Page 2318 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2318
2060 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
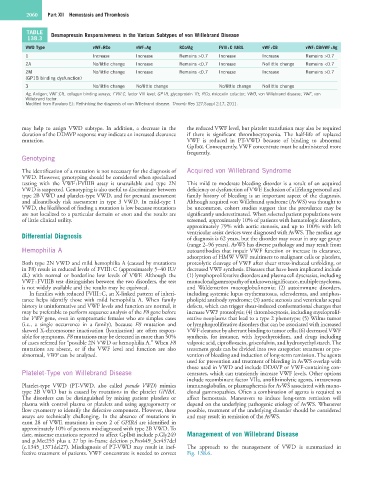
TABLE Desmopressin Responsiveness in the Various Subtypes of von Willebrand Disease
138.3
VWD Type vWF : RCo vWF : Ag RCo/Ag FVIII : C IU/dL vWF : CB vWF : CB/vWF : Ag
1 Increase Increase Remains >0.7 Increase Increase Remains >0.7
2A No/little change Increase Remains <0.7 Increase No/little change Remains <0.7
2M No/little change Increase Remains <0.7 Increase Increase Remains >0.7
(GP1B binding dysfunction)
3 No/little change No/little change No/little change No/little change
Ag, Antigen; VWF:CB, collagen binding assays; FVIII:C, factor VIII level; GP1B, glycoprotein 1B; RCo, ristocetin cofactor; VWD, von Willebrand disease; VWF, von
Willebrand factor.
Modified from Favaloro EJ: Rethinking the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease. Thromb Res 127;Suppl 2:17, 2011.
may help to assign VWD subtype. In addition, a decrease in the the reduced VWF level, but platelet transfusion may also be required
duration of the DDAVP response may indicate an increased clearance if there is significant thrombocytopenia. The half-life of replaced
mutation. VWF is reduced in PT-VWD because of binding to abnormal
GpIbα. Consequently, VWF concentrate must be administered more
frequently.
Genotyping
The identification of a mutation is not necessary for the diagnosis of Acquired von Willebrand Syndrome
VWD. However, genotyping should be considered when specialized
testing with the VWF : FVIIIB assay is unavailable and type 2N This mild to moderate bleeding disorder is a result of an acquired
VWD is suspected. Genotyping is also useful to discriminate between deficiency or dysfunction of VWF. Exclusion of a lifelong personal and
type 2B VWD and platelet-type VWD, and for prenatal assessment family history of bleeding is an important aspect of the diagnosis.
and alloantibody risk assessment in type 3 VWD. In mild-type 1 Although acquired von Willebrand syndrome (AvWS) was thought to
VWD, the likelihood of finding a mutation is low because mutations be uncommon, cohort studies suggest that the prevalence may be
are not localized to a particular domain or exon and the results are significantly underestimated. When selected patient populations were
of little clinical utility. screened, approximately 10% of patients with hematologic disorders,
approximately 79% with aortic stenosis, and up to 100% with left
Differential Diagnosis ventricular assist devices were diagnosed with AvWS. The median age
of diagnosis is 62 years, but the disorder may occur in any age group
(range 2–96 years). AvWS has diverse pathology and may result from
Hemophilia A autoantibodies that impair VWF function or increase its clearance,
adsorption of HMW VWF multimers to malignant cells or platelets,
Both type 2N VWD and mild hemophilia A (caused by mutations proteolytic cleavage of VWF after shear stress-induced unfolding, or
in F8) result in reduced levels of FVIII : C (approximately 5–40 IU/ decreased VWF synthesis. Diseases that have been implicated include
dL) with normal or borderline low levels of VWF. Although the (1) lymphoproliferative disorders and plasma cell dyscrasias, including
VWF : FVIIIB test distinguishes between the two disorders, the test monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance, multiple myeloma,
is not widely available and the results may be equivocal. and Waldenström macroglobulinemia; (2) autoimmune disorders,
In families with reduced FVIII : C, an X-linked pattern of inheri- including systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and antiphos-
tance helps identify those with mild hemophilia A. When family pholipid antibody syndrome; (3) aortic stenosis and ventricular septal
history is uninformative and VWF levels and function are normal, it defects, which can trigger shear-induced conformational changes that
may be preferable to perform sequence analysis of the F8 gene before increase VWF proteolysis; (4) thrombocytosis, including myeloprolif-
the VWF gene, even in symptomatic females who are simplex cases erative neoplasms that lead to a type 2 phenotype; (5) Wilms tumor
(i.e., a single occurrence in a family), because F8 mutation and or lymphoproliferative disorders that can be associated with increased
skewed X-chromosome inactivation (lyonization) are often respon- VWF clearance by aberrant binding to tumor cells; (6) decreased VWF
sible for symptoms. F8 mutations may be detected in more than 50% synthesis, for instance, with hypothyroidism, and drugs including
of cases referred for “possible 2N VWD or hemophilia A.” When F8 valproic acid, ciprofloxacin, griseofulvin, and hydroxyethyl starch. The
mutations are absent, or if the VWF level and function are also treatment goals can be divided into two categories: treatment or pre-
abnormal, VWF can be analyzed. vention of bleeding and induction of long-term remission. The agents
used for prevention and treatment of bleeding in AvWS overlap with
those used in VWD and include DDAVP or VWF-containing con-
Platelet-Type von Willebrand Disease centrates, which can transiently increase VWF levels. Other options
include recombinant factor VIIa, antifibrinolytic agents, intravenous
Platelet-type VWD (PT-VWD, also called pseudo VWD) mimics immunoglobulin, or plasmapheresis for AvWS associated with mono-
type 2B VWD but is caused by mutations in the platelet GPIBA. clonal gammopathies. Often a combination of agents is required to
The disorders can be distinguished by mixing patient platelets or affect hemostasis. Maneuvers to induce long-term remission will
plasma with control plasma or platelets and using aggregometry or depend on the underlying pathogenic etiology of AvWS. Whenever
flow cytometry to identify the defective component. However, these possible, treatment of the underlying disorder should be considered
assays are technically challenging. In the absence of mutations in and may result in remission of the AvWS.
exon 28 of VWF, mutations in exon 2 of GPIBA are identified in
approximately 10% of persons misdiagnosed with type 2B VWD. To
date, missense mutations reported to affect GpIbα include p.Gly249 Management of von Willebrand Disease
and p.Met255 plus a 27 bp in-frame deletion p.Pro449_Ser457del
(c.1345_1371del27). Misdiagnosis of PT-VWD may result in inef- The approach to the management of VWD is summarized in
fective treatment of patients. VWF concentrate is needed to correct Fig. 138.6.