Page 1390 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1390
1236 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
TNFRSF14 cSNVs
BCL10 CD58 CNV loss
BTG2 CNV gain
CNV high-level gain
LOH
MEF2B
CD70
BCL2
GNA13
STAT3 MYD88
CD79B
TP53
IRF8
CREBBP KLHL6
BCL2
B2M
IGH
FOXO1
BTG1
MLL2 HIST1H1C
CCND3
ETS1
TMEM30A
SGK1
FAS CARD11
EZH2
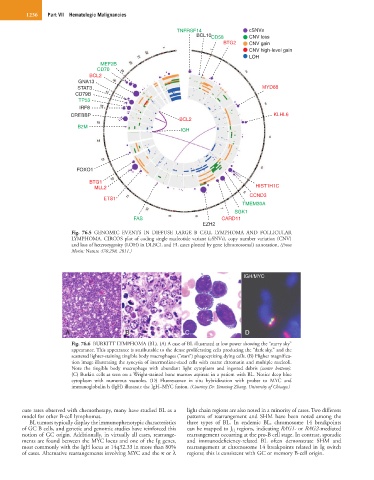
Fig. 76.5 GENOMIC EVENTS IN DIFFUSE LARGE B CELL LYMPHOMA AND FOLLICULAR
LYMPHOMA. CIRCOS plot of coding single nucleotide variant (cSNVs), copy number variation (CNV)
and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) in DLBCL and FL cases plotted by gene (chromosomal) annotation. (From
Morin: Nature 476:298, 2011.)
IGH/MYC
A B C D
Fig. 76.6 BURKITT LYMPHOMA (BL). (A) A case of BL illustrated at low power showing the “starry sky”
appearance. This appearance is attributable to the dense proliferating cells producing the “dark sky,” and the
scattered lighter-staining tingible body macrophages (“stars”) phagocytizing dying cells. (B) Higher magnifica-
tion image illustrating the syncytia of intermediate-sized cells with coarse chromatin and multiple nucleoli.
Note the tingible body macrophage with abundant light cytoplasm and ingested debris (center bottom).
(C) Burkitt cells as seen on a Wright-stained bone marrow aspirate in a patient with BL. Notice deep blue
cytoplasm with numerous vacuoles. (D) Fluorescence in situ hybridization with probes to MYC and
immunoglobulin h (IgH) illustrate the IgH–MYC fusion. (Courtesy Dr. Yanming Zhang, University of Chicago.)
cure rates observed with chemotherapy, many have studied BL as a light chain regions are also noted in a minority of cases. Two different
model for other B-cell lymphomas. patterns of rearrangement and SHM have been noted among the
BL tumors typically display the immunophenotypic characteristics three types of BL. In endemic BL, chromosome 14 breakpoints
of GC B cells, and genetic and genomic studies have reinforced this can be mapped to J H regions, indicating RAG1- or RAG2-mediated
notion of GC origin. Additionally, in virtually all cases, rearrange- rearrangement occurring at the pro-B cell stage. In contrast, sporadic
ments are found between the MYC locus and one of the Ig genes, and immunodeficiency-related BL often demonstrate SHM and
most commonly with the IgH locus at 14q32.33 in more than 80% rearrangement at chromosome 14 breakpoints related in Ig switch
of cases. Alternative rearrangements involving MYC and the κ or λ regions; this is consistent with GC or memory B-cell origin.