Page 62 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 62
CHaPTEr 3 Innate Immunity 47
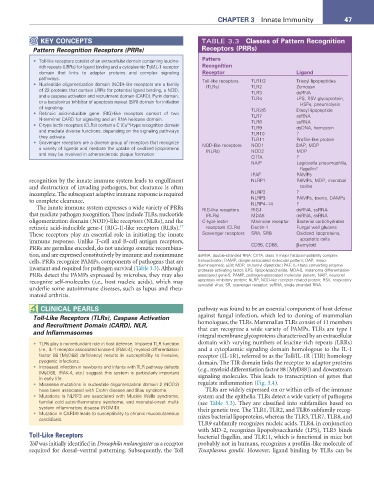
KEY CONCEPTS TABLE 3.3 Classes of Pattern recognition
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) receptors (Prrs)
• Toll-like receptors consist of an extracellular domain containing leucine- Pattern
rich repeats (LRRs) for ligand binding and a cytoplasmic Toll/IL-1 receptor recognition
domain that links to adapter proteins and complex signaling receptor Ligand
pathways. Toll-like receptors TLR1/2 Triacyl lipopeptides
• Nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors are a family (TLRs) TLR2 Zymosan
of 22 proteins that contain LRRs for potential ligand binding, a NOD, TLR3 dsRNA
and a caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD), Pyrin domain, TLR4 LPS, RSV glycoprotein,
or a baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis repeat (BIR) domain for initiation HSPs, pneumolysin
of signaling. TLR2/6 Diacyl lipopeptide
• Retinoic acid-inducible gene (RIG)-like receptors consist of two TLR7 ssRNA
N-terminal CARD for signaling and an RNA helicase domain. TLR8 ssRNA
2+
• C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) contain a C (Ca )-type recognition domain TLR9 dsDNA, hemozoin
and mediate diverse functions, depending on the signaling pathways TLR10 ?
they activate.
• Scavenger receptors are a diverse group of receptors that recognize NOD-like receptors TLR11 Profilin-like protein
NOD1
DAP, MDP
a variety of ligands and mediate the uptake of oxidized lipoproteins (NLRs) NOD2 MDP
and may be involved in atherosclerotic plaque formation.
CIITA ?
NAIP Legionella pneumophilia,
flagellin?
IPAF PAMPs
recognition by the innate immune system leads to engulfment NLRP1 PAMPs, MDP, microbial
and destruction of invading pathogens, but clearance is often toxins
incomplete. The subsequent adaptive immune response is required NLRP2 ?
to complete clearance. NLRP3 PAMPs, toxins, DAMPs
NLRP4–14
?
The innate immune system expresses a wide variety of PRRs RIG-like receptors RIG-I dsRNA, ssRNA
that mediate pathogen recognition. These include TLRs, nucleotide (RLRs) MDA5 dsRNA, ssRNA
oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors (NLRs), and the C-type lectin Mannose receptor Bacterial carbohydrates
47
retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I)-like receptors (RLRs). receptors (CLRs) Dectin-1 Fungal wall glucans
These receptors play an essential role in initiating the innate Scavenger receptors SRA, SRB Oxidized lipoproteins,
immune response. Unlike T-cell and B-cell antigen receptors, apoptotic cells
PRRs are germline encoded, do not undergo somatic recombina- CD36, CD68, β-amyloid
tion, and are expressed constitutively by immune and nonimmune dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; CIITA, class II major histocompatibility complex
cells. PRRs recognize PAMPs, components of pathogens that are transactivator; DAMP, danger-associated molecular pattern; DAP, meso-
invariant and required for pathogen survival (Table 3.3). Although diaminopimelic acid; MDP, muramyl dipeptide; IPAF, IL-1beta converting enzyme
protease activating factor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MDA-5, melanoma differentiation-
PRRs detect the PAMPs expressed by microbes, they may also associated gene-5; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; NAIP, neuronal
recognize self-molecules (i.e., host nucleic acids), which may apoptosis inhibitory protein; NLRP, NOD-like receptor related protein; RSV, respiratory
syncytial virus; SR, scavenger receptor; ssRNA, single stranded RNA.
underlie some autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheu-
matoid arthritis.
CLINICaL PEarLS pathway was found to be an essential component of host defense
Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs), Caspase Activation against fungal infection, which led to cloning of mammalian
and Recruitment Domain (CARD), NLR, homologues, the TLRs. Mammalian TLRs consist of 11 members
and Inflammasomes that can recognize a wide variety of PAMPs. TLRs are type 1
integral membrane glycoproteins characterized by an extracellular
• TLRs play a nonredundant role in host defense. Impaired TLR function domain with varying numbers of leucine-rich repeats (LRRs)
(i.e., IL-1 receptor associated kinase-4 [IRAK-4], myeloid differentiation and a cytoplasmic signaling domain homologous to the IL-1
factor 88 [MyD88] deficiency) results in susceptibility to invasive, receptor (IL-1R), referred to as the Toll/IL-1R (TIR) homology
pyogenic infections. domain. The TIR domain links the receptor to adaptor proteins
• Increased infection in newborns and infants with TLR pathway defects (e.g., myeloid differentiation factor 88 [MyD88]) and downstream
(MyD88, IRAK-4, etc.) suggest this system is particularly important
in early life. signaling molecules. This leads to transcription of genes that
• Missense mutations in nucleotide oligomerization domain 2 (NOD2) regulate inflammation (Fig. 3.4).
have been associated with Crohn disease and Blau syndrome. TLRs are widely expressed on or within cells of the immune
• Mutations in NLRP3 are associated with Muckle Wells syndrome, system and the epithelia. TLRs detect a wide variety of pathogens
familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, and neonatal-onset multi- (see Table 3.3). They are classified into subfamilies based on
system inflammatory disease (NOMID). their genetic tree. The TLR1, TLR2, and TLR6 subfamily recog-
• Mutation in CARD9 leads to susceptibility to chronic mucocutaneous
candidiasis. nizes bacterial lipoproteins, whereas the TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and
TLR9 subfamily recognizes nucleic acids. TLR4, in conjunction
with MD-2, recognizes lipopolysaccharide (LPS), TLR5 binds
Toll-Like Receptors bacterial flagellin, and TLR11, which is functional in mice but
Toll was initially identified in Drosophila melanogaster as a receptor probably not in humans, recognizes a profilin-like molecule of
required for dorsal–ventral patterning. Subsequently, the Toll Toxoplasma gondii. However, ligand binding by TLRs can be