Page 259 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 259
234 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 235
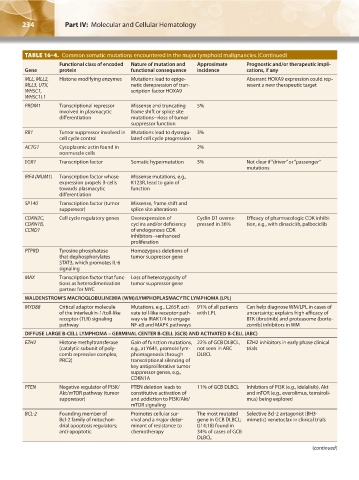
TABLE 16–4. Common somatic mutations encountered in the major lymphoid malignancies.(Continued)
Functional class of encoded Nature of mutation and Approximate Prognostic and/or therapeutic impli-
Gene protein functional consequence incidence cations, if any
MLL, MLL2, Histone modifying enzymes Mutations lead to epige- Aberrant HOXA9 expression could rep-
MLL3, UTX, netic derepression of tran- resent a new therapeutic target
WHSC1, scription factor HOXA9
WHSC1L1
PRDM1 Transcriptional repressor Missense and truncating 5%
involved in plasmacytic frame shift or splice site
differentiation mutations→loss of tumor
suppressor function
RB1 Tumor suppressor involved in Mutations lead to dysregu- 3%
cell cycle control lated cell cycle progression
ACTG1 Cytoplasmic actin found in 2%
nonmuscle cells
EGR1 Transcription factor Somatic hypermutation 3% Not clear if “driver” or “passenger”
mutations
IRF4 (MUM1) Transcription factor whose Missense mutations, e.g.,
expression propels B-cells K123R, lead to gain of
towards plasmacytic function
differentiation
SP140 Transcription factor (tumor Missense, frame shift and
suppressor) splice site alterations
CDKN2C, Cell cycle regulatory genes Overexpression of Cyclin D1 overex- Efficacy of pharmacologic CDK inhibi-
CDKN1B, cyclins and/or deficiency pressed in 36% tion, e.g., with dinaciclib, palbociclib
CCND1 of endogenous CDK
inhibitors→enhanced
proliferation
PTPRD Tyrosine phosphatase Homozygous deletions of
that dephosphorylates tumor suppressor gene
STAT3, which promotes IL-6
signaling
MAX Transcription factor that func- Loss of heterozygosity of
tions as heterodimerization tumor suppressor gene
partner for MYC
WALDENSTROM’S MACROGLOBULINEMIA (WM)/LYMPHOPLASMACYTIC LYMPHOMA (LPL)
MYD88 Critical adaptor molecule Mutations, e.g., L265P, acti- 91% of all patients Can help diagnose WM/LPL in cases of
of the interleukin-1/toll-like vate toll-like receptor path- with LPL uncertainty; explains high efficacy of
receptor (TLR) signaling way via IRAK1/4 to engage BTK (ibrutinib) and proteasome (borte-
pathway NF-κB and MAPK pathways zomib) inhibitors in WM
DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA – GERMINAL CENTER B-CELL (GCB) AND ACTIVATED B-CELL (ABC)
EZH2 Histone methyltransferase Gain of function mutations, 22% of GCB DLBCL, EZH2 inhibitors in early phase clinical
(catalytic subunit of poly- e.g., at Y641, promote lym- not seen in ABC trials
comb repressive complex, phomagenesis through DLBCL
PRC2) transcriptional silencing of
key antiproliferative tumor
suppressor genes, e.g.,
CDKN1A
PTEN Negative regulator of PI3K/ PTEN deletion leads to 11% of GCB DLBCL Inhibtiors of PI3K (e.g., idelalisib), Akt
Akt/mTOR pathway (tumor constitutive activation of and mTOR (e.g., everolimus, temsiroli-
suppressor) and addiction to PI3K/Akt/ mus) being explored
mTOR signaling
BCL-2 Founding member of Promotes cellular sur- The most mutated Selective Bcl-2 antagonist (BH3-
Bcl-2 family of mitochon- vival and a major deter- gene in GCB DLBCL; mimetic) venetoclax in clinical trials
drial apoptosis regulators; minant of resistance to t(14;18) found in
anti-apoptotic chemotherapy 34% of cases of GCB
DLBCL
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 234 9/18/15 11:57 PM