Page 260 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 260
234 Part IV: Molecular and Cellular Hematology Chapter 16: Cell-Cycle Regulation and Hematologic Disorders 235
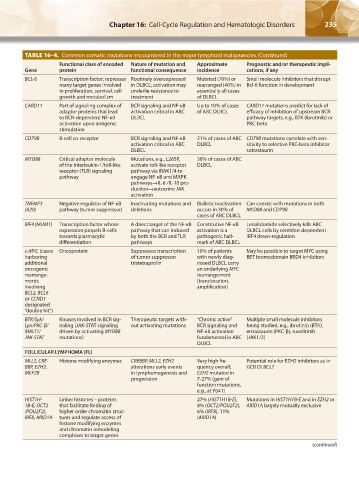
TABLE 16–4. Common somatic mutations encountered in the major lymphoid malignancies.(Continued)
Functional class of encoded Nature of mutation and Approximate Prognostic and/or therapeutic impli-
Gene protein functional consequence incidence cations, if any
BCL-6 Transcription factor; represses Routinely overexpressed Mutated (70%) or Small molecule inhibitors that disrupt
many target genes involved in DLBCL; activation may rearranged (40%) in Bcl-6 function in development
in proliferation, survival, cell underlie resistance to essentially all cases
growth and metabolism treatment of DLBCL
CARD11 Part of signaling complex of BCR signaling and NF-κB Up to 10% of cases CARD11 mutations predict for lack of
adaptor proteins that lead activation critical in ABC of ABC DLBCL efficacy of inhibition of upstream BCR
to BCR-dependent NF-κB DLBCL pathway targets, e.g., BTK (ibrutinib) or
activation upon antigenic PKC-beta
stimulation
CD79B B-cell co-receptor BCR signaling and NF-κB 21% of cases of ABC CD79B mutations correlate with sen-
activation critical in ABC DLBCL sitivity to selective PKC-beta inhibitor
DLBCL sotrastaurin
MYD88 Critical adaptor molecule Mutations, e.g., L265P, 30% of cases of ABC
of the interleukin-1/toll-like activate toll-like receptor DLBCL
receptor (TLR) signaling pathway via IRAK1/4 to
pathway engage NF-κB and MAPK
pathways→IL-6 /IL-10 pro-
duction→autocrine JAK
activation
TNFAIP3 Negative regulator of NF-κB Inactivating mutations and Biallelic inactivation Can coexist with mutations in both
(A20) pathway (tumor suppressor) deletions occurs in 30% of MYD88 and CD79B
cases of ABC DLBCL
IRF4 (MUM1) Transcription factor whose A direct target of the NF-κB Constitutive NF-κB Lenalidomide selectively kills ABC
expression propels B-cells pathway that can induced activation is a DLBCL cells by cereblon-dependent
towards plasmacytic by both the BCR and TLR pathogenic hall- IRF4 down-regulation
differentiation pathways mark of ABC DLBCL
c-MYC (cases Oncoprotein Suppresses transcription 10% of patients May be possible to target MYC using
harboring of tumor suppressor with newly diag- BET bromodomain BRD4 inhibitors
additional tristetraprolin nosed DLBCL carry
oncogenic an underlying MYC
rearrange- rearrangement
ments (translocation,
involving amplification)
BCL2, BCL6
or CCND1
designated
“double hit”)
BTK/Syk/ Kinases involved in BCR sig- Therapeutic targets with- “Chronic active” Multiple small molecule inhibitors
Lyn/PKC-β/ naling (JAK-STAT signaling out activating mutations BCR signaling and being studied, e.g., ibrutinib (BTK),
MALT1/ driven by activating MYD88 NF-κB activation enzastaurin (PKC-β), ruxolitinib
JAK-STAT mutations) fundamental in ABC (JAK1/2)
DLBCL
FOLLICULAR LYMPHOMA (FL)
MLL2, CRE- Histone modifying enzymes CREBBP, MLL2, EZH2 Very high fre- Potential role for EZH2 inhibitors as in
BBP, EZH2, alterations early events quency overall; GCB DLBCL?
MEF2B in lymphomagenesis and EZH2 mutated in
progression 7-27% (gain of
function mutations,
e.g., at Y641)
HIST1H- Linker histones – proteins 27% (HIST1H1B-E), Mutations in HIST1H1B-E and in EZH2 or
1B-E, OCT2 that facilitate folding of 8% (OCT2/POU2F2), ARID1A largely mutually exclusive
(POU2F2), higher order chromatin struc- 6% (IRF8), 11%
IRF8, ARID1A tures and regulate access of (ARID1A)
histone modifying enzymes
and chromatin remodeling
complexes to target genes
(continued)
Kaushansky_chapter 16_p0213-0246.indd 235 9/18/15 11:57 PM