Page 1600 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1600
1574 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 95: General Considerations for Lymphomas 1575
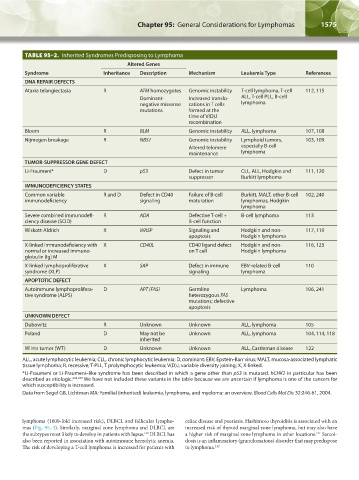
TABLE 95–2. Inherited Syndromes Predisposing to Lymphoma
Altered Genes
Syndrome Inheritance Description Mechanism Leukemia Type References
DNA REPAIR DEFECTS
Ataxia telangiectasia R ATM homozygotes Genomic instability T-cell lymphoma, T-cell 112, 115
Dominant- Increased translo- ALL, T-cell PLL, B-cell
negative missense cations in T cells lymphoma
mutations formed at the
time of V(D)J
recombination
Bloom R BLM Genomic instability ALL, lymphoma 107, 108
Nijmegen breakage R NBS1 Genomic instability Lymphoid tumors, 103, 109
Altered telomere especially B-cell
maintenance lymphoma
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENE DEFECT
Li-Fraumeni* D p53 Defect in tumor CLL, ALL, Hodgkin and 111, 120
suppressor Burkitt lymphoma
IMMUNODEFICIENCY STATES
Common variable R and D Defect in CD40 Failure of B-cell Burkitt, MALT, other B-cell 102, 240
immunodeficiency signaling maturation lymphomas, Hodgkin
lymphoma
Severe combined immunodefi- R ADA Defective T-cell + B-cell lymphoma 113
ciency disease (SCID) B-cell function
Wiskott-Aldrich X WASP Signaling and Hodgkin and non- 117, 119
apoptosis Hodgkin lymphoma
X-linked immunodeficiency with X CD40L CD40 ligand defect Hodgkin and non- 116, 123
normal or increased immuno- on T cell Hodgkin lymphoma
globulin (Ig) M
X-linked lymphoproliferative X SAP Defect in immune EBV-related B-cell 110
syndrome (XLP) signaling lymphoma
APOPTOTIC DEFECT
Autoimmune lymphoprolifera- D APT (FAS) Germline Lymphoma 106, 241
tive syndrome (ALPS) heterozygous FAS
mutations; defective
apoptosis
UNKNOWN DEFECT
Dubowitz R Unknown Unknown ALL, lymphoma 105
Poland D May not be Unknown ALL, lymphoma 104, 114, 118
inherited
Wilms tumor (WT) D Unknown Unknown ALL, Castleman disease 122
ALL, acute lymphocytic leukemia; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; D, dominant; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; MALT, mucosa-associated lymphatic
tissue lymphoma; R, recessive; T-PLL, T prolymphocytic leukemia; V(D)J, variable diversity joining; X, X-linked.
*Li-Fraumeni or Li-Fraumeni–like syndrome has been described in which a gene other than p53 is mutated. hCHK2 in particular has been
described as etiologic. 242,243 We have not included these variants in the table because we are uncertain if lymphoma is one of the cancers for
which susceptibility is increased.
Data from Segel GB, Lichtman MA: Familial (inherited) leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma: an overview. Blood Cells Mol Dis 32:246-61, 2004.
lymphoma (1000-fold increased risk), DLBCL and follicular lympho- celiac disease and psoriasis. Hashimoto thyroiditis is associated with an
mas (Fig. 95–3). Similarly, marginal zone lymphoma and DLBCL are increased risk of thyroid marginal zone lymphoma, but may also have
131
the subtypes most likely to develop in patients with lupus. DLBCL has a higher risk of marginal zone lymphoma in other locations. Sarcoi-
130
also been reported in association with autoimmune hemolytic anemia. dosis is an inflammatory (granulomatous) disorder that may predispose
The risk of developing a T-cell lymphoma is increased for patients with to lymphoma. 132
Kaushansky_chapter 95_p1569-1586.indd 1575 9/21/15 12:16 PM