Page 258 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 258
232 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 233
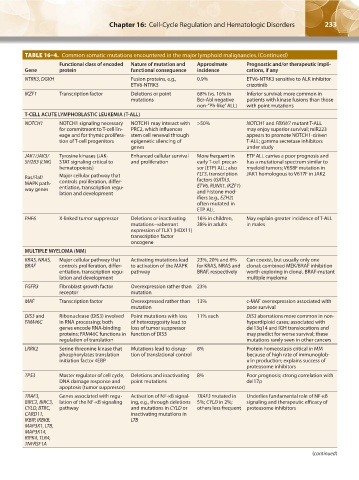
TABLE 16–4. Common somatic mutations encountered in the major lymphoid malignancies.(Continued)
Functional class of encoded Nature of mutation and Approximate Prognostic and/or therapeutic impli-
Gene protein functional consequence incidence cations, if any
NTRK3, DGKH Fusion proteins, e.g., 0.9% ETV6-NTRK3 sensitive to ALK inhibitor
ETV6-NTRK3 crizotinib
IKZF1 Transcription factor Deletions or point 68% (vs. 16% in Inferior survival; more common in
mutations Bcr-Abl negative patients with kinase fusions than those
non-”Ph-like” ALL) with point mutations
T-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA (T-ALL)
NOTCH1 NOTCH1 signaling necessary NOTCH1 may interact with >50% NOTCH1 and FBXW7 mutant T-ALL
for commitment to T-cell lin- PRC2, which influences may enjoy superior survival; miR223
eage and for thymic prolifera- stem cell renewal through appears to promote NOTCH1-driven
tion of T-cell progenitors epigenetic silencing of T-ALL; gamma secretase inhibitors
genes under study
JAK1/JAK3/ Tyrosine kinases (JAK- Enhanced cellular survival More frequent in ETP ALL carries a poor prognosis and
SH2B3 (LNK) STAT signaling critical to and proliferation early T-cell precur- has a mutational spectrum similar to
hematopoiesis) sor (ETP) ALL; also myeloid tumors; V658F mutation in
Ras/Raf/ Major cellular pathway that FLT3, transcription JAK1 homologous to V617F in JAK2
factors (GATA3,
MAPK path- controls proliferation, differ- ETV6, RUNX1, IKZF1)
way genes entiation, transcription regu-
lation and development and histone mod-
ifiers (e.g., EZH2)
often mutated in
ETP ALL
PHF6 X-linked tumor suppressor Deletions or inactivating 16% in children, May explain greater incidence of T-ALL
mutations→aberrant 38% in adults in males
expression of TLX1 (HOX11)
transcription factor
oncogene
MULTIPLE MYELOMA (MM)
KRAS, NRAS, Major cellular pathway that Activating mutations lead 23%, 20% and 6% Can coexist, but usually only one
BRAF controls proliferation, differ- to activation of the MAPK for KRAS, NRAS and clonal; combined MEK/BRAF inhibition
entiation, transcription regu- pathway BRAF, respectively worth exploring in clonal, BRAF-mutant
lation and development multiple myeloma
FGFR3 Fibroblast growth factor Overexpression rather than 23%
receptor mutation
MAF Transcription factor Overexpressed rather than 13% c-MAF overexpression associated with
mutation poor survival
DIS3 and Ribonuclease (DIS3) involved Point mutations with loss 11% each DIS3 aberrations more common in non-
FAM46C in RNA processing; both of heterozygosity lead to hyperdiploid cases; associated with
genes encode RNA-binding loss of tumor suppressor del13q14 and IGH translocations and
proteins; FAM46C functions in function of DIS3 may predict for worse survival; these
regulation of translation mutations rarely seen in other cancers
LRRK2 Serine threonine kinase that Mutations lead to disrup- 8% Protein homeostasis critical in MM
phosphorylates translation tion of translational control because of high rate of immunoglob-
initiation factor 4EBP ulin production; explains success of
proteasome inhibitors
TP53 Master regulator of cell cycle, Deletions and inactivating 8% Poor prognosis; strong correlation with
DNA damage response and point mutations del17p
apoptosis (tumor suppressor)
TRAF3, Genes associated with regu- Activation of NF-κB signal- TRAF3 mutated in Underlies fundamental role of NF-κB
BIRC2, BIRC3, lation of the NF-κB signaling ing, e.g., through deletions 5%; CYLD in 2%; signaling and therapeutic efficacy of
CYLD, BTRC, pathway and mutations in CYLD or others less frequent proteasome inhibitors
CARD11, inactivating mutations in
IKBIP, IKBKB, LTB
MAP3K1, LTB,
MAP3K14,
RIPK4, TLR4,
TNFRSF1A
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 233 9/18/15 11:57 PM