Page 942 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 942
Chapter 56 Conventional and Molecular Cytogenomic Basis of Hematologic Malignancies 825
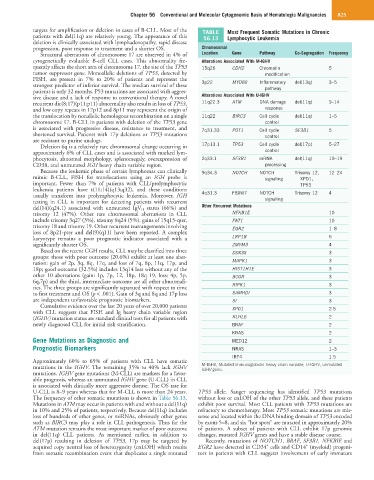
targets for amplification or deletion in cases of B-CLL. Most of the TABLE Most Frequent Somatic Mutations in Chronic
patients with del(11q) are relatively young. The appearance of this 56.13 Lymphocytic Leukemia
deletion is clinically associated with lymphadenopathy, rapid disease
progression, poor response to treatment and a shorter OS. Chromosomal
Structural aberrations of chromosome 17 are observed in 4% of Location Gene Pathway Co-Segregation Frequency
cytogenetically evaluable B-cell CLL cases. This abnormality fre- Alterations Associated With M-IGHV
quently affects the short arm of chromosome 17, the site of the TP53 15q26 CDH2 Chromatin 5
tumor suppressor gene. Monoallelic deletions of TP53, detected by modification
FISH, are present in 7% to 20% of patients and represent the
strongest predictor of inferior survival. The median survival of these 3p22 MYD88 Inflammatory del(13q) 3–5
patients is only 32 months. P53 mutations are associated with aggres- pathway
sive disease and a lack of response to conventional therapy. A novel Alterations Associated With U-IGHV
recurrent dic(8;17)(p11;p11) abnormality also results in loss of TP53, 11q22.3 ATM DNA damage del(11q) 9–14
and low copy repeats in 17p12 and 8p11 may represent the origin of response
the translocation by nonallelic homologous recombination on a single 11q22 BIRC3 Cell cycle del(11q) 1–5
chromosome 17. B-CLL in patients with deletion of the TP53 gene control
is associated with progressive disease, resistance to treatment, and 7q31.33 POT1 Cell cycle SF3B1 5
shortened survival. Patients with 17p deletions or TP53 mutations control
are resistant to purine analogs.
Deletion 6q is a relatively rare chromosomal change occurring in 17p13.1 TP53 Cell cycle del(17p) 5–27
approximately 6% of CLL cases and is associated with marked lym- control
phocytosis, abnormal morphology, splenomegaly, overexpression of 2q33.1 SF3B1 mRNA del(11q) 10–19
CD38, and unmutated IGH heavy chain variable region. processing
Because the leukemic phase of certain lymphomas can clinically 9q34.3 NOTCH NOTCH Trisomy 12, 12–24
mimic B-CLL, FISH for translocations using an IGH probe is signaling XPO1,
important. Fewer than 7% of patients with CLL/prolymphocytic TP53
leukemia patients have t(11;14)(q13;q32), and these conditions
usually transform into prolymphocytic leukemia. Moreover, IGH 4q31.3 FBXW7 NOTCH Trisomy 12 4
testing in CLL is important for detecting patients with recurrent signaling
del(14)(q24.1) associated with unmutated IgV H status (66%) and Other Recurrent Mutations
trisomy 12 (47%). Other rare chromosomal aberrations in CLL NFKB1E 10
include trisomy 3q27 (3%), trisomy 8q24 (5%), gains of 15q15-qter, FAT1 10
trisomy 18 and trisomy 19. Other recurrent rearrangements involving EGR2 1–8
loss of 8p21-pter and del(9)(q11) have been reported. A complex
karyotype remains a poor prognostic indicator associated with a LRP1B 5
significantly shorter OS. ZMYM3 4
Based on the recent CGH results, CLL may be classified into three DDX3X 3
groups: those with poor outcome (20.6%) exhibit at least one aber-
ration: gain of 2p, 3q, 8q, 17q, and loss of 7q, 8p, 11q, 17p, and MAPK1 3
18p; good outcome (32.5%) includes 13q14 loss without any of the HIST1H1E 3
other 10 aberrations (gain: 1p, 7p, 12, 18p, 18q 19, loss: 4p, 5p, BCOR 3
6q,7p) and the third, intermediate outcome are all other abnormali-
ties. The three groups are significantly separated with respect to time RIPK1 3
to first treatment and OS (p < .001). Gain of 3q and 8q and 17p loss SAMHDI 3
are independent unfavorable prognostic biomarkers. SI 3
Cumulative evidence over the last 20 years of over 20,000 patients
with CLL suggests that FISH and Ig heavy chain variable region XPO1 2.5
(IGHV) mutation status are standard clinical tests for all patients with KLHL6 2
newly diagnosed CLL for initial risk stratification. BRAF 2
KRAS 2
Gene Mutations as Diagnostic and MED12 2
Prognostic Biomarkers NRAS 1–3
IRF4 1.5
Approximately 60% to 65% of patients with CLL have somatic
mutations in the IGHV. The remaining 35% to 40% lack IGHV M-IGHV, Mutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable; U-IGHV, unmutated
IGHV gene.
mutations. IGHV gene mutations (M-CLL) are markers for a favor-
able prognosis, whereas an unmutated IGHV gene (U-CLL) in CLL
is associated with clinically more aggressive disease. The OS rate for
U-CLL is 8–9 years whereas that for M-CLL is more than 24 years. TP53 allele. Sanger sequencing has identified TP53 mutations
The frequency of other somatic mutations is shown in Table 56.13. without loss or cnLOH of the other TP53 allele, and these patients
Mutations in ATM may occur in patients with and without a del(11q) exhibit poor survival. Most CLL patients with TP53 mutations are
in 10% and 25% of patients, respectively. Because del(11q) includes refractory to chemotherapy. Most TP53 somatic mutations are mis-
loss of hundreds of other genes, or miRNAs, obviously other genes sense and located within the DNA binding domain of TP53 encoded
such as BIRC3 may play a role in CLL pathogenesis. Thus far the by exons 5–8, and six “hot spots” are mutated in approximately 20%
ATM mutation remains the most important marker of poor outcome of patients. A subset of patients with CLL exhibit 17p genomic
in del(11q) CLL patients. As mentioned earlier, in addition to changes, mutated IGHV genes and have a stable disease course.
del(17p) resulting in deletion of TP53, 17p may be targeted by Recently, mutations of NOTCH1, BRAF, SF3B1, NFKBIE and
+
+
acquired copy neutral loss of heterozygosity (cnLOH) which results EGR2 have detected in CD34 cells and CD14 (myeloid) progeni-
from somatic recombination event that duplicates a single mutated tors in patients with CLL suggests involvement of early immature