Page 959 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 959
842 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
A B C
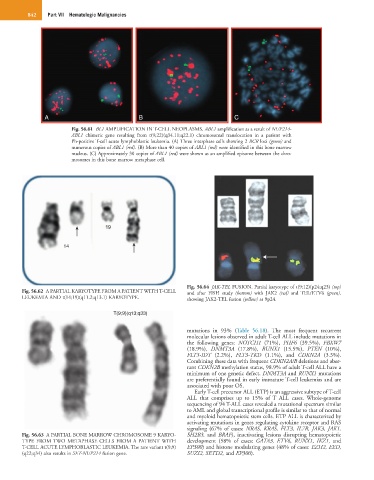
Fig. 56.61 BL1 AMPLIFICATION IN T-CELL NEOPLASMS. ABL1 amplification as a result of NUP214-
ABL1 chimeric gene resulting from t(9;22)(q34.11;q22.1) chromosomal translocation in a patient with
Ph-positive T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. (A) Three interphase cells showing 2 BCR loci (green) and
numerous copies of ABL1 (red). (B) More than 40 copies of ABL1 (red) were identified in this bone marrow
nucleus. (C) Approximately 30 copies of ABL1 (red) were shown as an amplified episome between the chro-
mosomes in this bone marrow metaphase cell.
19
14
Fig. 56.64 JAK-TEL FUSION. Partial karyotype of t(9;12)(p24;q23) (top)
Fig. 56.62 A PARTIAL KARYOTYPE FROM A PATIENT WITH T-CELL and after FISH study (bottom) with JAK2 (red) and TEL/ETV6 (green),
LEUKEMIA AND t(14;19)(q11.2;q13.1) KARYOTYPE. showing JAK2-TEL fusion (yellow) at 9p24.
T(9;9)(q13;q33)
mutations in 93% (Table 56.18). The most frequent recurrent
molecular lesions observed in adult T-cell ALL include mutations in
the following genes: NOTCH1 (71%), PHF6 (39.5%), FBXW7
(18.9%), DNMT3A (17.8%), RUNX1 (15.5%), PTEN (10%),
FLT3-IDT (2.2%), FLT3-TKD (1.1%), and CDKN2A (3.3%).
Combining these data with frequent CDKN2A/B deletions and aber-
rant CDKN2B methylation status, 98.9% of adult T-cell ALL have a
minimum of one genetic defect. DNMT3A and RUNX1 mutations
are preferentially found in early immature T-cell leukemias and are
associated with poor OS.
Early T-cell precursor ALL (ETP) is an aggressive subtype of T-cell
ALL that comprises up to 15% of T ALL cases. Whole-genome
sequencing of 94 T-ALL cases revealed a mutational spectrum similar
to AML and global transcriptional profile is similar to that of normal
and myeloid hematopoietic stem cells. ETP ALL is characterized by
activating mutations in genes regulating cytokine receptor and RAS
signaling (67% of cases: NRAS, KRAS, FLT3, IL7R, JAK3, JAK1,
Fig. 56.63 A PARTIAL BONE MARROW CHROMOSOME 9 KARYO- SH2B3, and BRAF), inactivating lesions disrupting hematopoietic
TYPE FROM TWO METAPHASE CELLS FROM A PATIENT WITH development (58% of cases: GATA3, ETV6, RUNX1, IKZ1, and
T-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA. The rare variant t(9;9) EP300) and histone modulating genes (48% of cases: EZH2, EED,
(q22;q34) also results in SET-NUP214 fusion gene. SUZI2, SETD2, and EP300).