-
NLPHL usually has a nodular growth pattern, with or without diffuse tinum is thought to be closely related to PMBL, and both types of
areas; it is rarely purely diffuse (Fig. 73.15). Nodularity may be more tumors can be seen in the same patient, either as composite malig-
easily recognized using immunohistologic stains with anti–B-cell or nancy, or sequentially. 39
antifollicular dendritic cell (FDC) antibodies. Progressively trans- The tumor has at least a partially nodular pattern, with fibrous
formed germinal centers are often seen in partially involved lymph bands separating the nodules in most cases (Fig. 73.16). Diffuse areas
nodes or other lymph node sites. The atypical cells have vesicular, may be present, as is necrosis. The characteristic cell is the lacunar-
polylobated nuclei, and small nucleoli. These had been called lym- type RS cell, which may be very numerous. Diagnostic RS cells are
phocytic and/or histiocytic (L&H) cells, or “popcorn” cells, but the usually also present. The background contains lymphocytes, histio-
term LP cell is now preferred. Although these cells may be very cytes, plasma cells, eosinophils, and neutrophils. It can be graded
numerous, usually no diagnostic HRS cells are found. The back- according to the proportion of the tumor cells and the presence of
ground is predominantly lymphocytes with or without epithelioid necrosis: Grades I and II. However, grading is considered optional.
histiocyte clusters. Plasma cells are infrequent, and eosinophils and The immunophenotype and genotype are characteristic of CHL.
neutrophils are rarely seen. Occasionally sclerosis may cause lesions However, EBV is infrequently positive, less than 15% of cases.
to resemble nodular sclerosis.
+
The atypical cells are CD45 -expressing B-cell–associated antigens
+/−
−/+
−
+
(CD19, 20, 22, 79a), CDw75 , EMA CD15 , CD30 and usually Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma, Mixed Cellularity
−
SIg by routine techniques, although one study reported light-chain
restriction. Neoplastic cells positive for IgD are more often found in Patients are usually adults; males outnumber females and the stage is
young males. J chain has been demonstrated in many cases. Small often advanced. The course is moderately aggressive but is often
lymphocytes in the nodules are predominantly B cells with a mantle- curable. Classic Hodgkin lymphoma, mixed cellularity (CHLMC)
zone phenotype. However, numerous T cells are present, with T cells has a bimodal age distribution, with a peak in young children, and
positive for CD57 and PD-1 (CD279) surrounding the LP cells. The again in older adults. It is often EBV-positive, seen in up to 75% of
proportion of T cells tends to increase over time in sequential biopsies. cases. Both CHLMC and the lymphocyte depleted form can be
A prominent meshwork of FDC is present within the nodules. LP associated with underlying HIV-infection. The infiltrate is diffuse,
cells, when isolated by microdissection, have clonally rearranged Ig without band-forming sclerosis, although fine interstitial fibrosis may
genes with evidence of somatic hypermutation. be present (see Fig. 73.16C). HRS cells are of the classic type.
NLPHL occurs at all ages, in adults more commonly than in
children, and in males more than in females. It usually involves
peripheral lymph nodes, with sparing of the mediastinum. It is Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma, Lymphocyte Depletion
usually localized at diagnosis, but may be rarely disseminated. Survival
is long, with or without treatment, for localized cases. However, when This is the least common variant of CHL and is most common in
disseminated the prognosis is often poor. Patients with advanced stage older people, in HIV-positive individuals, and in nonindustrialized
disease may benefit from treatment regimens used for aggressive countries. It frequently presents with abdominal lymphadenopathy,
B-cell lymphomas. Late relapses have been reported to be more spleen, liver, and bone marrow involvement, without peripheral
common than in other types of HL; it may be associated with, or adenopathy. The stage is usually advanced at diagnosis. It shares many
progress to, large B-cell lymphoma. Progression to a process resem- features with CHLMC, and appears to represent a continuum with
bling T-cell/histiocyte rich large B-cell lymphoma may also been seen, this variant, associated with more frequent neoplastic cells and fewer
and recent data suggest that these diseases may be different ends of normal T cells. The infiltrate is diffuse and often appears hypocellular,
a spectrum, with a close biologic relationship. 38 owing to the presence of diffuse fibrosis and necrosis. Relative to
the number of normal lymphocytes there are large numbers of HRS
cells and occasional bizarre ‘sarcomatous’ variants, with a paucity of
Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma, Nodular Sclerosis other inflammatory cells. The immunophenotype is characteristic
of CHL. Since the histologic differential diagnosis often includes
This variant is most common in adolescents and young adults, but B or T-large-cell lymphoma or ALCL, immunohistochemistry
can occur at any age; female cases equal or exceed those in males. The should be performed in most cases. EBV is positive in the majority
mediastinum is commonly involved; stage and bulk of disease have of cases.