Page 2319 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2319
Chapter 138 Structure, Biology, and Genetics of von Willebrand Factor 2061
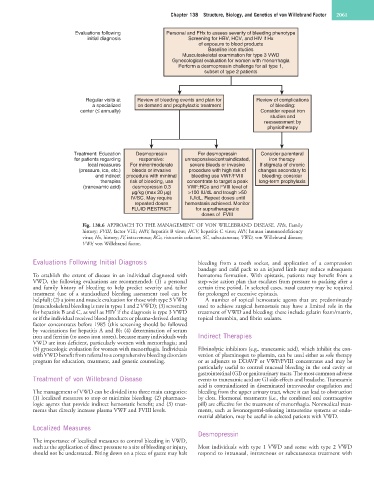
Evaluations following Personal and FHx to assess severity of bleeding phenotype
initial diagnosis Screening for HBV, HCV, and HIV if Hx
of exposure to blood products
Baseline iron studies
Musculoskeletal examination for type 3 VWD
Gynecological evaluation for women with menorrhagia
Perform a desmopressin challenge for all type 1,
subset of type 2 patients
Regular visits at Review of bleeding events and plan for Review of complications
a specialized on demand and prophylactic treatment of bleeding:
center (≤ annually) Consider repeat iron
studies and
reassessment by
physiotherapy
Treatment: Education Desmopressin For desmopressin Consider parenteral
for patients regarding responsive: unresponsive/contraindicated, iron therapy
local measures For minor/moderate severe bleeds or invasive If stigmata of chronic
(pressure, ice, etc.) bleeds or invasive procedure with high risk of changes secondary to
and indirect procedure with minimal bleeding use VWF/FVIII bleeding: consider
therapies risk of bleeding, use concentrate to target a peak long-term prophylaxis
(tranexamic acid) desmopressin 0.3 VWF:RCo and FVIII level of
µg/kg (max 20 µg) >100 IU/dL and trough >50
IV/SC. May require IU/dL. Repeat doses until
repeated doses hemostasis achieved. Monitor
FLUID RESTRICT for supratherapeutic
doses of FVIII
Fig. 138.6 APPROACH TO THE MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE. FHx, Family
history; FVIII, factor VIII; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency
virus; Hx, history; IV, intravenous; RCo, ristocetin cofactor; SC, subcutaneous; VWD, von Willebrand disease;
VWF, von Willebrand factor.
Evaluations Following Initial Diagnosis bleeding from a tooth socket, and application of a compression
bandage and cold pack to an injured limb may reduce subsequent
To establish the extent of disease in an individual diagnosed with hematoma formation. With epistaxis, patients may benefit from a
VWD, the following evaluations are recommended: (1) a personal step-wise action plan that escalates from pressure to packing after a
and family history of bleeding to help predict severity and tailor certain time period. In selected cases, nasal cautery may be required
treatment (use of a standardized bleeding assessment tool can be for prolonged or excessive epistaxis.
helpful); (2) a joint and muscle evaluation for those with type 3 VWD A number of topical hemostatic agents that are predominately
(musculoskeletal bleeding is rare in types 1 and 2 VWD); (3) screening used to achieve surgical hemostasis may have a limited role in the
for hepatitis B and C, as well as HIV if the diagnosis is type 3 VWD treatment of VWD and bleeding; these include gelatin foam/matrix,
or if the individual received blood products or plasma-derived clotting topical thrombin, and fibrin sealants.
factor concentrates before 1985 (this screening should be followed
by vaccinations for hepatitis A and B); (4) determination of serum
iron and ferritin (to assess iron stores), because many individuals with Indirect Therapies
VWD are iron deficient, particularly women with menorrhagia; and
(5) gynecologic evaluation for women with menorrhagia. Individuals Fibrinolytic inhibitors (e.g., tranexamic acid), which inhibit the con-
with VWD benefit from referral to a comprehensive bleeding disorders version of plasminogen to plasmin, can be used either as sole therapy
program for education, treatment, and genetic counseling. or as adjuncts to DDAVP or VWF/FVIII concentrates and may be
particularly useful to control mucosal bleeding in the oral cavity or
gastrointestinal (GI) or genitourinary tracts. The most common adverse
Treatment of von Willebrand Disease events to tranexamic acid are GI side-effects and headache. Tranexamic
acid is contraindicated in disseminated intravascular coagulation and
The management of VWD can be divided into three main categories: bleeding from the upper urinary tract, where it can lead to obstruction
(1) localized measures to stop or minimize bleeding; (2) pharmaco- by clots. Hormonal treatments (i.e., the combined oral contraceptive
logic agents that provide indirect hemostatic benefit; and (3) treat- pill) are effective for the treatment of menorrhagia. Nonmedical treat-
ments that directly increase plasma VWF and FVIII levels. ments, such as levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine systems or endo-
metrial ablation, may be useful in selected patients with VWD.
Localized Measures
Desmopressin
The importance of localized measures to control bleeding in VWD,
such as the application of direct pressure to a site of bleeding or injury, Most individuals with type 1 VWD and some with type 2 VWD
should not be understated. Biting down on a piece of gauze may halt respond to intranasal, intravenous or subcutaneous treatment with