Page 1579 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1579
1406 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
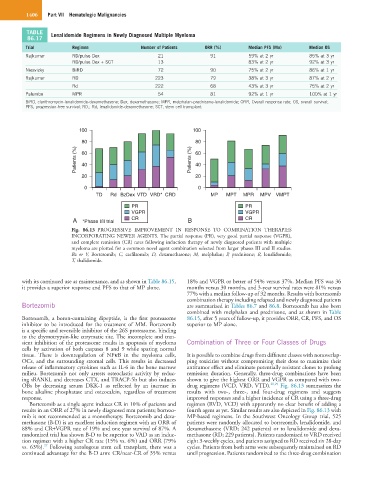
TABLE Lenalidomide Regimens in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma
86.17
Trial Regimen Number of Patients ORR (%) Median PFS (Mo) Median OS
Rajkumar RD/pulse Dex 21 91 59% at 2 yr 85% at 3 yr
RD/pulse Dex + SCT 13 83% at 2 yr 92% at 3 yr
Niesvizky BiRD 72 90 75% at 2 yr 86% at 1 yr
Rajkumar RD 223 79 38% at 3 yr 87% at 2 yr
Rd 222 68 43% at 3 yr 75% at 2 yr
Palumbo MPR 54 81 92% at 1 yr 100% at 1 yr
BiRD, clarithromycin-lenalidomide-dexamethasone; Dex, dexamethasone; MPR, melphalan-prednisone-lenalidomide; ORR, Overall response rate; OS, overall survival;
PFS, progression-free survival; RD,; Rd, lenalidomide-dexamethasone; SCT, stem cell transplant.
100 100
80 80
Patients (%) 60 Patients (%) 60
40
40
20 20
0 0
TD Rd BzDex VTD VRD* CRD MP MPT MPR MPV VMPT
PR PR
VGPR VGPR
A *Phase I/II trial CR B CR
Fig. 86.13 PROGRESSIVE IMPROVEMENT IN RESPONSE TO COMBINATION THERAPIES
INCORPORATING NEWER AGENTS. The partial response (PR), very good partial response (VGPR),
and complete remission (CR) rates following induction therapy of newly diagnosed patients with multiple
myeloma are plotted for a common novel agent combination selected from larger phases III and II studies.
Bz or V, Bortezomib; C, carfilzomib; D, dexamethasone; M, melphalan; P, prednisone; R, lenalidomide;
T, thalidomide.
with its continued use as maintenance, and as shown in Table 86.15, 18% and VGPR or better of 54% versus 37%. Median PFS was 36
it provides a superior response and PFS to that of MP alone. months versus 30 months, and 3-year survival rates were 81% versus
77% with a median follow-up of 32 months. Results with bortezomib
combination therapy including relapsed and newly diagnosed patients
Bortezomib are summarized in Tables 86.7 and 86.8. Bortezomib has also been
combined with melphalan and prednisone, and as shown in Table
Bortezomib, a boron-containing dipeptide, is the first proteasome 86.15, after 5 years of follow-up, it provides ORR, CR, PFS, and OS
inhibitor to be introduced for the treatment of MM. Bortezomib superior to MP alone.
is a specific and reversible inhibitor of the 26S proteasome, binding
to the chymotrypsin-like enzymatic site. The incomplete and tran-
sient inhibition of the proteasome results in apoptosis of myeloma Combination of Three or Four Classes of Drugs
cells by activation of both caspases 8 and 9 while sparing normal
tissue. There is downregulation of NFκB in the myeloma cells, It is possible to combine drugs from different classes with nonoverlap-
OCs, and the surrounding stromal cells. This results in decreased ping toxicities without compromising their dose to maximize their
release of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 in the bone marrow antitumor effect and eliminate potentially resistant clones to prolong
milieu. Bortezomib not only arrests osteoclastic activity by reduc- remission duration. Generally, three-drug combinations have been
ing sRANKL and decreases CTX, and TRACP-5b but also induces shown to give the highest ORR and VGPR as compared with two-
OBs by decreasing serum DKK-1 as reflected by an increase in drug regimens (VCD, VRD, VTD). 28,29 Fig. 86.13 summarizes the
bone alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin, regardless of treatment results with two-, three-, and four-drug regimens and suggests
response. improved responses and a higher incidence of CR using a three-drug
Bortezomib as a single agent induces CR in 10% of patients and regimen (RVD, VCD) with apparently no clear benefit of adding a
results in an ORR of 27% in newly diagnosed mm patients; bortezo- fourth agent as yet. Similar results are also depicted in Fig. 86.13 with
mib is not recommended as a monotherapy. Bortezomib and dexa- MP-based regimens. In the Southwest Oncology Group trial, 525
methasone (B-D) is an excellent induction regimen with an ORR of patients were randomly allocated to bortezomib, lenalidomide, and
88% and CR+VGPR rate of 19% and one year survival of 87%. A dexamethasone (VRD; 242 patients) or to lenalidomide and dexa-
randomized trial has shown B-D to be superior to VAD as an induc- methasone (RD; 229 patients). Patients randomized to VRD received
tion regimen with a higher CR rate (15% vs. 6%) and ORR (79% eight 3-weekly cycles, and patients assigned to RD received six 28-day
27
vs. 63%). Following autologous stem cell transplant, there was a cycles. Patients from both arms were subsequently maintained on RD
continued advantage for the B-D arm: CR/near-CR of 35% versus until progression. Patients randomized to the three-drug combination