Page 955 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 955
838 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
B
3 der(3) 22 der(22)
13 14 15 16 17 18
A C
19 20 21 22 X Y
7 7 der(7) 8 der(8) 14 der(14) 18 der(18)
D
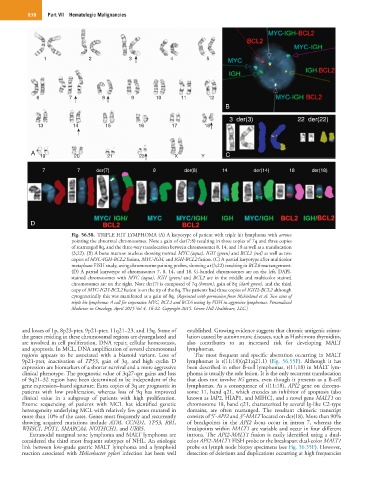
Fig. 56.58. TRIPLE HIT LYMPHOMA (A) A karyotype of patient with triple hit lymphoma with arrows
pointing the abnormal chromosomes. Note a gain of der(7;8) resulting in three copies of 7q and three copies
of rearranged 8q, and the three-way translocation between chromosomes 8, 14, and 18 as well as a translocation
(3;22). (B) A bone marrow nucleus showing normal MYC (aqua), IGH (green) and BCL2 (red) as well as two
copies of MYC-IGH-BCL2 fusion, MYC-IGH, and IGH-BCL2 fusion. (C) A partial karyotype after multicolor
metaphase FISH study, using chromosome paining probes, showing a t(3;22) resulting in BCL6 rearrangement.
(D) A partial karyotype of chromosomes 7, 8, 14, and 18. G-banded chromosomes are on the left, DAPI-
stained chromosomes with MYC (aqua), IGH (green) and BCL2 are in the middle and multicolor stained
chromosomes are on the right. Note der(7) is composed of 7q (brown), gain of 8q (dark green), and the third
copy of MYC-IGH-BCL2 fusion is on the tip of the 8q. The patients had three copies of IGH2-BCL2 although
cytogenetically this was manifested as a gain of 8q. (Reprinted with permission from McFarland et al: Two cases of
triple hit lymphoma: A call for imperative MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 testing by FISH in aggressive lymphomas. Personalized
Medicine in Oncology, April 2015 Vol 4, 16-22. Copyright 2015. Green Hill Healthcare, LLC.)
and losses of 1p, 8p23-pter, 9p21-pter, 11q21–23, and 13q. Some of established. Growing evidence suggests that chronic antigenic stimu-
the genes residing in these chromosomal regions are dysregulated and lation caused by autoimmune diseases, such as Hashimoto thyroiditis,
are involved in cell proliferation, DNA repair, cellular homeostasis, also contributes to an increased risk for developing MALT
and apoptosis. In MCL, DNA amplification of several chromosomal lymphomas.
regions appears to be associated with a blastoid variant. Loss of The most frequent and specific aberration occurring in MALT
9p21-pter, inactivation of TP53, gain of 3q, and high cyclin D lymphomas is t(11;18)(q21;q21.1) (Fig. 56.55F). Although it has
expression are biomarkers of a shorter survival and a more aggressive been described in other B-cell lymphomas, t(11;18) in MALT lym-
clinical phenotype. The prognostic value of 3q27-qer gains and loss phoma is usually the sole lesion. It is the only recurrent translocation
of 9q21–32 region have been determined to be independent of the that does not involve IG genes, even though it presents as a B-cell
gene expression–based signature. Extra copies of 3q are prognostic in lymphomas. As a consequence of t(11;18), API2 gene on chromo-
patients with low proliferation, whereas loss of 9q has improved some 11, band q21, which encodes an inhibitor of apoptosis (also
clinical value in a subgroup of patients with high proliferation. known as IAP2, HIAP1, and MIHC), and a novel gene MALT1 on
Exome sequencing of patients with MCL has identified genetic chromosome 18, band q21, characterized by several Ig-like C2-type
heterogeneity underlying MCL with relatively few genes mutated in domains, are often rearranged. The resultant chimeric transcript
more than 10% of the cases. Genes most frequently and recurrently consists of 5′-API2 and 3′-MALT located on der(18). More than 90%
showing acquired mutations include ATM, CCND1, TP53, RB1, of breakpoints in the API2 locus occur in intron 7, whereas the
WHSC1, POT1, SMARCA4, NOTHCH1, and UBR5. breakpoints within MALT1 are variable and occur in four different
Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma and MALT lymphoma are introns. The API2-MALT1 fusion is easily identified using a dual-
considered the third most frequent subtypes of NHL. An etiologic color API2-MALT1 FISH probe or the breakapart dual-color MALT1
link between low-grade gastric MALT lymphoma and a lymphoid probe on lymph node biopsy specimens (see Fig. 56.55F). However,
reaction associated with Helicobacter pylori infection has been well detection of deletions and duplications occurring at high frequencies