Page 1941 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1941
1916 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 113: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry of the Coagulation Factors 1917
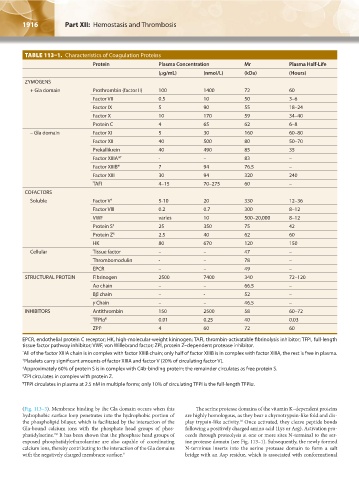
TABLE 113–1. Characteristics of Coagulation Proteins
Protein Plasma Concentration Mr Plasma Half-Life
(μg/mL) (nmol/L) (kDa) (Hours)
ZYMOGENS
+ Gla domain Prothrombin (factor II) 100 1400 72 60
Factor VII 0.5 10 50 3–6
Factor IX 5 90 55 18–24
Factor X 10 170 59 34–40
Protein C 4 65 62 6–8
– Gla domain Factor XI 5 30 160 60–80
Factor XII 40 500 80 50–70
Prekallikrein 40 490 85 35
Factor XIIIA* † - – 83 –
Factor XIIIB* 7 94 76.5 –
Factor XIII 30 94 320 240
TAFI 4–15 70–275 60 –
COFACTORS
Soluble Factor V † 5-10 20 330 12–36
Factor VIII 0.2 0.7 300 8–12
VWF varies 10 500–20,000 8–12
Protein S ‡ 25 350 75 42
Protein Z § 2.5 40 62 60
HK 80 670 120 150
Cellular Tissue factor – – 47 –
Thrombomodulin - – 78 –
EPCR – – 49 –
STRUCTURAL PROTEIN Fibrinogen 2500 7400 340 72–120
Aα chain – – 66.5 –
Bβ chain – - 52 –
γ Chain – – 46.5 –
INHIBITORS Antithrombin 150 2500 58 60–72
TFPIα ¶ 0.01 0.25 40 0.03
ZPI § 4 60 72 60
EPCR, endothelial protein C receptor; HK, high-molecular-weight kininogen; TAFI, thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor; TFPI, full-length
tissue factor pathway inhibitor; VWF, von Willebrand factor; ZPI, protein Z–dependent protease inhibitor.
* All of the factor XIIIA chain is in complex with factor XIIIB chain; only half of factor XIIIB is in complex with factor XIIIA, the rest is free in plasma.
† Platelets carry significant amounts of factor XIIIA and factor V (20% of circulating factor V).
‡ Approximately 60% of protein S is in complex with C4b-binding protein; the remainder circulates as free protein S.
§ ZPI circulates in complex with protein Z.
¶ TFPI circulates in plasma at 2.5 nM in multiple forms; only 10% of circulating TFPI is the full-length TFPIα.
(Fig. 113–3). Membrane binding by the Gla domain occurs when this The serine protease domains of the vitamin K–dependent proteins
hydrophobic surface loop penetrates into the hydrophobic portion of are highly homologous, as they bear a chymotrypsin-like fold and dis-
the phospholipid bilayer, which is facilitated by the interaction of the play trypsin-like activity. Once activated, they cleave peptide bonds
10
Gla-bound calcium ions with the phosphate head groups of phos- following a positively charged amino acid (Lys or Arg). Activation pro-
phatidylserine. It has been shown that the phosphate head groups of ceeds through proteolysis at one or more sites N-terminal to the ser-
7,8
exposed phosphatidylethanolamine are also capable of coordinating ine protease domain (see Fig. 113–1). Subsequently, the newly formed
calcium ions, thereby contributing to the interaction of the Gla domains N-terminus inserts into the serine protease domain to form a salt
with the negatively charged membrane surface. 9 bridge with an Asp residue, which is associated with conformational
Kaushansky_chapter 113_p1915-1948.indd 1916 9/21/15 2:39 PM