Page 938 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 938
Chapter 56 Conventional and Molecular Cytogenomic Basis of Hematologic Malignancies 821
worse prognosis when treated with risk-adapted or subtype oriented
protocols. Monosomal karyotype did not have an impact on prognosis
in Ph-positive ALL irrespective of imatinib treatment.
The lymphoid leukemias associated with Down syndrome (DS-
ALL) are almost exclusively B-precursor ALLs. In a recent large series
of DS-ALLs, there were only five cases of T-ALL among 700 patients.
Also, in a sharp contrast to the myeloid neoplasms, they almost never
occur in infants. Clinically the outcome of DS-ALL is significantly
worse than sporadic childhood B-cell precursor ALLs because of
intrinsic resistance to therapy and increased treatment-related mortal-
ity. Although all known cytogenetic subgroups of childhood B-cell
ALLs have been observed, the common abnormalities such as ETV6/
RUNX1 fusion and hyperdiploidy, are less frequent.
Up to 60% of DS-ALLs have aberrant expression of the cytokine
receptor CRLF2 that is often associated with additional mutations
activating JAK-STAT signaling. The aberrant expression of this recep-
tor is caused by genomic rearrangements consisting either of a
translocation into the IgH locus control region or a microdeletion
upstream to the CRLF2 gene, located on the pseudoautosomal
component of the sex chromosomes. This deletion fuses CRLF2 with
the promoter of an upstream constitutively expressed P2RY8 gene.
Analysis of the breakpoint sequences suggest that this rearrangement
is mediated by RAG1 or RAG2 in early B-cell precursors.
Somatic Mutations
The most commonly altered pathways in ALL, involving the tran-
MYC/IgH
scriptional regulation of lymphoid development, such as PAX5
(9p13.2), IKZF1 (7p12.2) and EBF1 (5q33.3), are frequently
mutated. PAX5 is required for B-lymphoid lineage commitment and
maturation. PAX5 genetic alterations include deletions, sequence
mutations, and chimeric genes with at least 16 different chromosomal
partners (http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/Genes/PAX5ID62.html).
IKAROS is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages and
its genetic lesions are implicated in resistance to chemotherapy and
TKIs.
Other commonly mutated pathways in ALL include genes
involved in tumor suppression and cell cycle regulation (TP53, Rb1,
and CDKN2A), cytokine receptor, RAS-signaling, lymphoid signal-
ing and epigenetic modification such as EZH2.
Multistep Pathogenesis of Acute
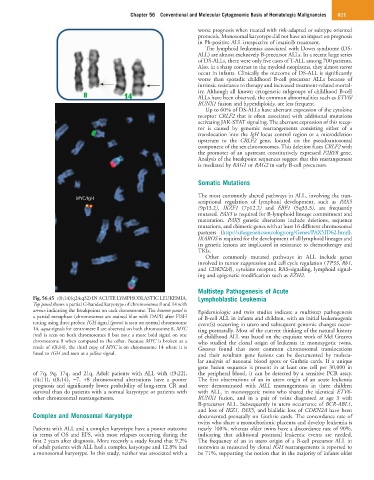
Fig. 56.45 t(8;14)(q24;q32) IN ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA. Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Top panel shows a partial G-banded karyotype of chromosomes 8 and 14 with
arrows indicating the breakpoints on each chromosome. The bottom panel is Epidemiologic and twin studies indicate a multistep pathogenesis
a partial metaphase (chromosomes are stained blue with DAPI) after FISH of B-cell ALL in infants and children, with an initial leukemogenic
testing using three probes: IGH signal (green) is seen on normal chromosome event(s) occurring in utero and subsequent genomic changes occur-
14, aqua signals for centromere 8 are observed on both chromosome 8, MYC ring postnatally. Most of the current thinking of the natural history
(red) is seen on both chromosomes 8 but note a more bold signal on one of childhood ALL was based on the exquisite work of Mel Greaves
chromosome 8 when compared to the other. Because MYC is broken as a who studied the clonal origin of leukemia in monozygotic twins.
result of t(8;14), the third copy of MYC is on chromosome 14 where it is Greaves found that most common chromosomal translocations
fused to IGH and seen as a yellow signal. and their resultant gene fusions can be documented by molecu-
lar analysis of neonatal blood spots or Guthrie cards. If a unique
gene fusion sequence is present in at least one cell per 30,000 in
of 7q, 9q, 17q, and 21q. Adult patients with ALL with t(9;22), the peripheral blood, it can be detected by a sensitive PCR assay.
t(4;11), t(8;14), −7, +8 chromosomal aberrations have a poorer The first observations of an in utero origin of an acute leukemia
prognosis and significantly lower probability of long-term CR and were demonstrated with MLL rearrangements in three children
survival than do patients with a normal karyotype or patients with with ALL, in monozygotic twins who shared the identical ETV6-
other chromosomal rearrangements. RUNX1 fusion, and in a pair of twins diagnosed at age 3 with
B-precursor ALL. Subsequently in utero occurrence of BCR-ABL1,
and loss of IKZ1, PAX5, and biallelic loss of CDKN2A have been
Complex and Monosomal Karyotype documented prenatally on Guthrie cards. The concordance rate of
twins who share a monochorionic placenta and develop leukemia is
Patients with ALL and a complex karyotype have a poorer outcome nearly 100%, whereas older twins have a discordance rate of 90%,
in terms of OS and EFS, with most relapses occurring during the indicating that additional postnatal leukemic events are needed.
first 2 years after diagnosis. More recently a study found that 9.2% The frequency of an in utero origin of a B-cell precursor ALL in
of adult patients with ALL had a complex karyotype and 12.8% had nontwins as measured by clonal IGH rearrangements is reported to
a monosomal karyotype. In this study, neither was associated with a be 71%, supporting the notion that in the majority of infants older