Page 1391 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1391
Chapter 76 Origin of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma 1237
A BL ABC GCB PMBL B BL ABC GCB PMBL
AVG AVG AVG AVG AVG AVG AVG AVG
--MYC --BMP7
--TERT --CADPS
--DLEU1 --MME
--GRSF1 --ACY3
--BUB1B --VPREB3
--TRIP13 --SSBP2 BL
--NOL5A --BCL7A High
--LRPPRC --DOK3
--HDGF --CD38
MYC --UCK2 --PEX5
--GCET2
--GNL3
and --HMGB1 --TRAP1
target --SRPK1 --LMO2
--SFPQ
genes --MATR3 --MET
--TOX
--HDAC2 --SERPINA9
--MAPKAPK5 --RRAS2
--CSTF3 --TEX9
--NOLC1 --AIM2
--NP
--GLO1 --CYLN2 BL
C --HLA-A Germinal --MAML3 Low
--CD80
MYC --HLA-B --FGD6
--CD86
--HLA-C center
class --LRCH3
--HLA-E B-cell
genes --HLA-F --LOXL2
--HLA-G genes --GSN
--ELL3
D --CD40 --COTL1
--CXCL9
--CD83 --BCL6
--CXCL10 --DCK
--IRF4 --SYNE2
--DUSP2 --TERF2
--TRAF1 --MBD4
--BCL2A1 --PAG
NFκB --LTA --PRSPAP2
target --CCL22 --TRIM14 BL GCB
~
--PIM1 --POLD4 ~
genes --NFKB1 --NLK
--NFKB2 --VNN2
--C6orf32 --IMP3
--CD44 --POLH
--EBI3 --KLF12
--NFKBIA --ANUBL1
--ID2
--TNFAIP3 --MARK3
--TNF --MIXL1
--GADD45B --PIK3CG
--BIRC3 --VNN3
--SMARCA2 --P2RY12
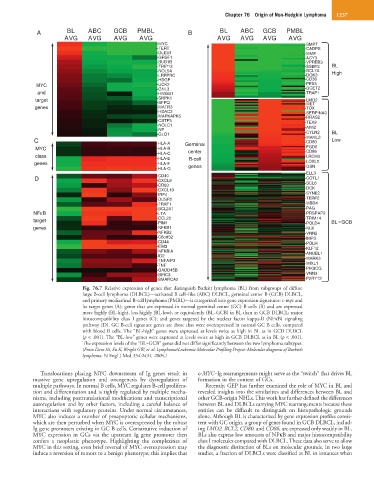
Fig. 76.7 Relative expression of genes that distinguish Burkitt lymphoma (BL) from subgroups of diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)—activated B cell–like (ABC) DLBCL, germinal center B (GCB) DLBCL,
and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBL)—is categorized into gene expression signatures: c-myc and
its target genes (A); genes that are expressed in normal germinal center (GC) B cells (B) and are expressed
more highly (BL-high), less highly (BL-low), or equivalently (BL~GCB) in BL than in GCB DLBCL; major
histocompatibility class I genes (C); and genes targeted by the nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB) signaling
pathway (D). GC B-cell signature genes are those that were overexpressed in normal GC B cells, compared
with blood B cells. The “BL-high” genes were expressed at levels twice as high in BL as in GCB DLBCL
(p < .001). The “BL-low” genes were expressed at levels twice as high in GCB DLBCL as in BL (p < .001).
The expression levels of the “BL~GCB” genes did not differ significantly between the two lymphoma subtypes.
(From Dave SS, Fu K, Wright GW, et al: Lymphoma/Leukemia Molecular Profiling Project: Molecular diagnosis of Burkitt’s
lymphoma. N Engl J Med 354:2431, 2006.)
Translocations placing MYC downstream of Ig genes result in c-MYC–Ig rearrangements might serve as the “switch” that drives BL
massive gene upregulation and oncogenesis by dysregulation of formation in the context of GCs.
multiple pathways. In normal B cells, MYC regulates B-cell prolifera- Recently, GEP has further examined the role of MYC in BL and
tion and differentiation and is tightly regulated by multiple mecha- revealed insights into the similarities and differences between BL and
nisms, including posttranslational modifications and transcriptional other GCB-origin NHLs. This work has further defined the differences
autoregulation and by other factors, including a careful balance of between BL and DLBCLs carrying MYC rearrangements because these
interactions with regulatory proteins. Under normal circumstances, entities can be difficult to distinguish on histopathologic grounds
MYC also induces a number of proapoptotic cellular mechanisms, alone. Although BL is characterized by gene expression profiles consis-
which are then perturbed when MYC is overexpressed by the robust tent with GC origin, a group of genes found in GCB DLBCL, includ-
Ig gene promoters existing in GC B cells. Constitutive induction of ing LMO2, BCL2, CD80, and CD86, are expressed only weakly in BL.
MYC expression in GCs via the upstream Ig gene promoter then BLs also express low amounts of NFκB and major histocompatibility
confers a neoplastic phenotype. Highlighting the complexities of class I molecules compared with DLBCL. These data also serve to allow
MYC in this setting, even brief reversal of MYC overexpression may the diagnostic distinction of BLs on molecular grounds. In two large
induce a reversion of tumors to a benign phenotype; this implies that studies, a fraction of DLBCLs were classified as BL in instances when