Page 1081 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1081
1056 Part VIII: Monocytes and Macrophages Chapter 67: Structure, Receptors, and Functions of Monocytes and Macrophages 1057
N
E
E C
C
E
C
E
E EGF-TM7
N Scavenger receptor AI
Toll-like N
receptor N N C
C
C
N MARCO
N
C N
C N
CD36
N
CD68 C
CD200R
C
C
|
|
S
S
S
S
S | S S | S
CD200
C N Mannose
receptor
S
|
S
C
TREM1/DAP12 Dectin1
Siglec1
N
N
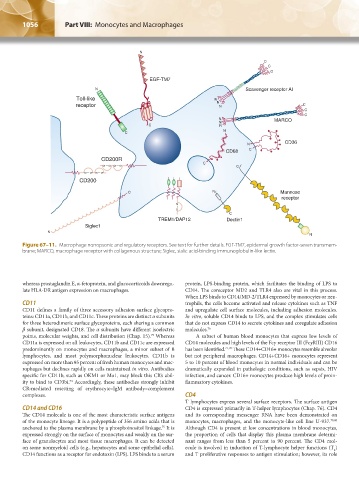
Figure 67–11. Macrophage nonopsonic and regulatory receptors. See text for further details. EGF-TM7, epidermal growth factor-seven transmem-
brane; MARCO, macrophage receptor with collagenous structure; Siglec, sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin.
whereas prostaglandin E, α-fetoprotein, and glucocorticoids downregu- protein, LPS-binding protein, which facilitates the binding of LPS to
late HLA-DR antigen expression on macrophages. CD14. The coreceptor MD2 and TLR4 also are vital in this process.
When LPS binds to CD14/MD-2/TLR4 expressed by monocytes or neu-
CD11 trophils, the cells become activated and release cytokines such as TNF
CD11 defines a family of three accessory adhesion surface glycopro- and upregulate cell surface molecules, including adhesion molecules.
teins: CD11a, CD11b, and CD11c. These proteins are distinct α subunits In vitro, soluble CD14 binds to LPS, and the complex stimulates cells
for three heterodimeric surface glycoproteins, each sharing a common that do not express CD14 to secrete cytokines and coregulate adhesion
β subunit, designated CD18. The α subunits have different isoelectric molecules. 76
points, molecular weights, and cell distribution (Chap. 15). Whereas A subset of human blood monocytes that express low levels of
73
CD11a is expressed on all leukocytes, CD11b and CD11c are expressed CD14 molecules and high levels of the Fcγ receptor III (FcγRIII) CD16
predominantly on monocytes and macrophages, a minor subset of B has been identified. 77,78 These CD14+CD16+ monocytes resemble alveolar
lymphocytes, and most polymorphonuclear leukocytes. CD11b is but not peripheral macrophages. CD14+CD16+ monocytes represent
expressed on more than 95 percent of fresh human monocytes and mac- 5 to 10 percent of blood monocytes in normal individuals and can be
rophages but declines rapidly on cells maintained in vitro. Antibodies dramatically expanded in pathologic conditions, such as sepsis, HIV
specific for CD11b, such as OKM1 or Mo1, may block this CR’s abil- infection, and cancer. CD16+ monocytes produce high levels of proin-
ity to bind to CD3bi. Accordingly, these antibodies strongly inhibit flammatory cytokines.
74
CR-mediated rosetting of erythrocyte–IgM antibody–complement
complexes. CD4
T lymphocytes express several surface receptors. The surface antigen
CD14 and CD16 CD4 is expressed primarily in T-helper lymphocytes (Chap. 76). CD4
The CD14 molecule is one of the most characteristic surface antigens and its corresponding messenger RNA have been demonstrated on
of the monocyte lineage. It is a polypeptide of 356 amino acids that is monocytes, macrophages, and the monocyte-like cell line U-937. 79,80
anchored to the plasma membrane by a phosphoinositol linkage. It is Although CD4 is present at low concentrations in blood monocytes,
75
expressed strongly on the surface of monocytes and weakly on the sur- the proportion of cells that display this plasma membrane determi-
face of granulocytes and most tissue macrophages. It can be detected nant ranges from less than 5 percent to 90 percent. The CD4 mol-
on some nonmyeloid cells (e.g., hepatocytes and some epithelial cells). ecule is involved in induction of T-lymphocyte helper functions (T )
4
CD14 functions as a receptor for endotoxin (LPS). LPS binds to a serum and T proliferative responses to antigen stimulation; however, its role
Kaushansky_chapter 67_p1043-1074.indd 1056 9/21/15 10:43 AM