Page 1582 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1582
Chapter 86 Plasma Cell Neoplasms 1409
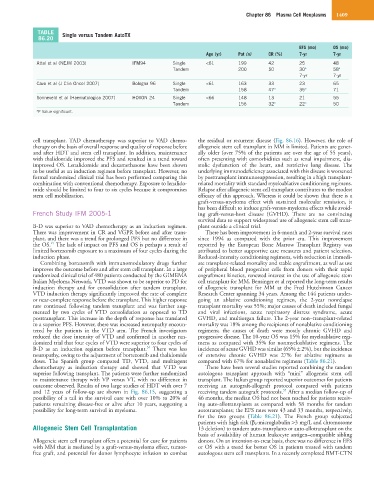
TABLE Single versus Tandem AutoTX
86.20
EFS (mo) OS (mo)
Age (yr) Pat (n) CR (%) 7-yr 7-yr
Attal et al (NEJM 2003) IFM94 Single <61 199 42 25 48
Tandem 200 50 30 a 58 a
7-yr 7-yr
Cavo et al (J Clin Oncol 2007) Bologna 96 Single <61 163 33 23 65
Tandem 158 47 a 35 a 71
Sonneveld et al (Haematologica 2007) HOVON 24 Single <66 148 13 21 55
Tandem 156 32 a 22 a 50
a P Value significant.
cell transplant. TAD chemotherapy was superior to VAD chemo- the residual or recurrent disease (Fig. 86.16). However, the role of
therapy on the basis of overall response and quality of response before allogeneic stem cell transplant in MM is limited. Patients are gener-
and after HDT and stem cell transplant. In addition, maintenance ally older (over 75% of the patients are over the age of 55 years),
with thalidomide improved the PFS and resulted in a trend toward often presenting with comorbidities such as renal impairment, dia-
improved OS. Lenalidomide and dexamethasone have been shown stolic dysfunction of the heart, and restrictive lung disease. The
to be useful as an induction regimen before transplant. However, no underlying immunodeficiency associated with this disease is worsened
formal randomized clinical trial has been performed comparing this by posttransplant immunosuppression, resulting in a high transplant-
combination with conventional chemotherapy. Exposure to lenalido- related mortality with standard myeloablative conditioning regimens.
mide should be limited to four to six cycles because it compromises Relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplant contributes to the modest
stem cell mobilization. efficacy of this approach. Whereas it could be shown that there is a
graft-versus-myeloma effect with sustained molecular remission, it
has been difficult to induce graft-versus-myeloma effects while avoid-
French Study IFM 2005-1 ing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). There are no convincing
survival data to support widespread use of allogeneic stem cell trans-
B-D was superior to VAD chemotherapy as an induction regimen. plant outside a clinical trial.
There was improvement in CR and VGPR before and after trans- There has been improvement in 6-month and 2-year survival rates
plant, and there was a trend for prolonged PFS but no difference in since 1994 as compared with the prior era. This improvement
27
the OS. The lack of impact on PFS and OS is perhaps a result of reported by the European Bone Marrow Transplant Registry was
limited bortezomib exposure to a maximum of four cycles during the attributed to better supportive care measures and patient selection.
induction phase. Reduced-intensity conditioning regimens, with reduction in immedi-
Combining bortezomib with immunomodulatory drugs further ate transplant-related mortality and stable engraftment, as well as use
improves the outcome before and after stem cell transplant. In a large of peripheral blood progenitor cells from donors with their rapid
randomized clinical trial of 480 patients conducted by the GIMEMA engraftment kinetics, renewed interest in the use of allogeneic stem
Italian Myeloma Network, VTD was shown to be superior to PD for cell transplant for MM. Bensinger et al reported the long-term results
induction therapy and for consolidation after tandem transplant. of allogeneic transplant for MM at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer
VTD induction therapy significantly improved the rate of complete Research Center spanning 34 years. Among the 144 patients under-
or near-complete response before the transplant. This higher response going an ablative conditioning regimen, the 2-year nonrelapse
rate continued following tandem transplant and was further aug- transplant mortality was 55%; major causes of death included fungal
mented by two cycles of VTD consolidation as opposed to TD and viral infections, acute respiratory distress syndrome, acute
posttransplant. This increase in the depth of response has translated GVHD, and multiorgan failure. The 2-year non–transplant-related
to a superior PFS. However, there was increased neuropathy encoun- mortality was 18% among the recipients of nonablative conditioning
tered by the patients in the VTD arm. The French investigators regimens; the causes of death were mostly chronic GVHD and
reduced the dose intensity of VTD and confirmed in another ran- progressive disease. The 10-year OS was 15% for myeloablative regi-
domized trial that four cycles of VTD were superior to four cycles of mens as compared with 35% for nonmyeloablative regimens. The
34
B-D as an induction regimen before transplant. There was less incidence of acute GVHD was similar (65% ± 2%), but the incidence
neuropathy, owing to the adjustment of bortezomib and thalidomide of extensive chronic GVHD was 27% for ablative regimens as
doses. The Spanish group compared TD, VTD, and multiagent compared with 67% for nonablative regimens (Table 86.21).
chemotherapy as induction therapy and showed that VTD was There have been several studies reported combining the tandem
superior following transplant. The patients were further randomized autologous transplant approach with “mini” allogeneic stem cell
to maintenance therapy with VP versus VT, with no difference in transplant. The Italian group reported superior outcomes for patients
outcome observed. Results of two large studies of HDT with over 7 receiving an autograft-allograft protocol compared with patients
35
and 12 years of follow-up are shown in Fig. 86.15, suggesting a receiving tandem autograft protocols. After a median follow-up of
possibility of a tail in the survival cure with over 10% to 20% of 46 months, the median OS had not been reached for patients receiv-
patients remaining disease-free or alive after 10 years, suggesting a ing auto-allotransplants as compared with 58 months for tandem
possibility for long-term survival in myeloma. autotransplants; the EFS rates were 43 and 33 months, respectively,
for the two groups (Table 86.21). The French group subjected
patients with high risk (β 2-microglobulin >3 mg/L and chromosome
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation 13 deletion) to tandem auto-transplants or auto-allotransplant on the
basis of availability of human leukocyte antigen–compatible sibling
Allogeneic stem cell transplant offers a potential for cure for patients donors. On an intention-to-treat basis, there was no difference in EFS
with MM that is mediated by a graft-versus-myeloma effect, tumor- or OS with a trend for better OS in patients treated with tandem
free graft, and potential for donor lymphocyte infusion to combat autologous stem cell transplants. In a recently completed BMT-CTN