Page 261 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 261
236 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 237
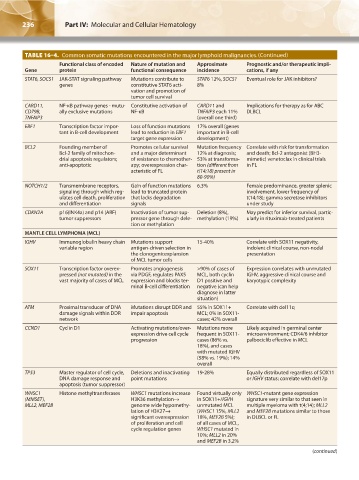
TABLE 16–4. Common somatic mutations encountered in the major lymphoid malignancies.(Continued)
Functional class of encoded Nature of mutation and Approximate Prognostic and/or therapeutic impli-
Gene protein functional consequence incidence cations, if any
STAT6, SOCS1 JAK-STAT signaling pathway Mutations contribute to STAT6 12%, SOCS1 Eventual role for JAK inhibitors?
genes constitutive STAT6 acti- 8%
vation and promotion of
tumor cell survival
CARD11, NF-κB pathway genes - mutu- Constitutive activation of CARD11 and Implications for therapy as for ABC
CD79B, ally exclusive mutations NF-κB TNFAIP3 each 11% DLBCL
TNFAIP3 (overall one third)
EBF1 Transcription factor impor- Loss of function mutations 17% overall (genes
tant in B-cell development lead to reduction in EBF1 important in B-cell
target gene expression development)
BCL2 Founding member of Promotes cellular survival Mutation frequency Correlate with risk for transformation
Bcl-2 family of mitochon- and a major determinant 12% at diagnosis; and death; Bcl-2 antagonist (BH3-
drial apoptosis regulators; of resistance to chemother- 53% at transforma- mimetic) venetoclax in clinical trials
anti-apoptotic apy; overexpression char- tion (different from in FL
acteristic of FL t(14;18) present in
80-90%)
NOTCH1/2 Transmembrane receptors, Gain of function mutations 6.3% Female predominance, greater splenic
signaling through which reg- lead to truncated protein involvement, lower frequency of
ulates cell death, proliferation that lacks degradation t(14;18); gamma secretase inhibitors
and differentiation signals under study
CDKN2A p16(INK4a) and p14 (ARF) Inactivation of tumor sup- Deletion (8%), May predict for inferior survival, partic-
tumor suppressors pressor gene through dele- methylation (19%) ularly in rituximab-treated patients
tion or methylation
MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA (MCL)
IGHV Immunoglobulin heavy chain Mutations support 15-40% Correlate with SOX11 negativity,
variable region antigen-driven selection in indolent clinical course, non-nodal
the clonogenicexplansion presentation
of MCL tumor cells
SOX11 Transcription factor overex- Promotes angiogenesis >90% of cases of Expression correlates with unmutated
pressed (not mutated) in the via PDGF, regulates PAX5 MCL, both cyclin IGHV, aggressive clinical course and
vast majority of cases of MCL expression and blocks ter- D1 positive and karyotypic complexity
minal B-cell differentiation negative (can help
diagnose in latter
situation)
ATM Proximal transducer of DNA Mutations disrupt DDR and 55% in SOX11+ Correlate with del11q
damage signals within DDR impair apoptosis MCL; 0% in SOX11-
network cases; 42% overall
CCND1 Cyclin D1 Activating mutations/over- Mutations more Likely acquired in germinal center
expression drive cell cycle frequent in SOX11- microenvironment; CDK4/6 inhibitor
progression cases (86% vs. palbociclib effective in MCL
18%), and cases
with mutated IGHV
(58% vs. 19%); 14%
overall
TP53 Master regulator of cell cycle, Deletions and inactivating 19-28% Equally distributed regardless of SOX11
DNA damage response and point mutations or IGHV status; correlate with del17p
apoptosis (tumor suppressor)
WHSC1 Histone methyltransferases WHSC1 mutations increase Found virtually only WHSC1-mutant gene expression
(MMSET), H3K36 methylation→ in SOX11+/IGVH signature very similar to that seen in
MLL2, MEF2B genome wide hypomethy- unmutated MCL multiple myeloma with t(4;14); MLL2
lation of H3K27→ (WHSC1 15%, MLL2 and MEF2B mutations similar to those
significant overexpression 18%, MEF2B 5%); in DLBCL or FL
of proliferation and cell of all cases of MCL,
cycle regulation genes WHSC1 mutated in
10%; MLL2 in 20%
and MEF2B in 3.2%
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 236 9/18/15 11:57 PM