Page 1300 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1300
1262 Part eleven Diagnostic Immunology
Unstimulated Stimulated
10 3 10 3
HLA B8 tetramer with
10 2 10 2 CD107 a expression after
CMV IE-1 peptide stimulation
Relevant tetramer 10 1 Relevant tetramer 10 1
10 0 10 0
0 0
0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3
CD107a/b CD107a/b
10 3 10 3
10 2 10 2
Relevant tetramer 10 1 Relevant tetramer 10 1 HLA B8 tetramer with
CD107 a expression after
CMV peptide stimulation
10 0 10 0
0 0
0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3
IFN-g IFN-g
B
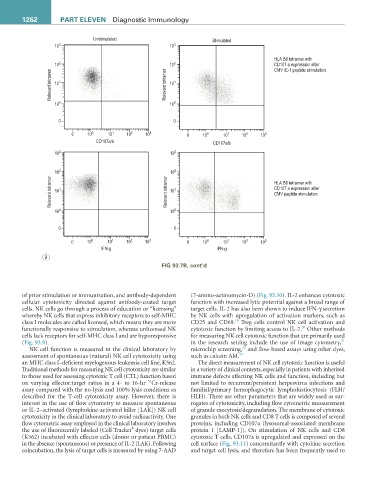
FIG 93.7B, cont’d
of prior stimulation or immunization, and antibody-dependent (7-amino-actinomycin-D) (Fig. 93.10). IL-2 enhances cytotoxic
cellular cytotoxicity directed against antibody-coated target function with increased lytic potential against a broad range of
cells. NK cells go through a process of education or “licensing” target cells. IL-2 has also been shown to induce IFN-γ secretion
whereby NK cells that express inhibitory receptors to self-MHC by NK cells with upregulation of activation markers, such as
19
class I molecules are called licensed, which means they are more CD25 and CD69. Treg cells control NK cell activation and
20
functionally responsive to stimulation, whereas unlicensed NK cytotoxic function by limiting access to IL-2. Other methods
cells lack receptors for self-MHC class I and are hyporesponsive for measuring NK cell cytotoxic function that are primarily used
21
(Fig. 93.9). in the research setting include the use of image cytometry,
22
NK cell function is measured in the clinical laboratory by microchip screening, and flow-based assays using other dyes,
assessment of spontaneous (natural) NK cell cytotoxicity using such as calcein AM. 23
an MHC class I–deficient myelogenous leukemia cell line, K562. The direct measurement of NK cell cytotoxic function is useful
Traditional methods for measuring NK cell cytotoxicity are similar in a variety of clinical contexts, especially in patients with inherited
to those used for assessing cytotoxic T cell (CTL) function based immune defects affecting NK cells and function, including but
51
on varying effector:target ratios in a 4- to 16-hr Cr-release not limited to recurrent/persistent herpesvirus infections and
assay compared with the no-lysis and 100% lysis conditions as familial/primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FLH/
described for the T-cell cytotoxicity assay. However, there is HLH). There are other parameters that are widely used as sur-
interest in the use of flow cytometry to measure spontaneous rogates of cytotoxicity, including flow cytometric measurement
or IL-2–activated (lymphokine-activated killer [LAK]) NK cell of granule exocytosis/degranulation. The membrane of cytotoxic
cytotoxicity in the clinical laboratory to avoid radioactivity. One granules in both NK cells and CD8 T cells is composed of several
flow cytometric assay employed in the clinical laboratory involves proteins, including CD107a (lysosomal-associated membrane
®
the use of fluorescently labeled (Cell Tracker dyes) target cells protein 1 [LAMP-1]). On stimulation of NK cells and CD8
(K562) incubated with effector cells (donor or patient PBMC) cytotoxic T cells, CD107a is upregulated and expressed on the
in the absence (spontaneous) or presence of IL-2 (LAK). Following cell surface (Fig. 93.11) concomitantly with cytokine secretion
coincubation, the lysis of target cells is measured by using 7-AAD and target cell lysis, and therefore has been frequently used to