Page 2013 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2013
1784 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
transfused sickle cell patients shows that 85% of heavily transfused Leukapheresis
patients are alloimmunized to human leukocyte antigens (HLAs),
platelet-specific antigens, or both. Most centers avoid inducing Therapeutic leukapheresis has been used most successfully to help
nonhemolytic transfusion reactions and HLA alloimmunization by manage patients with acute leukemia and extremely high WBC
using leukocyte-depleted RBCs. Extended RBC phenotyping at numbers, so-called acute hyperleukocytic leukemia (AHL). When the
diagnosis and provision of phenotypically matched blood, when fractional volume of leukocytes (leukocrit) exceeds 20%, blood vis-
practical, can reduce the risk of RBC alloimmunization and associ- cosity increases and leukocytes can interfere with pulmonary and
ated hemolytic transfusion reactions. Despite the removal of RBCs cerebral blood flow and compete with tissue for oxygen in the
during exchange, most patients remain in positive iron balance, microcirculation. Investigations of the expression and function of
although iron accumulation is slow and chelation is rarely required adhesion receptors in leukemic cells and the role of adhesion mol-
to prevent transfusional hemosiderosis. ecules in leukocyte-induced acute lung injury in sepsis suggest that
Other indications for RBC exchange are rare. The procedure the pathophysiology of leukostasis in AHL may also be related to
has been used for patients with overwhelming RBC parasitic infec- interactions between leukemic blasts, platelets, and endothelial cells
tions, such as severe and complicated malaria and babesiosis. In mediated by locally released adhesion molecules. A single-volume
malaria, exchange transfusion may have at least three beneficial leukapheresis procedure generally reduces the WBC count by 20%
effects. An automated exchange rapidly decreases the concentration to 50%, depending on the differing sedimentation characteristics of
of circulating parasites while improving the rheologic properties of the specific blast cell population. Ordinarily, leukapheresis is initiated
the blood by replacing the infected RBCs. The exchange may also in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or in the accelerated
reduce levels of proinflammatory cytokines and may help sustain phases of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) when the blast count
3
life until conventional therapy and natural immunity take effect. exceeds 100,000/mm or when rapidly rising blast counts are higher
3
Although the efficacy of this therapy has not been evaluated by than 50,000/mm , especially when evidence of central nervous system
controlled trials, prospective studies and review of published cases or pulmonary symptoms appears. The threshold for initiation of
suggest the use of erythrocytapheresis for parasitemia greater than leukapheresis in patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is
3
10% to 15% or even less in selected patients such as those with generally higher (WBC count >200,000/mm ). Leukostatic syn-
cerebral malaria or pulmonary edema. Case reports document RBC dromes do not occur when concentrations of well-differentiated
3
exchange in such diverse conditions as carbon monoxide poison- lymphocytes exceed even several million/mm .
ing and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)–deficient Although leukapheresis is effective in reducing the number of
hemolysis. circulating blasts, the evidence for clinical benefit is anecdotal. Case
Automated RBC removal with volume replacement (isovolemic reports and small series describe dramatic improvement of patients
hemodilution) can be performed rapidly and safely in polycythemic with evolving strokes and respiratory insufficiency, but the absence
subjects. This maneuver should be reserved for polycythemic patients of a randomized controlled trial necessitates reliance on retrospective
with an urgent clinical indication to lower the hematocrit (e.g., studies. Leukapheresis may reduce early death (ED) rates but does
6
evolving thrombotic stroke) for which standard single-unit manual not improve the overall survival of patients with AML. Trials report-
phlebotomy might be inadvisably slow. Automated double RBC ing reduction in ED should be interpreted with caution. Because one
apheresis technology has more recently been used to treat indi- retrospective cohort study associated leukapheresis with a poorer
7
viduals with hereditary hemochromatosis. This procedure removes outcome attributed to a delay in commencing chemotherapy, it
excess iron more rapidly than manual phlebotomy and is well seems imprudent to delay other immediate measures for treatment
received by patients because it lowers the frequency of clinic visits of patients with AHL (infusion of intravenous [IV] fluids, adminis-
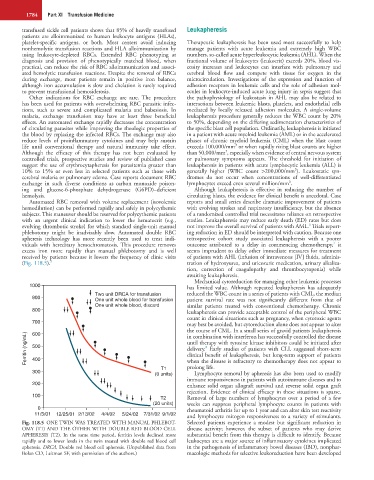
(Fig. 118.5). 5 tration of hydroxyurea, and uricosuric medication, urinary alkaliza-
tion, correction of coagulopathy and thrombocytopenia) while
awaiting leukapheresis.
Mechanical cytoreduction for managing other leukemic processes
1000 has limited value. Although repeated leukapheresis has adequately
Two unit DRCA for transfusion reduced the WBC count in a series of patients with CML, the median
900 One unit whole blood for transfusion patient survival rate was not significantly different from that of
One unit whole blood, discard similar patients treated with conventional chemotherapy. Chronic
800 leukapheresis can provide acceptable control of the peripheral WBC
count in clinical situations such as pregnancy, when cytotoxic agents
700 may best be avoided, but cytoreduction alone does not appear to alter
the course of CML. In a small series of gravid patients leukapheresis
600
Ferritin (ng/mL) 500 until therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors could be initiated after
in combination with interferon has successfully controlled the disease
8
delivery. Early studies of patients with CLL suggested short-term
clinical benefit of leukapheresis, but long-term support of patients
400
prolong life.
T1
300 (0 units) when the disease is refractory to chemotherapy does not appear to
Lymphocyte removal by apheresis has also been used to modify
immune responsiveness in patients with autoimmune diseases and to
200 enhance solid organ allograft survival and reverse solid organ graft
rejection. Evidence of clinical efficacy in these situations is sparse.
100 T2 Removal of large numbers of lymphocytes over a period of a few
(20 units) weeks can suppress peripheral lymphocyte counts in patients with
0 rheumatoid arthritis for up to 1 year and can alter skin test reactivity
11/5/01 12/25/01 2/13/02 4/4/02 5/24/02 7/31/02 9/1/02 and lymphocyte mitogen responsiveness to a variety of stimulants.
Fig. 118.5 ONE TWIN WAS TREATED WITH MANUAL PHLEBOT- Selected patients experience a modest but significant reduction in
OMY (T1) AND THE OTHER WITH DOUBLE RED BLOOD CELL disease activity; however, the subset of patients who may derive
APHERESIS (T2). In the same time period, ferritin levels declined more substantial benefit from this therapy is difficult to identify. Because
rapidly and to lower levels in the twin treated with double red blood cell leukocytes are a major source of inflammatory cytokines implicated
apheresis. DRCA, Double red blood cell apheresis. (Unpublished data from in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), nonphar-
Bolan CD, Leitman SF, with permission of the authors.) macologic methods for selective leukoreduction have been developed