Page 958 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 958
Chapter 56 Conventional and Molecular Cytogenomic Basis of Hematologic Malignancies 841
inv(14)(q11.2q32)
A
B 7 14
C
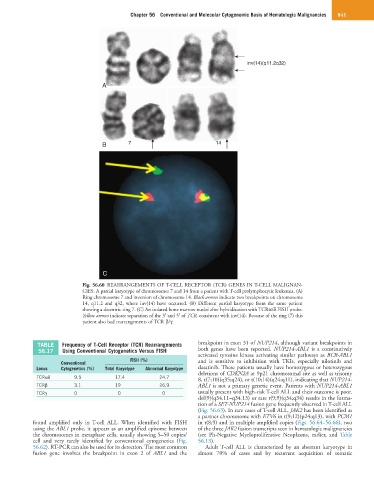
Fig. 56.60 REARRANGEMENTS OF T-CELL RECEPTOR (TCR) GENES IN T-CELL MALIGNAN-
CIES. A partial karyotype of chromosomes 7 and 14 from a patient with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia. (A)
Ring chromosome 7 and inversion of chromosome 14. Black arrows indicate two breakpoints on chromosome
14, q11.2 and q32, where inv(14) have occurred. (B) Different partial karyotype from the same patient
showing a dicentric ring 7. (C) An isolated bone marrow nuclei after hybridization with TCRα/δ FISH probe.
Yellow arrows indicate separation of the 3′ and 5′ of TCR, consistent with inv(14). Because of the ring (7) this
patient also had rearrangements of TCR β/γ.
TABLE Frequency of T-Cell Receptor (TCR) Rearrangements breakpoint in exon 31 of NUP214, although variant breakpoints in
56.17 Using Conventional Cytogenetics Versus FISH both genes have been reported. NUP214-ABL1 is a constitutively
activated tyrosine kinase activating similar pathways as BCR-ABL1
FISH (%) and is sensitive to inhibition with TKIs, especially nilotinib and
Conventional
Locus Cytogenetics (%) Total Karyotype Abnormal Karyotype dasatinib. These patients usually have homozygous or heterozygous
deletions of CDKN2A at 9p21 chromosomal site as well as trisomy
TCRαδ 9.5 17.4 24.7 8, t(7;10)(q35;q24), or t(10;14)(q24;q11), indicating that NUP214-
TCRβ 3.1 19 26.9 ABL1 is not a primary genetic event. Patients with NUP214-ABL1
TCRγ 0 0 0 usually present with high-risk T-cell ALL and their outcome is poor.
del(9)(q34.11–q34.13) or rare t(9;9)(q34;q34) results in the forma-
tion of a SET-NUP214 fusion gene frequently observed in T-cell ALL
(Fig. 56.63). In rare cases of T-cell ALL, JAK2 has been identified as
a partner chromosome with ETV6 in t(9;12)(p24;q13), with PCM1
found amplified only in T-cell ALL. When identified with FISH in t(8;9) and in multiple amplified copies (Figs. 56.64–56.66), two
using the ABL1 probe, it appears as an amplified episome between of the three JAK2 fusion transcripts seen in hematologic malignancies
the chromosomes in metaphase cells, usually showing 5–50 copies/ (see Ph-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms, earlier, and Table
cell and very rarely identified by conventional cytogenetics (Fig. 56.13).
56.62). RT-PCR can also be used for its detection. The most common Adult T-cell ALL is characterized by an aberrant karyotype in
fusion gene involves the breakpoint in exon 2 of ABL1 and the almost 70% of cases and by recurrent acquisition of somatic